File:G-protein coupled receptors.jpg
Original file (900 × 655 pixels, file size: 109 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
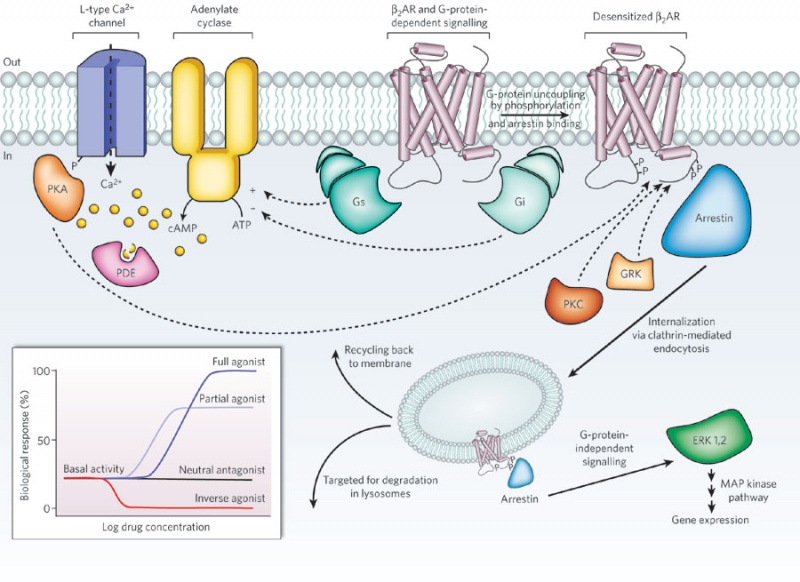
Signal Transduction in G-protein-coupled Receptors
- Common structural motif of 7 membrane spanning regions
- Receptor binding promotes interaction
- between receptor
- G protein on interior surface of membrane
- Induces an exchange of GDP for GTP on G protein α subunit and dissociation of the α subunit from the βγ heterodimer
Type 2 Beta Adrenergic Receptor (2AR)
The 2AR can activate two G proteins, Gs and Gi (part of the Gs and Gi heterotrimers, respectively), which differentially regulate adenylate cyclase. Adenylate cyclase generates cyclic AMP (cAMP), which activates protein kinase A (PKA), a kinase that regulates the activity of several cellular proteins including the L-type Ca2+ channel and the 2AR. cAMP second messenger levels are downregulated by specific phosphodiesterase proteins (PDEs).
Activation of the 2AR also leads to phosphorylation by a G-protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) and subsequent coupling to arrestin. Arrestin is a signalling and regulatory protein that promotes the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK), prevents the activation of G proteins and promotes the internalization of the receptor through clathrin-coated pits. PKC, protein kinase C. The inset shows classification of ligand efficacy for GPCRs. Many GPCRs exhibit basal, agonist-independent activity. Inverse agonists inhibit this activity, and neutral antagonists have no effect. Agonists and partial agonists stimulate biological responses above the basal activity. Efficacy is not directly related to affinity; for example, a partial agonist can have a higher affinity for a GPCR than a full agonist.
- Links: Adrenal Development | Pituitary Development
Reference
<pubmed>19458711</pubmed>
Copyright
Reprinted by Permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: from The structure and function of G-protein-coupled receptors. Rosenbaum DM, Rasmussen SG, Kobilka BK. Nature. 2009 May 21;459(7245):356-63. Review.
Original file name: Nature08144-f1.2.jpg http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v459/n7245/fig_tab/nature08144_F1.html
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v459/n7245/full/nature08144.html
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 27) Embryology G-protein coupled receptors.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:G-protein_coupled_receptors.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 10:57, 23 May 2016 |  | 900 × 655 (109 KB) | Z8600021 (talk | contribs) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: