2011 Lab 1 - Spermatogenesis
From Embryology
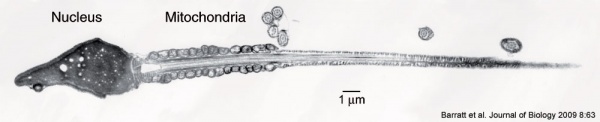
Human Spermatozoa Development
- Spermatogenesis process of spermatagonia mature into spermatazoa (sperm).
- Continuously throughout life occurs in the seminiferous tubules in the male gonad- testis (plural testes).
- At puberty spermatagonia activate and proliferate (mitosis).
- about 48 days from entering meiosis until morphologically mature spermatozoa
- about 64 days to complete spermatogenesis, depending reproduction time of spermatogonia
- follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) - stimulates the spermatogenic epithelium
- luteinizing-hormone (LH) - stimulates testosterone production by Leydig cells
Links: Spermatozoa Development | MBoC - Sperm | MBoC - Highly simplified drawing of a cross-section of a seminiferous tubule in a mammalian testis | MBoC - Cytoplasmic bridges in developing sperm cells and their precursors
Puberty
- In humans at puberty, hormonal and morphological changes occur within the gonad and other systems (secondary sex characteristics).
- Within the testis the immature Sertoli cells cease to proliferate and differentiate.
- Spermatogonium proliferate and spermatogenesis begins.
- It takes about 70 days for cells to mature from the diploid spermatogonium to a primary spermatocyte.
- This maturation occurs in waves along the seminiferous tubules.
Ejeculate
- release of spermatozoa and accessory gland secretions from the male genital tract (3.5 ml)
- 200-600 million sperm, by volume less than 10 % spermatozoa
- Accessory Gland secretions - 60 % seminal vesicle, 30 % prostate and 10 % bulbourethral
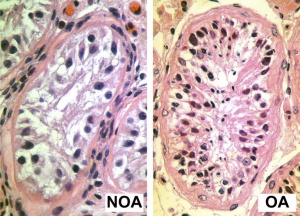
Male Abnormalities
- Oligospermia - (Low Sperm Count) less than 20 million sperm after 72 hour abstinence from sex
- Azoospermia - (Absent Sperm) blockage of duct network
- Immotile Cilia Syndrome - lack of sperm motility