File:Inner ear development cartoon 01.jpg
Original file (714 × 800 pixels, file size: 94 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
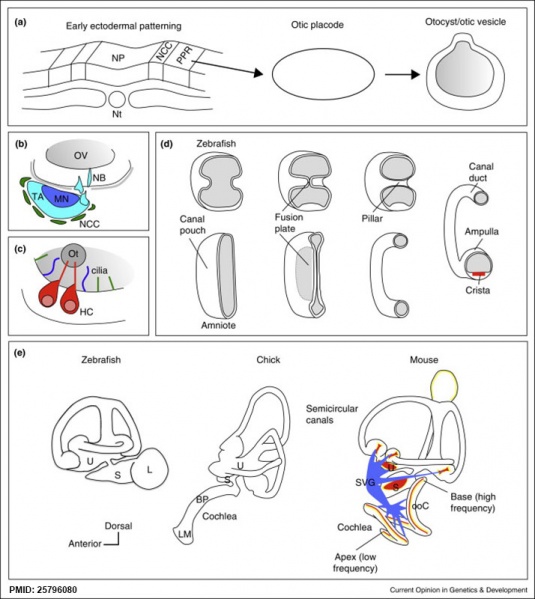
Stages of Inner Ear Development
(a) Formation of the pre-placodal region (PPR), otic placode and otocyst (otic vesicle) from cranial ectoderm. The otocyst is the source of nearly all cell types of the mature ear.
(b) Otic neurogenesis: neuroblasts are specified from otic vesicle epithelium, but delaminate from it and accumulate beneath the ear in a transit amplifying population (light blue). Neurons (dark blue) differentiate from this population, and innervate sensory hair cells in the overlying otic epithelium. The ganglion develops in close association with neural crest cells (green), which give rise to glia.
(c) Early otolith formation in the zebrafish otic vesicle. At least three distinct populations of cilia can be distinguished: immotile hair cell kinocilia (red), which tether the otolith at early stages; motile cilia (blue) in the vicinity of the sensory hair cells, which do not bind otolithic material, and shorter immotile cilia (green).
(d) Schematic comparison of semicircular canal formation in the zebrafish ear (top row) and a generalised amniote ear (bottom row). A single canal is illustrated for clarity. Epithelia adhere at a fusion plate, from which cells are cleared to make the duct. The end result of both events is the same (right hand image), but the fusion plate is much smaller in the zebrafish.
(e) Comparative sketches of inner ears from adult zebrafish and late stage chick and mouse embryos. Sensory (red), neuronal (blue) and endolymph-regulating (yellow) cells are shown for the mouse ear.
Abbreviations: A, ampulla; BP, basilar papilla; HC, hair cell; L, lagena; LM, lagenar macula; MN, maturing neurons; NB, neuroblasts; NCC, neural crest cells; NP, neural plate; Nt, notochord; ooC, organ of Corti; Ot, otolith; OV, otic vesicle; PPR, preplacodal region; S, saccule; SVG, spiral and vestibular ganglion; TA, transit amplifying population of neuroblasts; U, utricle.
Reference
<pubmed>25796080</pubmed>| Curr Opin Genet Dev.
Copyright
© 2015 Whitfield TT. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figure 1. 1-s2.0-S0959437X15000180-gr1.jpg
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:48, 25 March 2015 |  | 714 × 800 (94 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Stages of inner ear development== (a) Formation of the PPR, otic placode and otocyst (otic vesicle) from cranial ectoderm. The otocyst is the source of nearly all cell types of the mature ear (F). (b) Otic neurogenesis: neuroblasts are specified... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: