File:Integumentary touch dome functions.jpg: Difference between revisions
(Merkel cells and touch domes: more than mechanosensory functions? Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23(10):692-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12456. Epub 2014 Jul 16. ==Integumentary touch dome functions== Xiao Y1, Williams JS, Brownell I. Abstract The touch dome (TD) i...) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Merkel cells and touch | ==Integumentary touch dome functions== | ||
Schematic of the mouse touch dome. Markers reported to be expressed in Merkel cells and touch dome keratinocytes that suggest function. | |||
:'''Links:''' [[Sensory - Touch Development]] | [[Immune System Development]] | [[Endocrine System Development]] | |||
== | ===Reference=== | ||
<pubmed>24862916</pubmed> | |||
Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23(10):692-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12456. Epub 2014 Jul 16. | |||
PMID 24862916 PMCID: PMC4180785 DOI: 10.1111/exd.12456 | |||
====Copyright==== | |||
Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. | Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. | ||
Figure 1. Schematic of the mouse touch dome. Markers reported to be expressed in Merkel cells and touch dome keratinocytes that suggest function. | |||
{{Footer}} | |||
[[Category:Integumentary]][[Category:Cartoon]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:21, 22 September 2016
Integumentary touch dome functions
Schematic of the mouse touch dome. Markers reported to be expressed in Merkel cells and touch dome keratinocytes that suggest function.
Reference
<pubmed>24862916</pubmed>
Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23(10):692-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12456. Epub 2014 Jul 16.
PMID 24862916 PMCID: PMC4180785 DOI: 10.1111/exd.12456
Copyright
Published 2014. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. Figure 1. Schematic of the mouse touch dome. Markers reported to be expressed in Merkel cells and touch dome keratinocytes that suggest function.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 23) Embryology Integumentary touch dome functions.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Integumentary_touch_dome_functions.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:02, 22 September 2016 | 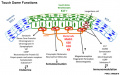 | 893 × 556 (97 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | |
| 10:02, 22 September 2016 |  | 950 × 664 (115 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | Merkel cells and touch domes: more than mechanosensory functions? Exp Dermatol. 2014 Oct;23(10):692-5. doi: 10.1111/exd.12456. Epub 2014 Jul 16. ==Integumentary touch dome functions== Xiao Y1, Williams JS, Brownell I. Abstract The touch dome (TD) i... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: