Trisomy 18: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
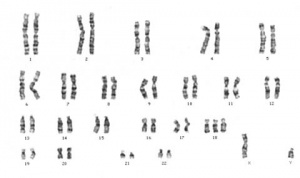
[[File:Trisomy18male.jpg|thumb|Karyotype Trisomy 18 male]] | |||
====Organ Malformations==== | ====Organ Malformations==== | ||
1. Central Nervous System | 1. Central Nervous System | ||
Revision as of 10:34, 27 March 2010
Organ Malformations
1. Central Nervous System
- severe mental retardation
- hypotonia -> hypertonia
- neural tube defects
- poor suck and weak cry
- failure to thrive
- ocular anomalies
2. Respiratory
- apnea
3. Cardiovascular( >95%)
- major: VSD, ASD, PDA
- minor: transposition, ToF, coarctation, anomalous coronary artery, dextrocardia, aberrant subclavian artery, arteriosclerosis, PS, bicuspid aortic and/or pulmonic valves
4. Gastrointestinal
- inguinal, umbilical, and/or diaphragmatic hernia
- congenital defects: diastasis recti, heterotopic pancreas, malrotation, Meckel's, tracheoesophageal fistula
5. Genitourinary
- cryptorchidism
- congenital defects: double ureter, ectopic kidney, horseshoe kidney, hydronephrosis, polycystic kidney
Investigations
Imaging Studies
- to rule out organ malformations:
- cardiovascular anomalies - Echo
- gastrointestinal anomalies - Barium Swallow, Endoscope
- genitourinary anomalies - Ultrasound
Karyotyping
Management
Supportive, very poor prognosis.
- 30% dying by 1 month of age
- 50% dying by 2 months of age
- 90% dying by 12 months of age
Genetic counselling, recurrence rate depends on genotype.
(modified from original 1999 Pedbase entry)