File:Lymphatic microvasculature model.jpg
Lymphatic_microvasculature_model.jpg (356 × 440 pixels, file size: 40 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
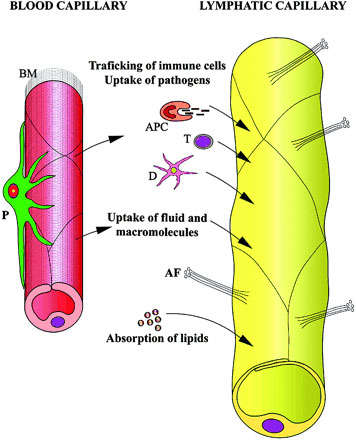
Characteristic structure and function of the lymphatic microvasculature
The lymphatic capillary is uniquely adapted for the uptake of fluid, lipids, macromolecules, and cells from the interstitium. In contrast to the blood capillary, the lymphatic capillary has poorly developed basal lamina (BM) and is devoid of pericytes (P). Lymphatic endothelium is highly attenuated, and cells are connected directly to the interstitial collagen via anchoring filaments (AF). T, T cell; D, dendritic cell; APC, antigen presenting cell.
Original file name: Figure 1. F1.medium.jpg http://jcb.rupress.org/content/163/2/209/F1.large.jpg
Reference
<pubmed>14581448</pubmed>| JCB
Copyright
Rockefeller University Press - Copyright Policy This article is distributed under the terms of an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike–No Mirror Sites license for the first six months after the publication date (see http://www.jcb.org/misc/terms.shtml). After six months it is available under a Creative Commons License (Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 4.0 Unported license, as described at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/ ). (More? Help:Copyright Tutorial)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 00:04, 22 February 2011 |  | 356 × 440 (40 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | ==Characteristic structure and function of the lymphatic microvasculature== The lymphatic capillary is uniquely adapted for the uptake of fluid, lipids, macromolecules, and cells from the interstitium. In contrast to the blood capillary, the lymphatic ca |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: