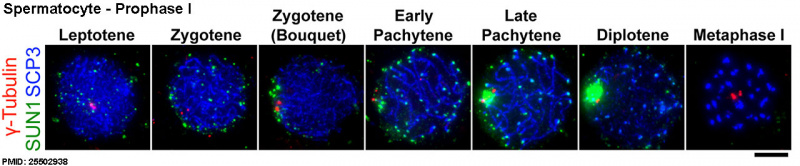
| Prophase I is divided into 5 stages (leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, diakinesis) The bouquet stage occurs at the transition from leptotene to zygotene stage, where the chromosome telomeres attachment to the inner nuclear envelope and form a cluster and occurs before the onset of homologous pairing and synapsis. The name comes from the chromosomes resembling a "bouquet of flowers".
- Prophase I Movies: leptotene-zygotene stage | bouquet stage | pachytene stage | pachytene stage | diplotene
| Cell Division Terms (expand to view)
|
meiosis | mitosis
- anaphase - (Greek, ana = up, again) Mitosis term referring to the fourth stage, where the paired chromatids now separate and migrate to spindle poles. This is followed by telophase.
- anaphase A - Mitosis term referring to the part of anaphase during which the chromosomes move.
- anaphase B - Mitosis term referring to the part of anaphase during which the poles of the mitotic spindle move apart.
- aneuploidy - (aneuploid) term used to describe an abnormal number of chromosomes mainly (90%) due to chromosome malsegregation mechanisms in maternal meiosis I.
- aster - (Latin, aster = star) star-like object visible in most dividing eukaryotic cells contains the microtubule organizing center.
- astral microtubule - spindle apparatus microtubule (MT) originating from the centrosome which does not connect to a kinetochore. These microtubules only exist during mitosis, the other spindle types are polar and kinetochore microtubules.
- autosomal inheritance - term used in hereditary diseases which means that the disease is due to a DNA error in one of the 22 chromosome pairs that are not sex chromosomes. Both boys and girls can then inherit this error. If the error is in a sex chromosome, the inheritance is said to be sex-linked.
- bivalent - (tetrad) a pair of homologous chromosomes physically held together by at least one DNA crossover.
- bouquet stage - meiosis term for when in prophase transition to the zygotene stage, the chromosome telomeres attachment to the inner nuclear envelope and form a cluster. This occurs before the onset of homologous pairing and synapsis. The name comes from the chromosomes resembling a "bouquet of flowers".
- diploid - (Greek, di = double + ploion = vessel) having two sets of chromosomes (2n), this is the normal euploidy state for all human cells, other than gametes that are haploid (n, a single set of chromosomes).
- diplotene stage- (diplotene phase, diplonema; Greek, diplonema = "two threads") meiotic stage seen during prophase I, the chromosomes separate from one another a small amount giving this appearance. In the developing human ovary, oocytes remain at the diplotene stage from fetal life through postnatal childhood, until puberty when the lutenizing hormone (LH) surges stimulate the resumption of meiosis. Prophase I, is divided into 5 stages (leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, diakinesis) based upon changes associated with the synaptonemal complex structure that forms between two pairs of homologous chromosomes.
- euploidy - the normal genome chromosomal set (n, 2n, 3n) or complement for a species, in humans this is diploid (2n). The other classes of numerical chromosomal abnormalities include aneuploidy, polyploidy and mixoploidy.
- FUCCI - Acronym for Fluorescence Ubiquitination Cell Cycle Indicator a molecular tool for identifying the stage in the cell cycle. In G0/G1 cells express a red fluorescent protein and S/G2/M cells express a green fluorescent protein. (More? Tooth Development Movie)
- haploid - (Greek, haploos = single) Having a single set of chromosomes (n) as in mature germ/sex cells (oocyte, spermatozoa) following reductive cell division by meiosis. Normally cells are diploid, containing 2 sets of chromosomes. Ploidy refers to the number of sets of chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell.
- heteroplasmy - presence of more than one type of organellar genome. In humans this can refer to variations in the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). (More? PMID 26281784)
- homologous chromosomes - meiosis term for the two matching (maternal and one paternal) chromosomes that align during meiosis I.
- homologous recombination - meiosis term when DNA of homologous chromosomes is covalently exchanged to produce chromosomes with new allele combinations, and also links homologous chromosomes with each other to form a bivalent
- human genome - DNA within the 23 nucleus chromosome pairs and the cytoplasmic mitochondrial DNA.
- kinetochore - the protein structure formed on chromatids where the spindle kinetochore microtubules attach during cell division.
- kinetochore microtubule - spindle apparatus microtubule (MT) that attaches to the chromosome kinetochore by its plus end, the other spindle types are astral and polar microtubules.
- kinesin - a microtubule (MT) motor protein that exists in many isoforms and most move towards the MT positive end. Different isoforms have different functions within the spindle apparatus. PMID 20109570
- meiosis - reductive cell division required to produce germ cells (oocyte, spermatozoa) and for sexual reproduction. Note that only spermatozoa complete meiosis before fertilisation. Chromosome number is reduced from diploid to haploid, during this process maternal and paternal genetic material are exchanged. All other non-germ cells in the body divide by mitosis. (More? Meiosis | Spermatozoa Development | Oocyte Development | Week 1)
- meiosis I - (MI) the first part of meiosis resulting in separation of homologous chromosomes, in humans producing two haploid cells (N chromosomes, 23), a reductional division.
- meiosis II - (MII) the second part of meiosis. In male human spermatogenesis, producing of four haploid cells (23 chromosomes, 1N) from the two haploid cells (23 chromosomes, 1N), each of the chromosomes consisting of two sister chromatids produced in meiosis I. In female human oogenesis, only a single haploid cell (23 chromosomes, 1N) is produced. Meiosis II: Prophase II - Metaphase II - Anaphase II - Telophase II.
