BGDA Practical 3 - Notochord
| Practical 3: Oogenesis and Ovulation | Gametogenesis | Fertilization | Early Cell Division | Week 1 | Implantation | Week 2 | Extraembryonic Spaces | Gastrulation | Notochord | Week 3 |
Introduction
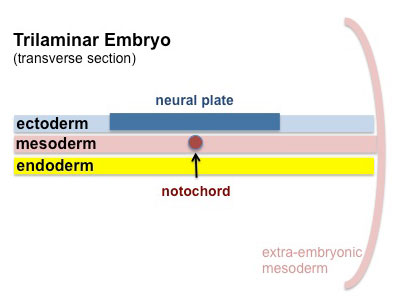
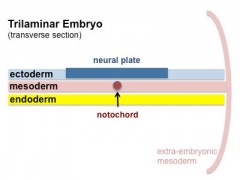
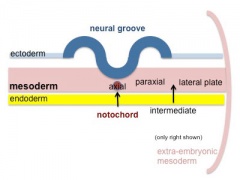
The embryonic structure which establishes body axes and patterns surrounding tissues is called the notochord.
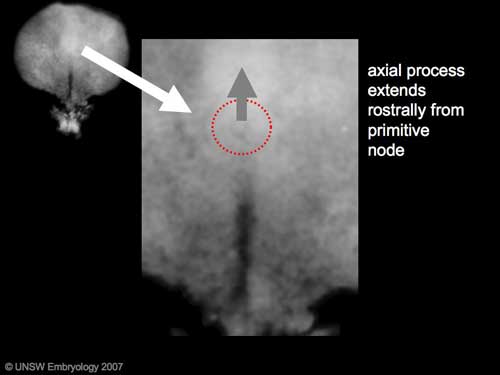
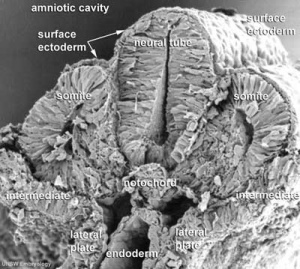
The notochord is a midline column of cells running in a rostrocaudal direction (head-tail) within the mesoderm layer. It exists as a transient developmental patterning structure with a role in molecular signaling (patterning) and controlling the direction of embryonic disc folding (mechanical). These images are of the embryonic disc in week 3 (stage 7).
The notochordal process begins as a fold of ectoderm extending cranially toward the prechordal plate region. The sequence of differentiation: notochordal process -> notochordal plate -> notochord.
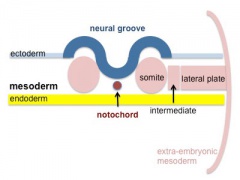
- Elongation of the notochordal process cranially from the primitive pit as a hollow tube (notochordal canal) in the midline of the embryonic disc underlying the ectoderm.
- The notochordal canal may appear to break down on the endodermal side forming a notochordal plate continuous with the endodermal layer.
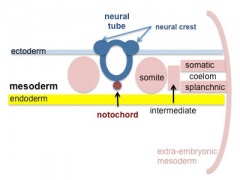
- Notochordal plate folds to form notochord. The notochord (also called axial mesoderm) is an embryonic structure that regulates differentiation of surrounding structures including the overlying ectoderm (neural plate) and mesoderm (somites).
| <html5media height="360" width="280">File:Notochord 02.mp4</html5media> | This animation shows the early development of the notochord occurring during week 3 of human development.
This is a dorsal view of the embryonic disc, caudal (tail and connecting stalk end) to the bottom and rostral (head end) to the top. The indentations show the location of the cloacal (bottom) and buccopharyngeal (top) membranes. The raised region in the middle of the embryonic disc is the primitive node (Hensen's node). The right hand side of the gastrulating embryonic disc is removed to the midline to show the the position of the initial axial process (purple). As the animation plays the axial process extends rostrally from the primitive node towards the buccopharyngeal membrane, where it stops. A cross-section view above the primitive node is shown in the second animation below.
|
| <html5media height="200" width="240">File:Notochord 01.mp4</html5media> |
The view is a cross-section showing how the axial process initially is formed, then fused with the endoderm, to finally separate as a midline mesoderm structure.
Yellow - endoderm | Purple - axial process
Links: MP4 version | Notochord |
Disc Folding
| |||||||||
| Folding: all edges of the embryonic disc will fold ventrally, forming a rostro-caudal "C" shaped tube. |
- Mesoderm and Ectoderm Cartoons
References
| Practical 3: Oogenesis and Ovulation | Gametogenesis | Fertilization | Early Cell Division | Week 1 | Implantation | Week 2 | Extraembryonic Spaces | Gastrulation | Notochord | Week 3 |