File:Cochlea stria vascularis cartoon 03.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Human Cochlea Stria Vascularis== | ==Human Cochlea Stria Vascularis== | ||
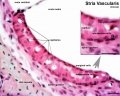
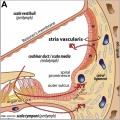
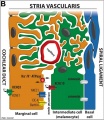
Anatomical (upper half) and compartmental (lower half) model of the adult stria vascularis. | |||
Showing the three cellular layers and depicting the location of potassium regulating channels. | |||
The stria vascularis is electrochemically isolated from neighboring structures by tight junctions (black bars). | |||
{| | |||
|-bgcolor="CEDFF2" | |||
! width=200px|Marginal cells | |||
! width=200px|Intermediate cells | |||
! width=200px|Basal cells | |||
|- | |||
| line the lumen of the cochlear duct | |||
| melanocyte-like cells lie between the marginal and basal cell layers | |||
| mesenchymal spiral ligament fibrocytes | |||
|-bgcolor="F5FAFF" | |||
| derived from epithelia | |||
| derived from the neural crest | |||
| derived from otic mesenchyme PMID 21925491. | |||
|} | |||
{{Stria vascularis links}} | {{Stria vascularis links}} | ||
| Line 8: | Line 26: | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
{{#pmid:25663387}} | |||
====Copyright==== | ====Copyright==== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 35: | ||
Figure 1. relabelled with pubmed ID | Figure 1. relabelled with pubmed ID | ||
[[Category:Hearing]][[Category:Inner Ear]][[Category:Cartoon]] | [[Category:Hearing]][[Category:Inner Ear]][[Category:Cartoon]][[Category:Neural Crest]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:38, 18 December 2018
Human Cochlea Stria Vascularis
Anatomical (upper half) and compartmental (lower half) model of the adult stria vascularis.
Showing the three cellular layers and depicting the location of potassium regulating channels.
The stria vascularis is electrochemically isolated from neighboring structures by tight junctions (black bars).
| Marginal cells | Intermediate cells | Basal cells |
|---|---|---|
| line the lumen of the cochlear duct | melanocyte-like cells lie between the marginal and basal cell layers | mesenchymal spiral ligament fibrocytes |
| derived from epithelia | derived from the neural crest | derived from otic mesenchyme PMID 21925491. |
- Cochlea Links: stria vascular histology | stria vascularis 1 | stria vascularis 2 | stria vascularis 3 | human vascularis development | Neural Crest Development | Inner Ear Development
Reference
Locher H, de Groot JC, van Iperen L, Huisman MA, Frijns JH & Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM. (2015). Development of the stria vascularis and potassium regulation in the human fetal cochlea: Insights into hereditary sensorineural hearing loss. Dev Neurobiol , 75, 1219-40. PMID: 25663387 DOI.
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors Developmental Neurobiology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.
Figure 1. relabelled with pubmed ID
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:47, 11 April 2015 | 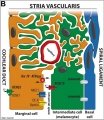 | 694 × 800 (125 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Human Cochlea Stria Vascularis== '''B''' A schematic anatomical (upper half) and compartmental (lower half) model of the adult stria vascularis showing the three cellular layers and depicting the location of potassium regulating channels. The stria... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 7 pages use this file: