2009 Lecture 1
A Course Introduction
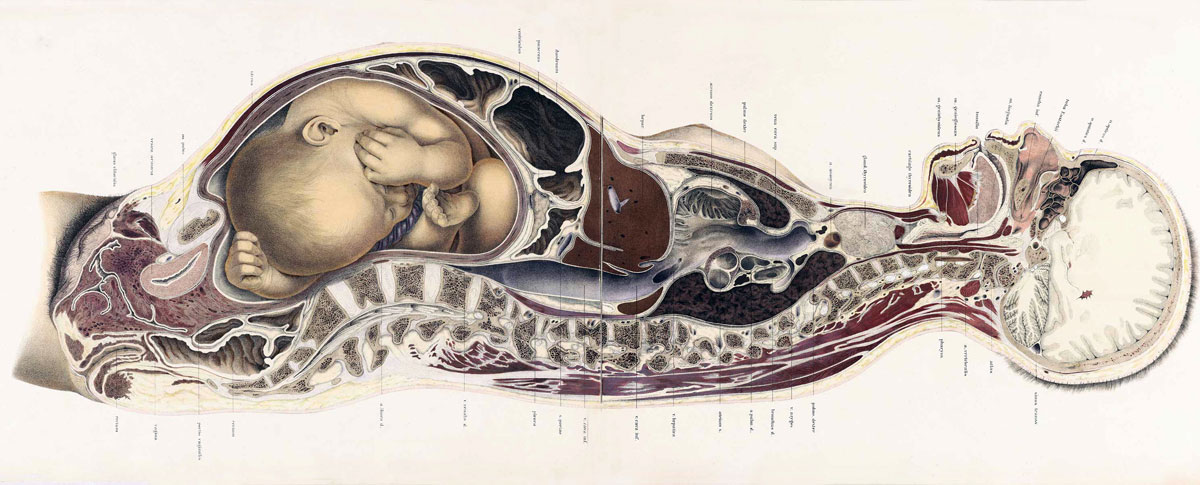
Anatomical image of late pregnancy by Wilhelm Braune (1831-1892): Topographisch-anatomischer Atlas : nach Durchschnitten an gefrornen Cadavern, Leipzig: Verlag von Veit & Comp., 1867-1872. (Topographic-anatomical Atlas) Wilhelm Braune (1831-1892)
This first lecture will introduce the course and the subject of Embryology.
Firstly, an introduction to the course, its content and assessment and an opportunity to ask questions.
Secondly, some historic background to the subject and related current Australian trends.
ANAT2341 Course 2009
Links: Course Homepage | UNSW Embryology
History
Long Ago
- A series of Anatomies from Early History 1600-1700.
- Harvey
- Leeuwenhoek
- 18C Anatomy and Physiology
19th Century
- 1824 - Rolando cut chemically hardened (fixed) pieces of brain tissues into thin sections for microscopical examination
- 1859 - Darwin - On the Origin of Species Evolution Darwin
- 1880 - image excerpts from a historic study of German embryologist Wilhelm His (1831-1904) Anatomie menschlicher Embryonen (1880).
- 1889 - Camille Golgi discovered a method of silver staining hardened brain tissues Brain and Mind Brain Structure
Early 20th Century
- 1914 - image excerpts from a historic study of The Anatomy of a 17.8 mm Human Embryo by Thyng, FW 1914,
- 1918 - links to images from Anatomy of the Human Body by Gray, W 1918
- 1935 - Hans Spemann's 1935 nobel speech.
Development in the early 20th century can also be seen in some Historic Movies 1920-1960.
Late 20th Century
Much of the modern history of Medicine/Embryology is documented in the Prizes for Medicine. Some key women in development 1953 Virginia Apgar and 1965 Le Douarin.
- 1953 - [../Child/apgar.htm Virginia Apgar] Apgar Test.
- 1965 - Neural Crest Research Nicole Le Douarin.
- 1978 - First IVF baby born
21st Century
- 2000 - Human Genome Complete
- 2001 talk given by Robert Winston "Engineering Reproduction: Will We Still Be Human At The End of the 21st Century".
- 2009 - Induced pluripotent stem (iPS) Stem Cells Embryology Blog 2009
Australian Statistics
The data below are highlights from the AIHW National Perinatal Statistics Unit recent annual publication: "Australia's mothers and babies 2005"
- 267,793 women gave birth to 272,419 babies, 15,214 more births (5.9%) than reported in Australia for 2004.
Mothers
- 29.8 years was the mean maternal age, continuing an upward trend. (More? Australian Statistics | Australian Maternal Statistics)
- 9,867 were of Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander origin, making up 3.7% of all mothers.
- 17.4% reported smoking at all during pregnancy. (More? Smoking)
- 58.5% had a spontaneous vaginal birth (0.4% vaginal breech birth, 3.5% forceps and 7.2% vacuum extractions). (More? Birth Overview)
- 30.3% gave birth by caesarean section (19.5% in 1996) (More? Caesarean Delivery)
- 83.2% had previously had a caesarean section
- 1.7% had a multiple pregnancy (More? Twinning)
- 3.0 days median length of stay in hospital (caesarean section 5.0 days)
Babies
- 8.1% were preterm (less than 37 weeks gestation) (More? [../Child/birthpremature.htm Premature Birth] | [../Child/birthweight.htm Low Birth Weight])
- 6.4% of liveborn babies were of low birthweight (less than 2,500 grams) (More? [../Child/birthweight.htm Low Birth Weight] | [../Defect/page10.htm Fetal Origins Hypothesis])
- 105.5 male / 100 female live births
- 15.5% of liveborn babies admitted to a special care nursery or neonatal intensive care unit.
- 6,044 were admitted to level III neonatal intensive care units in Australia and met ANZNN’s high risk criteria, of which 78.0% were preterm.
- 7.3 /1,000 births fetal death rate (More? [../Child/birth7.htm Stillbirth and Perinatal Death])
- 3.2 /1,000 neonatal death rate / live births
- 10.5 /1,000 perinatal death rate / births
Australian Developmental Abnormalities
Ten most frequently reported birth defects in Victoria between 2003-2004 (More? Australian Statistics - Victoria)
- Hypospadias (More? Genital Abnormalities - Hypospadia)
- Obstructive Defects of the Renal Pelvis (More? Urogenital Abnormalities)
- Ventricular Septal Defect (More? Cardiovascular Abnormalities - Ventricular Septal Defect)
- Congenital Dislocated Hip (More? Musculoskelal Abnormalities - Congenital Dislocation of the Hip (CDH))
- Trisomy 21 or Down syndrome - (More? Abnormal Development - Trisomy 21)
- Hydrocephalus (More? Neural Abnormalities - Hydrocephalus)
- Cleft Palate (More? Head Abnormalities)
- Trisomy 18 or Edward Syndrome - multiple abnormalities of the heart, diaphragm, lungs, kidneys, ureters and palate 86% discontinued (More? Abnormal Development - Trisomy 18)
- Renal Agenesis/Dysgenesis - reduction in neonatal death and stillbirth since 1993 may be due to the more severe cases being identified in utero and being represented amongst the increased proportion of terminations (approximately 31%). (More? Kidney Abnormalities - Renal Agenesis)
- Cleft Lip and Palate - occur with another defect in 33.7% of cases. (More? Head Abnormalities)
Links: Historical Embryology | The History of Childbirth | Classic Papers in Neonatal Medicine | Australian Data
UNSW Embryology Links
Next Lecture
- Dr Mark Hill, 2009 UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G