File:Human blastocyst derived stem cells.jpg
Original file (1,200 × 825 pixels, file size: 198 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
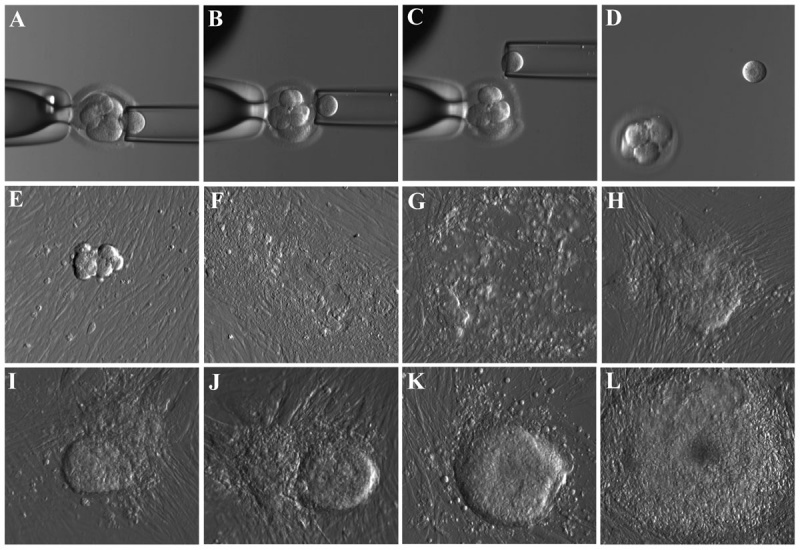
Derivation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells (hESC) from biopsied blastomere of the cleavage stage embryo
Micrographs showing the stepwise procedure of embryo biopsy using inverted microscope-attached micromanipulator (A–D) and the appearance of initial outgrowth and hESC colony during the derivation procedure (E–L). All pictures were taken using microscope mounted digital camera and Hoffman optics under 200X total magnification.
Figure 1. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026570.g001
http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0026570
Copyright: © 2011 Giritharan et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26570. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Human embryonic stem cells derived from embryos at different stages of development share similar transcription profiles. Giritharan G, Ilic D, Gormley M, Krtolica A. Source SLL Sciences, StemLifeLine, Inc., San Carlos, California, United States of America. Abstract We have derived hESC from biopsied blastomeres of cleavage stage embryos under virtually the same conditions we used for the derivation of hESC lines from inner cell mass of blastocyst stage embryos. Blastomere-derived hESC lines exhibited all the standard characteristics of hESC including undifferentiated proliferation, genomic stability, expression of pluripotency markers and the ability to differentiate into the cells of all three germ layers both in vitro and in vivo. To examine whether hESC lines derived from two developmental stages of the embryo differ in gene expression, we have subjected three blastomere-derived hESC lines and two ICM-derived hESC lines grown under identical culture conditions to transcriptome analysis using gene expression arrays. Unlike previously reported comparisons of hESC lines which demonstrated, apart from core hESC-associated pluripotency signature, significant variations in gene expression profiles of different lines, our data show that hESC lines derived and grown under well-controlled defined culture conditions adopt nearly identical gene expression profiles. Moreover, blastomere-derived and ICM-derived hESC exhibited very similar transcriptional profiles independent of the developmental stage of the embryo from which they originated. Furthermore, this profile was evident in very early passages of the cells and did not appear to be affected by extensive passaging. These results suggest that during derivation process cells which give rise to hESC acquire virtually identical stable phenotype and are not affected by the developmental stage of the starting cell population.
PMID 22039509
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 21:50, 7 November 2011 |  | 1,200 × 825 (198 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | == Derivation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells (hESC) from biopsied blastomere of the cleavage stage embryo== Micrographs showing the stepwise procedure of embryo biopsy using inverted microscope-attached micromanipulator (A–D) and the appearance of initi |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: