File:Odgers1938 fig04.jpg: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{ | {{Odgers1938 figures}} | ||
Latest revision as of 20:00, 22 April 2016
Plate I Fig 4
Abbreviations
- R.B.R. right bulbar ridge.
- L.B.R. left bulbar ridge.
- R.S.T. right superior tubercle of the A.-V. cushions.
- R.I.T. right inferior tubercle of the A.-V. cushions.
- I.V.S. interventricular septum.
- A.V.C. auriculoventricular cushions.
- B.A.C. bulbo-auricular channel.
Figs. 3-5. Sections through this region of the heart in a 12-5 mm. embryo ( x 80).
Fig. 3 shows the interventricular septum, I. V.S., capped by cushion tissue (X), which is in contact with the right bulbar ridge, R.B.R.
In Fig. 4, which is the next section below Fig. 3, this tissue X is connected with both the right bulbar ridge, R.B.R., and with the A.-V. cushions, A.V.0.
Fig. 5 is a section three below the last and shows the proliferating tissue joining the A.-V. cushions, A.V.0. The junction between the two is marked on either side by a notch. The bulbo-auricular channel, B.A.C., appears in Fig. 3 as a. narrow cleft between the right bulbar ridge, R.B.R., and the A.-V. cushions, A. V.0.: in Fig. 4 this channel is better marked, while in Fig. 5 it is seen to be continuous with the right auricle.
| Historic Disclaimer - information about historic embryology pages |
|---|
| Pages where the terms "Historic" (textbooks, papers, people, recommendations) appear on this site, and sections within pages where this disclaimer appears, indicate that the content and scientific understanding are specific to the time of publication. This means that while some scientific descriptions are still accurate, the terminology and interpretation of the developmental mechanisms reflect the understanding at the time of original publication and those of the preceding periods, these terms, interpretations and recommendations may not reflect our current scientific understanding. (More? Embryology History | Historic Embryology Papers) |
Reference
Odgers PN. The development of the pars membranacea septi in the human heart. (1938) J Anat. 72(2): 247-59. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17104688 PMID 17104688]
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 22) Embryology Odgers1938 fig04.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Odgers1938_fig04.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 11:16, 25 January 2016 | 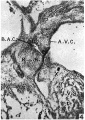 | 507 × 716 (112 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Plate I== Abbreviations * R.B.R. right bulbar ridge. * L.B.R. left bulbar ridge. * R.S.T. right superior tubercle of the A.-V. cushions. * R.I.T. right inferior tubercle of the A.-V. cushions. * I.V.S. interventricular septum. * A.V.C. auriculoventr... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file:
