BGDA Practical 3 - Gastrulation
| Practical 3: Oogenesis and Ovulation | Gametogenesis | Fertilization | Early Cell Division | Week 1 | Implantation | Week 2 | Extraembryonic Spaces | Gastrulation | Notochord | Week 3 |
Introduction
|
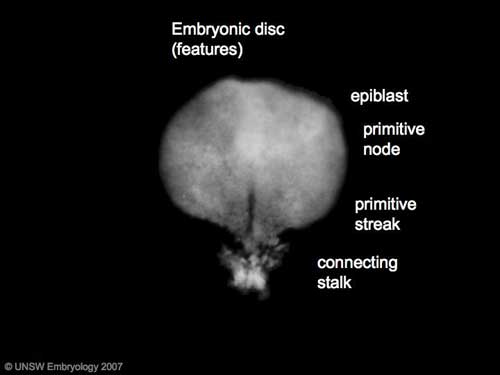
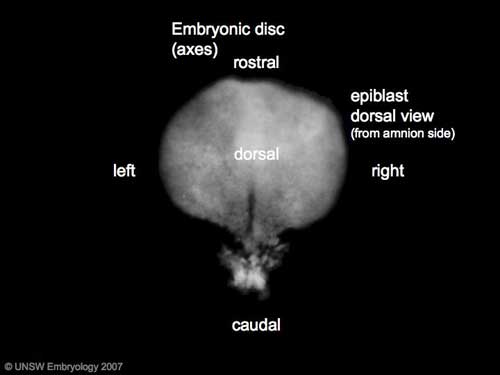
Gastrulation means "gut forming" and converts the inner cell mass which then formed the bilaminar embryo (epiblast, hypoblast) into the trilaminar embryo (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm).
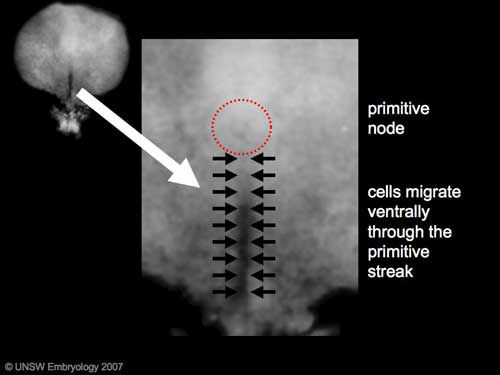
The process involves the migration of cells from the epiblast layer through the primitive streak to form first the endoderm layer and then a second intermediate layer the mesoderm layer. Once all cells have left the epiblast layer it now becomes the ectoderm layer. These three germ cell layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) will form in a layer specific manner all the future tissues of the developing embryo.
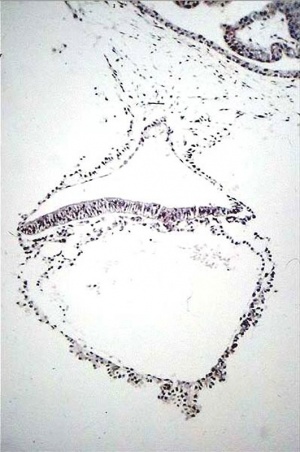
Approximate cross-section of an 18 day human conceptus. Identify the 3 layers of the trilaminar embryo: ectoderm (columnar cells), intraembryonic mesoderm (mesenchymal cells, endodermal cells (cuboidal single layer). Identify primitive groove with dense cluster of primitive streak cells below it.
|
Stage 7
Gastrulation
Carnegie Stage 7 and 8, gastrulation, migration of cells through the primitive streak to form endoderm and mesodermal layers of embryo.
|
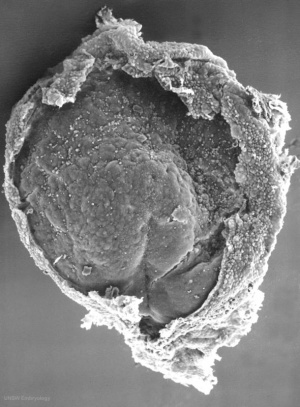
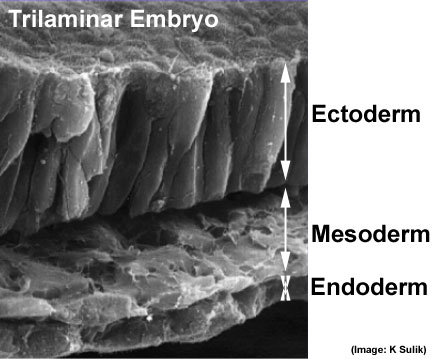
Scanning electron micrograph showing the early forming 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. The embryonic disc has been broken to expose these early layers that form the entire embryo.
|
| <html5media height="500" width="390">File:Mesoderm_001.mp4</html5media> |
Now observe this brief animation of mesoderm development during week 3. Mesoderm Development
|
References
- ↑ Nishimura H. Semba R. Tanimura T. and Tanaka O. Prenatal development of the human with special reference to craniofacial structures : An atlas. (1977) U.S. Dept. of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health ; Washington. Bethesda, Md.
Interactive Component
| Attempt the Quiz - Gastrulation |
|---|

Here are a few simple Quiz questions that relate to Gastrulation from the lecture and practical.
|
| Practical 3: Oogenesis and Ovulation | Gametogenesis | Fertilization | Early Cell Division | Week 1 | Implantation | Week 2 | Extraembryonic Spaces | Gastrulation | Notochord | Week 3 |