Brain Awareness Week 2012: Difference between revisions
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
This animation shows a real human adult brain being "sliced", the '''cortex''' (grey matter) is on the outside. | This animation shows a real human adult brain being "sliced", the '''cortex''' (grey matter) is on the outside. | ||
''This page has been prepared as a simplified introduction to neural development.'' | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 07:43, 9 March 2012
Welcome to Brain Development
| width=320px|height=260px|controller=false|autoplay=true</qt> | In today's demonstration we will be looking at how the brain develops from a simple tube into the complex folded structure that you will be seeing (and using) today.
|
Here is Human Development
Here is how the human nervous system grows
|
|||||
| Week 3 | Week 4 to 5 | Week 5 | Week 8 | Week 13 to 21 | Adult Human |
| Neural Plate | Neural Tube | Simple Tube | Central Nervous | Fetal Brain | Brain Slices |
Here is a developing mouse nervous system
| width=336px|height=415px|controller=true|autoplay=false</qt> |
This movie shows a mouse 11.5 days old. (Mouse development takes 21 days and is a model used in research)
Red - brain
|
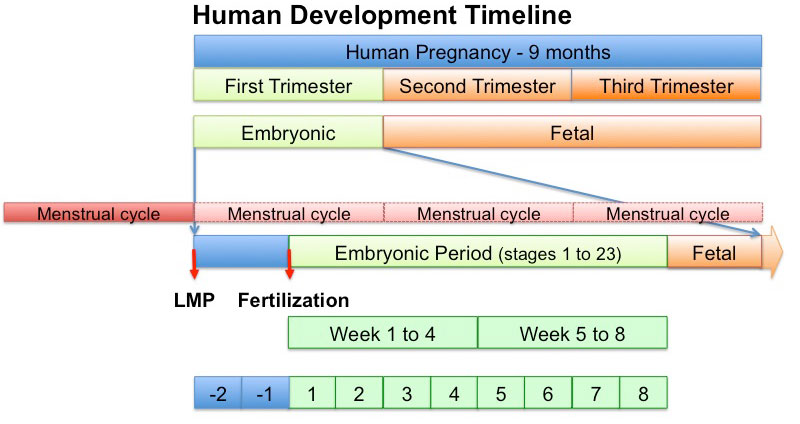
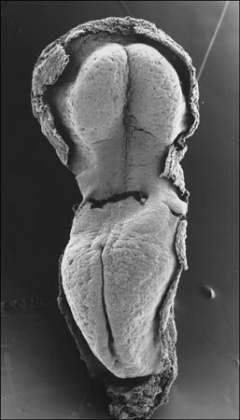
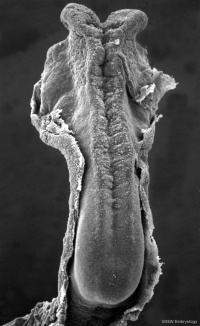
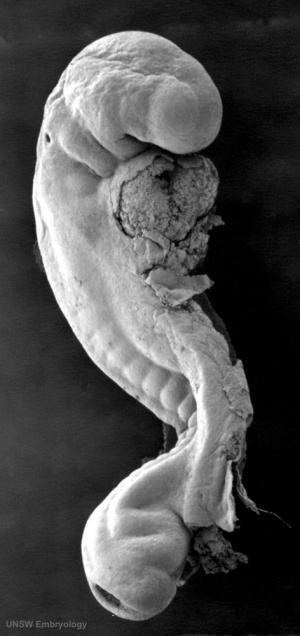
It begins as a Plate
That folds to a Tube
The tube then Closes at each End
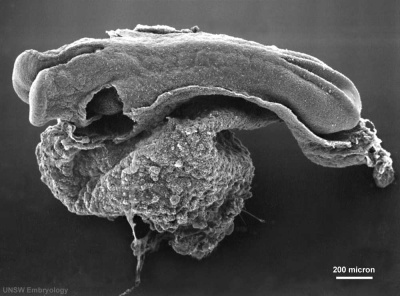
|

|
Why are these important? |
The brain end of the tube forms 3 Vesicles
At the brain end - the tube expands to form three vesicle (sac or bubble) regions. These will form different parts of the brain and brain stem.
At the spinal cord end - the tube stays narrow. This region begins to put out motor nerves to innervate muscle and sensory nerves grow towards the developing spinal cord.
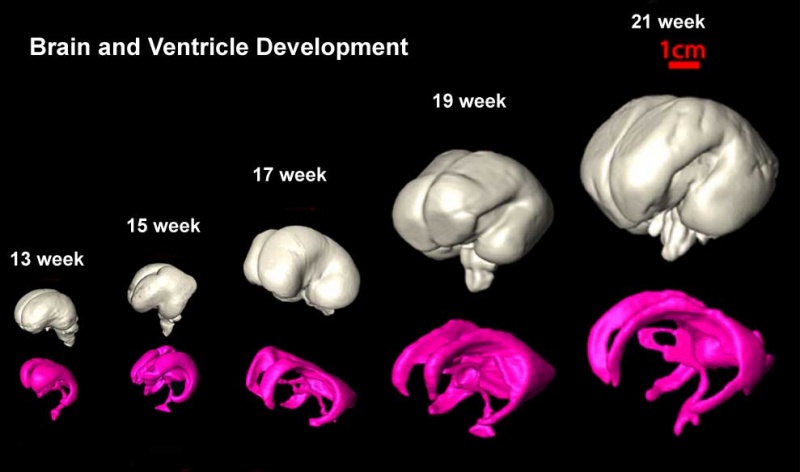
Fetal brain Grows
This shows the growth of the brain and the fluid-filled space within the brain (the red bar is 1 cm).
- The brain goes from having a smooth surface to begin to fold or "wrinkle" as the surface area grows.
- The fluid space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid or CSF.
Newborn brain Grows
The brain has not finished growing at birth.
Much of the growth in size after birth is due to "white matter" development, the support cells of the brain, spinal cord and nerves.