File:Bailey386.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(==Fig. 386. Section through the wall of the fore-brain vesicle of a chick embryo of 3.5 days== Cajal. A, b arid c, Differentiating nerve cells in apolar stage, the neurofibrils are black; a, cell in a stage transitional to the bipolar stage; B, bipolar) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
A, b arid c, Differentiating nerve cells in apolar stage, the neurofibrils are black; a, cell in a stage transitional to the bipolar stage; B, bipolar cells; c (at lower right corner), cone of "growth" of developing axone; e, tangential axone. The cells in the bipolar stage have migrated out ward, but the neuroblast or mantle layer has not yet been differentiated. | A, b arid c, Differentiating nerve cells in apolar stage, the neurofibrils are black; a, cell in a stage transitional to the bipolar stage; B, bipolar cells; c (at lower right corner), cone of "growth" of developing axone; e, tangential axone. The cells in the bipolar stage have migrated out ward, but the neuroblast or mantle layer has not yet been differentiated. | ||
[[Category:Chicken]] | |||
Revision as of 00:12, 14 February 2011
Fig. 386. Section through the wall of the fore-brain vesicle of a chick embryo of 3.5 days
Cajal.
A, b arid c, Differentiating nerve cells in apolar stage, the neurofibrils are black; a, cell in a stage transitional to the bipolar stage; B, bipolar cells; c (at lower right corner), cone of "growth" of developing axone; e, tangential axone. The cells in the bipolar stage have migrated out ward, but the neuroblast or mantle layer has not yet been differentiated.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 00:36, 30 January 2011 | 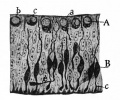 | 491 × 410 (53 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Fig. 386. Section through the wall of the fore-brain vesicle of a chick embryo of 3.5 days== Cajal. A, b arid c, Differentiating nerve cells in apolar stage, the neurofibrils are black; a, cell in a stage transitional to the bipolar stage; B, bipolar |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 4 pages use this file: