File:Spleen structure 02.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Spleen Structure Cartoon== | ==Spleen Structure Cartoon== | ||
* '''White pulp''' - consists of T cell zones (also known as the periarteriolar lymphoid sheath (PALS)) containing networks of fibroblastic reticular cells (FRC) surrounding a central arteriole, together with B cell follicles containing a central network of follicular dendritic cells (FDC). | |||
** Immune cells enter the white pulp at regions where the T cell zones abut the MZ, known as the MZ bridging channels. | |||
* | * '''Marginal zones''' - (MZ) surrounding the white pulp contain marginal reticular cells (MRC), particularly at the edges of the B cell follicles. | ||
* Marginal zones (MZ) surrounding the white pulp contain marginal reticular cells (MRC), particularly at the edges of the B cell follicles. | * '''Central arteriole''' - Blood and leukocytes entering the spleen pass through branches of the central arteriole, which end in the marginal sinuses and red pulp. | ||
* Blood and leukocytes entering the spleen pass through branches of the central arteriole, which end in the marginal sinuses and red pulp. | * '''Red pulp''' - In the cords of the red pulp, a dense network of reticular fibroblasts and fibres construct an open blood network, which is marked by its lack of a typical endothelial cell lining. | ||
* In the cords of the red pulp, a dense network of reticular fibroblasts and fibres construct an open blood network, which is marked by its lack of a typical endothelial cell lining. | ** Large numbers of macrophages phagocytose dying or damaged red blood cells in the red pulp (not shown). | ||
* Large numbers of macrophages phagocytose dying or damaged red blood cells in the red pulp (not shown) | |||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
Revision as of 19:01, 22 February 2012
Spleen Structure Cartoon
- White pulp - consists of T cell zones (also known as the periarteriolar lymphoid sheath (PALS)) containing networks of fibroblastic reticular cells (FRC) surrounding a central arteriole, together with B cell follicles containing a central network of follicular dendritic cells (FDC).
- Immune cells enter the white pulp at regions where the T cell zones abut the MZ, known as the MZ bridging channels.
- Marginal zones - (MZ) surrounding the white pulp contain marginal reticular cells (MRC), particularly at the edges of the B cell follicles.
- Central arteriole - Blood and leukocytes entering the spleen pass through branches of the central arteriole, which end in the marginal sinuses and red pulp.
- Red pulp - In the cords of the red pulp, a dense network of reticular fibroblasts and fibres construct an open blood network, which is marked by its lack of a typical endothelial cell lining.
- Large numbers of macrophages phagocytose dying or damaged red blood cells in the red pulp (not shown).
Reference
<pubmed>19644499</pubmed>| PMC2785037 | Nat Rev Immunol.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 18:55, 22 February 2012 | 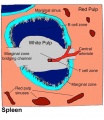 | 401 × 463 (46 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 4 pages use this file: