Bone Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Slides== | |||
'''UNSW Virtual Slidebox''' [http://web.med.unsw.edu.au/vslide/phase1/indexA1.asp Virtual Slidebox Phase 1] | '''UNSW Virtual Slidebox''' [http://web.med.unsw.edu.au/vslide/phase1/indexA1.asp Virtual Slidebox Phase 1] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
# Intramembranous ossification [http://vslide2.med.unsw.edu.au/slide.jsp?fn=anatomy/ANAT893.svs&mag=40&mag=40 Head (Neonatal) Rat H& Van Gieson] | # Intramembranous ossification [http://vslide2.med.unsw.edu.au/slide.jsp?fn=anatomy/ANAT893.svs&mag=40&mag=40 Head (Neonatal) Rat H& Van Gieson] | ||
==Haversian Systems== | |||
[[File:Bone structure cartoon.jpg|thumb|Bone structure cartoon]] | [[File:Bone structure cartoon.jpg|thumb|Bone structure cartoon]] | ||
* also called osteons | * also called osteons | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
Cells | Cells | ||
* osteocytes and canaliculi | * osteocytes and canaliculi | ||
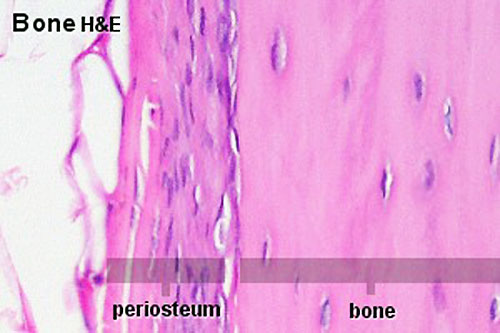
==Periosteum== | |||
[[File:Periosteum.jpg]] | |||
== Bone Cells == | == Bone Cells == | ||
Revision as of 11:28, 21 September 2009
Introduction
Macroscopic and microscopic bone structure in the adult and during development.
Textbook
Histology and Cell Biology: An Introduction to Pathology, A.L. Kierszenbaum, 2002 - Connective Tissue, Chapter 4 pp118-129; Osteogenesis, Chapter 5 pp131-145
Slides
UNSW Virtual Slidebox Virtual Slidebox Phase 1
- Compact Bone - Adult Bone , Adult (Ground, TS) Human Alizarin Red | Bone (Ground, LS) Human Alizarin Red
- Compact Bone Rib Decalcified rib, bone marrow
- Endochondral ossification Developing bone | Bone, Developing (LS, Femur) Cat H&E
- Intramembranous ossification Head (Neonatal) Rat H& Van Gieson
Haversian Systems
- also called osteons
- Volkmann's canals
Lamellae
- concentric - surrounding each Haversian System
- interstitial - bony plates that fill in between the haversian systems.
- circumferential - layers of bone that underlie the periosteum and endosteum
Cells
- osteocytes and canaliculi
Periosteum
Bone Cells
Osteocytes
- mature bone-forming cells embedded in bone matrix
- derive from osteogenic stem cells forming Osteoblasts
- line surface of bone, secrete organic matrix of bone (osteoid), converted into osteocytes when become embedded in matrix (which calcifies soon after deposition) (Google- osteoblast images)
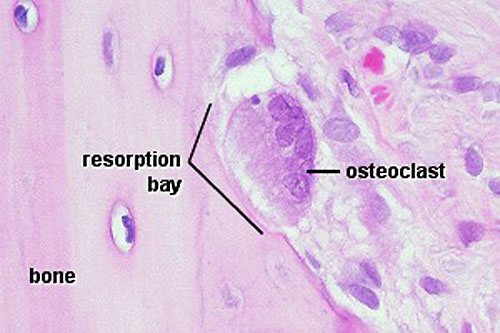
Osteoclasts
- bone-resorbing multinucleated macrophage-like cells, seal a small segment of extracellular space (between plasma membrane and bone surface), HCl secreted into this space by osteoclasts dissolves calcium phosphate crystals (give bone rigidity and strength) (Google- osteoclast images)
- do not mistake for megakaryocytes, found in bone marrow not associated with bone matrix.
Bone Matrix
The bone matrix has 2 major components. Organic portion composed of mainly collagen Type 1 (about 95%) and amorphous ground substance. Inorganic portion (50% dry weight of the matrix) composed of hydroxyapatite crystals, calcium, phosphorus, bicarbonate, nitrate, Mg, K, Na. (Google- bone matrix images)
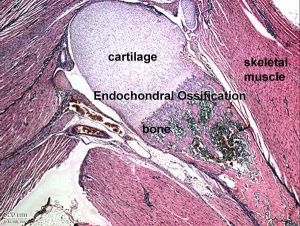
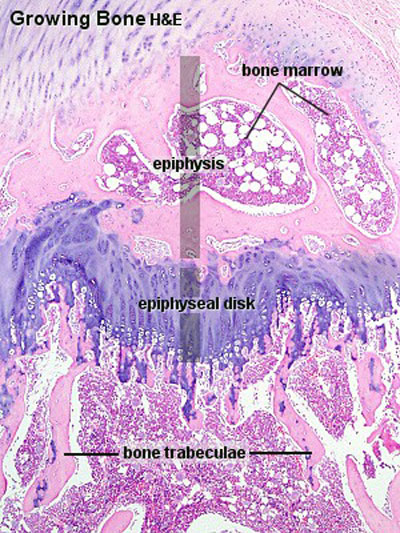
Endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification slides Developing bone | Bone, Developing (LS, Femur) Cat H&E
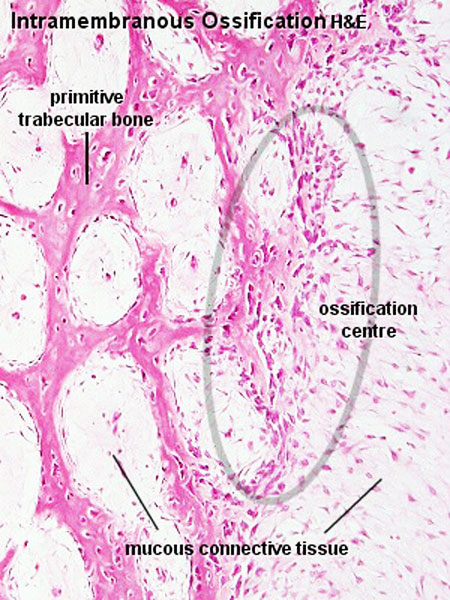
Intramembranous ossification
Links
- Original class notes
- UNSW Virtual Slidebox Virtual Slidebox Phase 1
- Virtual Slidebox of Histology (USA) Skeletal system
Other Textbooks
- Anatomy of the Human Body (H. Gray, 1918.) historical anatomy text Osteology
- Molecular Biology of the Cell Bone Is Continually Remodeled by the Cells Within ItImage: Figure 22-52. Deposition of bone matrix by osteoblasts.Image: Figure 22-56. The development of a long bone.
- Molecular Cell Biology Mutations in Collagen Reveal Aspects of Its Structure and Biosynthesis
- The Cell- A Molecular Approach Steroid Hormones and the Steroid Receptor Superfamily
- Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations 100. Alkaline Phosphatase and Gamma Glutamyltransferase
- Endocrinology: An Integrated Approach by Nussey, S.S. and Whitehead, S.A. Endocrinology: Definition and causes of osteoporosis
- Developmental Biology 6th ed. by Gilbert, Scott F. Aging: The Biology of Senescence