- meiotic silencing of unsynapsed chromatin - (MSUC) an aneuploidy protective mechanism for subsequent generations, during meiosis where chromosomes are silenced that fail to pair with their homologous partners.
- merotelic kinetochore - cell division abnormality in chromosomal attachment that occurs when a single kinetochore is attached to microtubules arising from both spindle poles. Normal chromosomal attachment in early mitosis, is by only one of the two sister kinetochores attached to spindle microtubules (monotelic attachment) later sister kinetochores attach to microtubules arising from opposite spindle poles (amphitelic attachment).
- metaphase - mitosis term referring to the third stage where mitotic spindle kinetochore microtubules align chromosomes in one midpoint plane. Metaphase ends when sister kinetochores separate. Originally based on light microscopy of living cells and electron microscopy of fixed and stained cells. A light microscope analysis called a "metaphase spread" was originally used to detect chromosomal abnormalities in cells. Mitosis Phases: prophase - prometaphase - metaphase - anaphase - telophase
- metaphase spread - In mitosis using light microscope analysis originally used to detect chromosomal abnormalities in cells, as chromosomes are only visible during cell division.
- microfilament - (MF) cytoskeleton filament normally required for cytoplasmic intracellular transport, motility and cell shape. Named by the actin monomers assembling into the smallest in cross-section of the three filament systems (microtubules and intermediate filaments). This system is disassembled and reassembled as the contractile ring for cytokinesis (cytoplasm division) following cell division mitosis and meiosis.
- microtubule - (MT) cytoskeleton filament normally required for cytoplasmic intracellular transport and motility. Named by the tubulin monomers assembling into "tubes", and are the largest in cross-section of the three filament systems (microfilaments and intermediate filaments). This system is disassembled and reassembled as the spindle apparatus during cell division.
- mitochondrial DNA - (mtDNA) multiple copies of a small circular DNA molecule located within the mitochondria matrix. In humans 16,568 bp in length containing 37 genes, originally inherited only from the oocyte (maternal inheritance).
- mitosis - (M phase) The normal division of all cells, except germ cells, where chromosome number is maintained (diploid). In germ cell division (oocyte, spermatozoa) meiosis is a modified form of this division resulting in reduction in genetic content (haploid). Mitosis, division of the nucleus, is followed by cytokinesis the division of the cell cytoplasm and the cytoplasmic contents. cytokinesis overlaps with telophase.
- p - chromosome short arm (possibly French, petit) and used along with chromosome and band number to indicate genes located on this arm of the chromosome. The chromosome long arm is identified as q (possibly French, tall) chosen as next letter in alphabet after p. These chromosomal arms are only seen when the chromosome is folded for cell division.
- polar microtubule - spindle apparatus microtubule (MT) that can arise from either pole and overlap at the spindle midzone. This interdigitating structure consisting of antiparallel microtubules is responsible for pushing the poles of the spindle apart. The other spindle types are astral and kinetochore microtubules.
- prometaphase - (Greek, pro = before) mitosis term referring to the second stage, when the nuclear envelope breaks down into vesicles. Microtubules then extend from the centrosomes at the spindle poles (ends) and reach the chromosomes. This is followed by metaphase.
- pronuclear fusion - (Greek, pro = before) the process of the fusion of the two haploid nuclear structures (pronuclei) contributed from the spermatazoa and oocyte to form the first diploid nucleus cell. Can also be called "fusion of pronuclei".
- pronucleus - (Greek, pro = before; plural, pronuclei) the two haploid nuclei or nuclear structures containing the genetic material from the spermatozoa and the oocyte. These two haploid nuclei will fuse together to form the first diploid nucleus cell, the zygote. Therefore the nuclear structures that exist "before the nucleus", the plural term is pronuclei.
- prophase - (Greek, pro = before) - mitosis term referring to the first stage, when the diffusely stained chromatin resolves into discrete chromosomes, each consisting of two chromatids joined together at the centromere.
- prophase I - meiosis term refers to the first phase of meiosis I, which together with meiosis II results in the reductive cell division only occurring gametes. Prophase can be further divided into a number of stages: leptotene zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, diakinesis.
- q - chromosome long arm (possibly French, tall), the next letter in alphabet after p, and used along with chromosome and band number to indicate genes located on this arm of the chromosome. The chromosome short arm is identified as p (possibly French, petit). These chromosomal arms are only seen when the chromosome is folded for cell division.
- S phase - during interphase of cell cycle where DNA is duplicated prior to second growth period (G2 phase) that is followed by mitosis (M phase).
- synapsis - (syndesis) meiosis term for the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occurs during prophase I.
- synaptonemal complex - meiosis term for a protein structure essential for synapsis of homologous chromosomes. (proteins SCP3 and SCP1).
- telomere - region found at each end of the chromosome and involved in cellular ageing and the capacity for division. The regions consist of repeated sequences protecting the ends of chromosomes and harbour DNA repair proteins. In the absence of the enzyme telomerase, these regions shorten during each cell division and becoming critically short, cell senescence occurs.
- telophase - mitosis term referring to the fifth stage, where the vesicles of the nuclear envelope reform around the daughter cells, the nucleoli reappear and the chromosomes unfold to allow gene expression to begin. This phase overlaps with cytokinesis, the division of the cell cytoplasm.
- telomerase - the enzyme that maintains the chromosome end length, the telomeres, involved in cellular ageing and the capacity for division. Absence of telomerase activity leads to the chromosome ends shorten during each cell division, becoming critically short and cell senescence then occurs.
- tetrad - (bivalent) a pair of homologous chromosomes physically held together by at least one DNA crossover.
|
|
|
|