File:Alveolus.png
Alveolus.png (431 × 330 pixels, file size: 82 KB, MIME type: image/png)
Alveolus
Original image legend
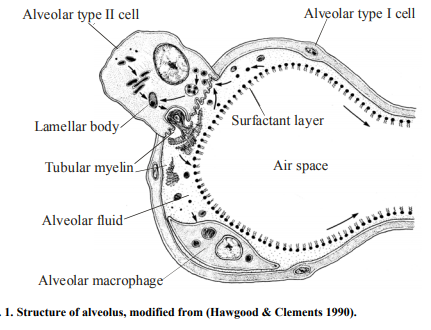
Fig. 1. Structure of alveolus, modified from (Hawgood & Clements 1990). Link to image: http://jultika.oulu.fi/Record/isbn951-42-7058-4
From Hagwood and Clements: Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the surfactant system. A single alveolus is shown with the location and movement of surfactant components depicted. Surfactant components are synthesized from precursors (1) in the endoplasmic reticulum (2) and transported via the Golgi apparatus(3) to lamellar bodies (4), which are the intracellular storage granules for surfactant. After secretion into the liquid lining the alveolus, the surfactant forms tubular myelin (5), which is thought to generate the surface monolayer (6) which lowers surface tension. Subsequently, surfactant components are taken back into type II cells, possibly in the form of small vesicles (7) apparently by a specific pathway involving endosomes (8) and multivesicular bodies (9) and culminating again in storage of surfactant in lamellar bodies. Some surfactant in the liquid layer is also taken up by alveolar macrophages (10). A single transit of the phospholipid components of surfactant through the alveolar lumen normally takes a few hours. The phospholipids in the lumen are taken back into the type II cell and reutilized - 10 times before being degraded. [1]
Copyright
© University of Oulu, 2003. This publication is copyrighted. You may download, display and print it for your own personal use. Commercial use is prohibited.
Reference
- ↑ Hawgood, S., & Clements, J. A. (1990). Pulmonary surfactant and its apoproteins. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 86(1), 1–6.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 15:37, 5 October 2017 |  | 431 × 330 (82 KB) | Z5059373 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: