File:Nuclear lamina cartoon.jpg: Difference between revisions
(==Functions of the nuclear lamina== A cartoon representation of the nuclear lamina, highlighting four key functions. (a) The lamina regulates genome organization and chromatin structure by direct interactions with chromatin and indirectly through associa) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Functions of the nuclear lamina== | ==Functions of the nuclear lamina== | ||
A cartoon representation of the nuclear lamina, highlighting four key functions | A cartoon representation of the nuclear lamina, highlighting four key functions. | ||
'''(a)''' The lamina regulates genome organization and chromatin structure by direct interactions with chromatin and indirectly through association with chromatin-modifying and regulatory proteins. | |||
'''(b)''' The lamina regulates gene expression by sequestering transcription factors at the nuclear envelope, which limits their availability in the nucleoplasm. | |||
'''(c)''' It also mediates structural linkages between the nucleus and cytoskeleton, through the LINC complex consisting of lamins, an inner nuclear membrane protein, and an interacting outer nuclear membrane protein, which in turn binds cytoskeletal elements. | |||
http://genomebiology.com/content/12/5/222 | '''(d)''' The lamina also provides a platform for assembly of protein complexes involved in signal transduction pathways. P, phosphate. | ||
===Reference=== | |||
<pubmed>21639948</pubmed>| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3219962 PMC3219962] | [http://genomebiology.com/content/12/5/222 Genome Biology] | |||
| Line 14: | Line 19: | ||
Gb-2011-12-5-222-5.jpg | Gb-2011-12-5-222-5.jpg | ||
[[Category:Cartoon]] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:31, 13 June 2012
Functions of the nuclear lamina
A cartoon representation of the nuclear lamina, highlighting four key functions.
(a) The lamina regulates genome organization and chromatin structure by direct interactions with chromatin and indirectly through association with chromatin-modifying and regulatory proteins.
(b) The lamina regulates gene expression by sequestering transcription factors at the nuclear envelope, which limits their availability in the nucleoplasm.
(c) It also mediates structural linkages between the nucleus and cytoskeleton, through the LINC complex consisting of lamins, an inner nuclear membrane protein, and an interacting outer nuclear membrane protein, which in turn binds cytoskeletal elements.
(d) The lamina also provides a platform for assembly of protein complexes involved in signal transduction pathways. P, phosphate.
Reference
<pubmed>21639948</pubmed>| PMC3219962 | Genome Biology
Authors of Research Articles, Methodologies and Software articles published in Genome Biology are the copyright holders of their articles and have granted to any third party, in advance and in perpetuity, the right to use, reproduce or disseminate the article, according to the BioMed Central copyright and license agreement.
Gb-2011-12-5-222-5.jpg
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 07:29, 13 June 2012 | 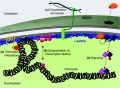 | 800 × 585 (114 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Functions of the nuclear lamina== A cartoon representation of the nuclear lamina, highlighting four key functions. (a) The lamina regulates genome organization and chromatin structure by direct interactions with chromatin and indirectly through associa |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: