File:Nuclear lamins protein structure.jpg
Nuclear_lamins_protein_structure.jpg (600 × 431 pixels, file size: 52 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
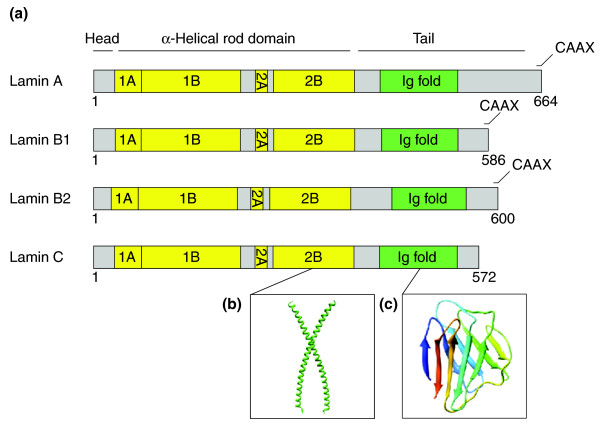
Nuclear lamins - domain organization and protein structure
(a) Domain organization of the major lamins in humans. The α-helical rod domain comprises four segments, 1A, 1B, 2A, 2B (yellow), which are separated by linker segments, L1, L12 and L2. The tail domain contains a nuclear localization signal, an immunoglobulin domain (green), and a conserved CAAX box, which undergoes farnesylation.
(b) The structure of a portion of the α-helical rod domain corresponding to human lamin A segment 2B (PDB code: 1X8Y) [1].
(c) The structure of the Ig domain from human lamin A/C (PDB: 1IFR)[2].
Reference
<pubmed>21639948</pubmed>| PMC3219962 | Genome Biology
Dittmer and Misteli Genome Biology 2011 12:222 doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-5-222
Authors of Research Articles, Methodologies and Software articles published in Genome Biology are the copyright holders of their articles and have granted to any third party, in advance and in perpetuity, the right to use, reproduce or disseminate the article, according to the BioMed Central copyright and license agreement.
Gb-2011-12-5-222-1.jpg
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 07:38, 13 June 2012 |  | 600 × 431 (52 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Nuclear lamins - domain organization and protein structure== (a) Domain organization of the major lamins in humans. The α-helical rod domain comprises four segments, 1A, 1B, 2A, 2B (yellow), which are separated by linker segments, L1, L12 and L2. The |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: