File:Male - inguinal hernia.jpg: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(==Male Inguinal Hernia== Category:Human Category:Abnormal Development Category:Genital Category:Gastrointestinal Tract) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Male Inguinal Hernia== | ==Male Inguinal Hernia== | ||
* Indirect inguinal hernia is a common condition in male infants | |||
* resulting from a '''patent processus vaginalis''' | |||
* allowing communication between the peritoneal cavity and the scrotal sac | |||
* through which portions or loops of small intestine may herniate. | |||
* This is a common surgical repair operation in young children. | |||
:'''Links:''' [[Genital System - Abnormalities]] | |||
===Hydrocele=== | |||
* a fluid-filled cavity of eiter testis or spermatic cord, where peritoneal fluid passes into a patent processus vaginalis. | |||
* Hydrocele of the testis is when a very small patent processus vaginalis may not herniate, but allow fluid to pass from the periotoneal cavity leading to the collection of serous fluid between the layers of the membrane (tunica vaginalis). | |||
** Normal - fluid around the testicle is absorbed | |||
** Noncommunicating hydrocele - fluid remains around the testicle | |||
** Communicating hydrocele - fluid flows back and forth between the scrotum and the abdomen | |||
** Hydrocele of the cord - fluid is located between the scrotum and the abdomen | |||
|} | |||
[[Category:Human]] [[Category:Abnormal Development]] [[Category:Genital]] [[Category:Gastrointestinal Tract]] | [[Category:Human]] [[Category:Abnormal Development]] [[Category:Genital]] [[Category:Gastrointestinal Tract]] | ||
Revision as of 18:31, 29 May 2011
Male Inguinal Hernia
- Indirect inguinal hernia is a common condition in male infants
- resulting from a patent processus vaginalis
- allowing communication between the peritoneal cavity and the scrotal sac
- through which portions or loops of small intestine may herniate.
- This is a common surgical repair operation in young children.
Hydrocele
- a fluid-filled cavity of eiter testis or spermatic cord, where peritoneal fluid passes into a patent processus vaginalis.
- Hydrocele of the testis is when a very small patent processus vaginalis may not herniate, but allow fluid to pass from the periotoneal cavity leading to the collection of serous fluid between the layers of the membrane (tunica vaginalis).
- Normal - fluid around the testicle is absorbed
- Noncommunicating hydrocele - fluid remains around the testicle
- Communicating hydrocele - fluid flows back and forth between the scrotum and the abdomen
- Hydrocele of the cord - fluid is located between the scrotum and the abdomen
|}
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 18:27, 29 May 2011 | 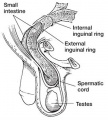 | 361 × 400 (34 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Male Inguinal Hernia== Category:Human Category:Abnormal Development Category:Genital Category:Gastrointestinal Tract |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: