File:Skeletal muscle basal lamina exp01.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Frog Skeletal Muscle Basal Lamina Experiment== | ==Frog Skeletal Muscle Basal Lamina Experiment== | ||
* Basal lamina directs acetylcholinesterase (AChE) accumulation at synaptic sites in regenerating muscle. | |||
* skeletal muscle damaged such that basal lamina sheaths of the muscle fibers spared | |||
* new myofibers develop within sheaths and neuromuscular junctions form at original synaptic sites | |||
* regenerated neuromuscular junctions have junctional folds and accumulations of acetylcholine receptors and AChE | |||
Sketch shows the paired cutaneous pectoris muscles with attached origin and insertion. | Sketch shows the paired cutaneous pectoris muscles with attached origin and insertion. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 16: | ||
Bar, | Bar, 3 mm. | ||
Latest revision as of 12:25, 16 September 2016
Frog Skeletal Muscle Basal Lamina Experiment
- Basal lamina directs acetylcholinesterase (AChE) accumulation at synaptic sites in regenerating muscle.
- skeletal muscle damaged such that basal lamina sheaths of the muscle fibers spared
- new myofibers develop within sheaths and neuromuscular junctions form at original synaptic sites
- regenerated neuromuscular junctions have junctional folds and accumulations of acetylcholine receptors and AChE
Sketch shows the paired cutaneous pectoris muscles with attached origin and insertion.
The muscle on the left is intact.
The nerve enters from the lateral edge.
Two rectangular areas have been cut from the muscle on the right, leaving behind a row of muscle fiber segments, a "bridge", between undamaged medial and lateral fibers.
In some experiments, a "foreign" nerve (arrow), which normally supplies the forelimb, was implanted near the bridge.
Bar, 3 mm.
Reference
<pubmed>307554</pubmed>
See also: Anglister L, McMahan UJ J Cell Biol 1985 Sep;101(3):735-43 PMC2117033
Copyright
Rockefeller University Press - Copyright Policy This article is distributed under the terms of an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike–No Mirror Sites license for the first six months after the publication date (see http://www.jcb.org/misc/terms.shtml). After six months it is available under a Creative Commons License (Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 4.0 Unported license, as described at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/ ). (More? Help:Copyright Tutorial)
Figure 1
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 25) Embryology Skeletal muscle basal lamina exp01.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Skeletal_muscle_basal_lamina_exp01.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 12:21, 16 September 2016 | 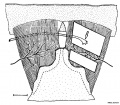 | 918 × 800 (190 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Frog Skeletal Muscle Basal Lamina Experiment== Sketch shows the paired cutaneous pectoris muscles with attached origin and insertion. The muscle on the left is intact. The nerve enters from the lateral edge. Two rectangular areas have been cut... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
There are no pages that use this file.