Abnormal Development - Ectopic Implantation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[File:Tubal_pregnancy.gif|thumb|Tubal Pregnancy]] | [[File:Tubal_pregnancy.gif|thumb|Tubal Pregnancy]] | ||
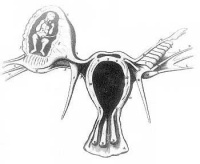
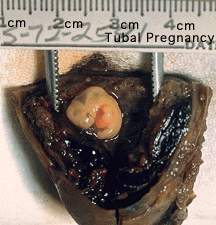
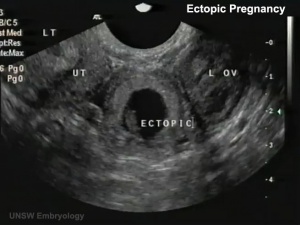
Human development during week 2 is about implantation and the endocrine signaling to block the normal menstrual cycle. The blastocyst implantation process should normally and does occur within the body of the uterus. There are a number of additional abnormal sites of implantation that are outside the uterine body, these are described as ectopic implantation or ectopic pregnancy. The most common form of human ectopic pregnancy is when implantation occurs within the uterine tube, described as a tubal pregnancy. Note that the endocrine signals blocking the menstrual cycle and indicating a pregnancy will still be released following this ectopic implantation. Ectopic pregnancies are therefore often identified by early ultrasound scans. | Human development during week 2 is about implantation and the endocrine signaling to block the normal menstrual cycle. The blastocyst implantation process should normally and does occur within the body of the uterus. There are a number of additional abnormal sites of implantation that are outside the uterine body, these are described as ectopic implantation or ectopic pregnancy. The most common form of human ectopic pregnancy is when implantation occurs within the uterine tube, described as a tubal pregnancy. Note that the endocrine signals blocking the menstrual cycle and indicating a pregnancy will still be released following this ectopic implantation. Ectopic pregnancies are therefore often identified by early ultrasound scans. | ||
==Some Recent Findings== | |||
==Ultrasound Ectopic Implantation== | ==Ultrasound Ectopic Implantation== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 10: | ||
[[Ultrasound - Ectopic 01]] | [[Ultrasound - Ectopic 01]] | ||
==References== | |||
<references/> | |||
===Reviews=== | |||
===Articles=== | |||
===Search Pubmed=== | |||
'''Search Pubmed:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=ectopic%20pregnancy ectopic pregnancy] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=ectopic%20implantation ectopic implantation] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=tubal%20pregnancy tubal pregnancy] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=pubmed&cmd=search&term=tubal%20implantation tubal implantation] | |||
[[Category:Ultrasound]] [[Category:Human Fetus]] [[Category:Abnormal Development]] [[Category:Ectopic Pregnancy]] | [[Category:Ultrasound]] [[Category:Human Fetus]] [[Category:Abnormal Development]] [[Category:Ectopic Pregnancy]] | ||
Revision as of 11:02, 7 June 2010
Introduction
Human development during week 2 is about implantation and the endocrine signaling to block the normal menstrual cycle. The blastocyst implantation process should normally and does occur within the body of the uterus. There are a number of additional abnormal sites of implantation that are outside the uterine body, these are described as ectopic implantation or ectopic pregnancy. The most common form of human ectopic pregnancy is when implantation occurs within the uterine tube, described as a tubal pregnancy. Note that the endocrine signals blocking the menstrual cycle and indicating a pregnancy will still be released following this ectopic implantation. Ectopic pregnancies are therefore often identified by early ultrasound scans.
Some Recent Findings
Ultrasound Ectopic Implantation
References
Reviews
Articles
Search Pubmed
Search Pubmed: ectopic pregnancy | ectopic implantation | tubal pregnancy | tubal implantation