File:Cord blood induced stem cells 01.jpg: Difference between revisions
(==Generation of non-viral induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) from CD34+ cord blood progenitors== (A) Representative immunocytochemistry of pluripotency markers POU5F1 (OCT4), NANOG, TRA-1-81, and SSEA4 in hiPSC line CBiPSC6.2 after >20 passages. (B) ) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Generation of non-viral induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) from CD34+ cord blood progenitors== | ==Generation of non-viral induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) from CD34+ cord blood progenitors== | ||
(A) Representative immunocytochemistry of pluripotency markers POU5F1 (OCT4), NANOG, TRA-1-81, and SSEA4 in hiPSC line CBiPSC6.2 after >20 passages | (A) Representative immunocytochemistry of pluripotency markers POU5F1 (OCT4), NANOG, TRA-1-81, and SSEA4 in hiPSC line CBiPSC6.2 after >20 passages. | ||
(B) Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of teratoma sections derived from CBiPSC6.2 after >20 passages demonstrating ectodermal, endodermal and mesodermal lineage differentiation. All CBiPSC clones in these studies formed similar teratomas. | |||
(C) Real-time RT-PCR studies p15 CBiPSC lines for endogenous pluripotency genes using primers that distinguish endogenous expression from transgenes (see Methods). | |||
Original image name: Figure 2. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018293.g002 (cropped A-C from full figure) | |||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3072973/ | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3072973/ | ||
| Line 12: | Line 17: | ||
Copyright: © 2011 Burridge et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | Copyright: © 2011 Burridge et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | ||
[[Category:Human]] [[Category:Placenta]] [[Category:Blood]] [[Category:Stem Cells]] | |||
Revision as of 12:44, 12 October 2011
Generation of non-viral induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) from CD34+ cord blood progenitors
(A) Representative immunocytochemistry of pluripotency markers POU5F1 (OCT4), NANOG, TRA-1-81, and SSEA4 in hiPSC line CBiPSC6.2 after >20 passages.
(B) Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of teratoma sections derived from CBiPSC6.2 after >20 passages demonstrating ectodermal, endodermal and mesodermal lineage differentiation. All CBiPSC clones in these studies formed similar teratomas.
(C) Real-time RT-PCR studies p15 CBiPSC lines for endogenous pluripotency genes using primers that distinguish endogenous expression from transgenes (see Methods).
Original image name: Figure 2. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018293.g002 (cropped A-C from full figure)
Reference
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3072973/
http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0018293
Copyright: © 2011 Burridge et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:42, 12 October 2011 | 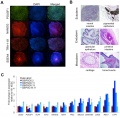 | 800 × 787 (157 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Generation of non-viral induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC) from CD34+ cord blood progenitors== (A) Representative immunocytochemistry of pluripotency markers POU5F1 (OCT4), NANOG, TRA-1-81, and SSEA4 in hiPSC line CBiPSC6.2 after >20 passages. (B) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
There are no pages that use this file.