File:Gray1096.jpg
Gray1096.jpg (600 × 380 pixels, file size: 63 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
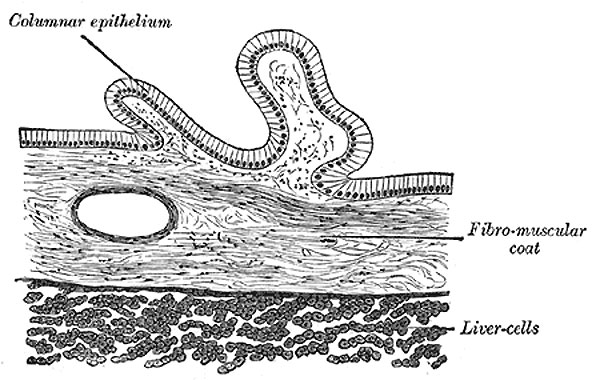
Gall Bladder
The internal or mucous coat (tunica mucosa vesicæ felleæ) is loosely connected with the fibrous layer. It is generally of a yellowish-brown color, and is elevated into minute rugæ. Opposite the neck of the gall-bladder the mucous membrane projects inward in the form of oblique ridges or folds, forming a sort of spiral valve.
The mucous membrane is continuous through the hepatic duct with the mucous membrane lining the ducts of the liver, and through the common bile duct with the mucous membrane of the duodenum. It is covered with columnar epithelium, and secretes mucin; in some animals it secretes a nucleoprotein instead of mucin.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 02:11, 8 July 2011 |  | 600 × 380 (63 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Gall Bladder== The internal or mucous coat (tunica mucosa vesicæ felleæ) is loosely connected with the fibrous layer. It is generally of a yellowish-brown color, and is elevated into minute rugæ. Opposite the neck of the gall-bladder the mucous memb |
You cannot overwrite this file.