User:Z3308968: Difference between revisions
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
===Lab 3 Questions=== | ===Lab 3 Questions=== | ||
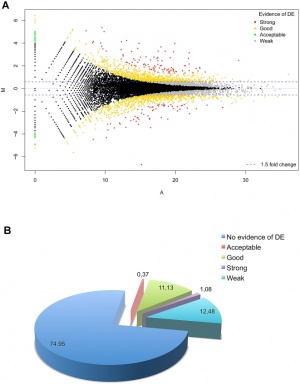
''' | # '''Upload the same image that was shown in class.''' | ||
[[File:Differentially expressed RefSeq genes in human trisomy 21.jpg|thumb|Differentially expressed RefSeq genes in human trisomy 21]] | [[File:Differentially expressed RefSeq genes in human trisomy 21.jpg|thumb|Differentially expressed RefSeq genes in human trisomy 21]] | ||
''' | # '''What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?''' | ||
Folic acid, which is the synthetic form of the vitamin folate, is responsible for the synthesis of DNA precursors. | Folic acid, which is the synthetic form of the vitamin folate, is responsible for the synthesis of DNA precursors. | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
Women who had 4 mg of folic acid in their systems due to supplementing 3 months before childbirth significantly reduced the risk of NTD within the fetus. This is now advocated by the UK department of health, recommending 400 µg per day of folic acid.<ref>Hibbard BM (August 1964). "The role of folic acid in pregnancy". An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 71 (4): 529–42</ref> | Women who had 4 mg of folic acid in their systems due to supplementing 3 months before childbirth significantly reduced the risk of NTD within the fetus. This is now advocated by the UK department of health, recommending 400 µg per day of folic acid.<ref>Hibbard BM (August 1964). "The role of folic acid in pregnancy". An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 71 (4): 529–42</ref> | ||
# '''Upload a picture relating to you group project.''' Add to both the Group discussion and your online assessment page. Image must be renamed appropriately, citation on "Summary" window with link to original paper and copyright information. As outlined in the Practical class tutorial. | |||
===Lab 4 Questions=== | ===Lab 4 Questions=== | ||
Revision as of 18:37, 15 August 2011
Group 11
Attendance
Lab 1. not enrolled yet
Lab 2. --Tahmina Lata 11:01, 4 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 3. --Tahmina Lata 11:10, 11 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 4.
Lab 5.
Lab 6.
Lab 7.
Lab 8.
Lab 9.
Lab 10
Lab 11.
Lab 12.
Lab Questions
Lab 1 Questions
1. Identify the origin of In Vitro Fertilization and the 2010 nobel prize winner associated with this technique.
In the year 1950 Robert G. Edwards started working on In Vitro Fertilization and on 25 July, 1978, his project succeeded in producing the world's first "test tube baby." The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2010 was consequently awarded to Robert G. Edwards for the development of in vitro fertilization.[1]
2. Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings.
A study of fertility after age 45 was attempted with the aim of reversing the age-related decline in oocyte quality through micro-manipulation of the nucleus and cytoplasm. However it has yielded disappointing results coupled with fears of ethical concerns. [2]
3. Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
Atrial septal defect (ASD)is a form of congenital heart defect that results in the mixing of arterial and venous blood.
Spina bifida is a congenital disorder that results from the incomplete closing of the embryonic neural tube. --Tahmina Lata 15:43, 9 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 2 Questions
1. Identify the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds and how is this changed (altered) after fertilisation.
Zona pellucida glycoprotein 3(ZP3) acts as the sperm receptor. ZP3 surrounds the oocyte, and the sperm binds to it as a way to enter the cell. Once a sperm is successful in entering the oocyte, the membrance is depolarised which acts as a primary block to polyspermy. Following this process the IP3 pathway is activated and an increase in intracellular calcium results in alteration of ZP3 thus posing a secondary block to polyspermy.
2. Identify a review and a research article related to your group topic. (Paste on both group discussion page with signature and on your own page)
Review Article "Cystic fibrosis: pathogenesis and future treatment strategies"-This review summarizes our current understanding of the pathophysiology and treatment of cystic fibrosis lung disease [3]
Research Article "Nasal endoscopic evaluation of children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis"-The questionnaire, clinical examination and especially nasal endoscopy performed as part of this research lead to a detailed assessment of the nasal characteristics of children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis. [4]
--Tahmina Lata 15:20, 9 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 3 Questions
- Upload the same image that was shown in class.
- What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?
Folic acid, which is the synthetic form of the vitamin folate, is responsible for the synthesis of DNA precursors. A deficiency of the vitamin intake results in defective cellular growth and the effects are most obvious on those tissues which grow most rapidly which is why it results in neural tube defect in fetal development.
Women who had 4 mg of folic acid in their systems due to supplementing 3 months before childbirth significantly reduced the risk of NTD within the fetus. This is now advocated by the UK department of health, recommending 400 µg per day of folic acid.[5]
- Upload a picture relating to you group project. Add to both the Group discussion and your online assessment page. Image must be renamed appropriately, citation on "Summary" window with link to original paper and copyright information. As outlined in the Practical class tutorial.
Lab 4 Questions
Lab 5 Questions
Lab 6 Questions
References
- ↑ Our founder editor, Robert G. Edwards, wins the Nobel Prize for Medicine.Reprod Biomed Online. 2010 Dec;21(7):829. PubMed PMID: 21112539
- ↑ Forman EJ, Treff NR, Scott RT Jr. Fertility after age 45: From natural conception to Assisted Reproductive Technology and beyond. Maturitas. 2011 Aug 1.[Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 21813248
- ↑ Ratjen FA. Cystic fibrosis: pathogenesis and future treatment strategies.Respir Care. 2009 May;54(5):595-605. Review. PubMed PMID: 19393104
- ↑ Franco LP, Camargos PA, Becker HM, Guimarães RE. Nasal endoscopic evaluation of children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2009 Dec;75(6):806-13. PubMed PMID: 20209279
- ↑ Hibbard BM (August 1964). "The role of folic acid in pregnancy". An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 71 (4): 529–42