User:Z3289301
Lab 4 Online Assessment
- The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
Lab Attendance
--Dona Cho 12:55, 28 July 2011 (EST)
--Dona Cho 13:01, 4 August 2011 (EST)
--Dona Cho 11:31, 11 August 2011 (EST)
--Dona Cho 11:18, 25 August 2011 (EST)
--Dona Cho 11:45, 1 September 2011 (EST)
--Dona Cho 11:59, 15 September 2011 (EST)
--Dona Cho 11:52, 22 September 2011 (EST)
Lab 1
1.Identify the origin of In Vitro Fertilization and the 2010 nobel prize winner associated with this technique.
The introduction of In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) dates back to the late 1800's where a team from the University of Cambridge, England, attempted and succeeded in transplanting embryos in rabbits. After many years, in 1959, Chang MC experienced a breakthrough as he succeeded in fertilizing a rabbit ova in vitro. Finally, through Patrick Steptoe and Robert Edwards' research, the first IVF human baby,Louise Brown, was born in England, 1978.
The Robert Edwards received the 2010 Nobel Prize associated with IVF.
2. Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings
The key findings: 1. The success rate of IVF when using fresh testicular sperm is similar to using cryopreserved testicular sperm. 2. Even if fresh testicular sperm lacks motility, it can still be cryopreserved and used for later an IVF treatment as the outcome is still favourable.
Reference: Levron, J.; Madgar, I.; Shefi, S.; Meirow, D.; Wiser, A.; Bider, D.; Dor, J.; Raviv, G.(2011) IVF outcome with cryopreserved testicular sperm. Andrologia,43:1.DOI: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2009.01014.
3. Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
1. Hypospadias 2. Trisomy 21 (Down’s syndrome)
--Dona Cho 18:34, 3 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 2
1. Identify the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds and how is this changed (altered) after fertilisation.
ZP3 is the sperm receptor. After fertilisation, a carbohydrates on the ZP3 is modified or removed. This then means that ZP3 can no longer bind to another sperm, preventing polysermy.
2. Identify a review and a research article related to your group topic.
Review article: [1]
Research article: [2]
--Dona Cho 18:05, 10 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 3
1. What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?
Folate is a dietary requirement. Adequate folate intake is recommended for women, particularly those in the periconceptual period. It greatly reduces chances of neural tube defects, such as anencephaly and spina bifida.
2. Upload a picture relating to you group project. Add to both the Group discussion and your online assessment page. Image must be renamed appropriately, citation on "Summary" window with link to original paper and copyright information. As outlined in the Practical class tutorial.
I have upload two versions of the file. The most recent one has the correct summary content.
--Dona Cho 13:03, 11 August 2011 (EST)
--Dona Cho 20:33, 17 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 4
1. The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
It is the endodermal evagination of the early embryo's hindgut.[1]
2. Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation
1. Foramen ovale: between the right and left atrium [2]
2. Ductus venosus: between the umbilical vein and inferior vena cava[3]
3. Ductus arteriosus: between the pulmonary artery and the arch of aorta[4]
3. Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching.
Signs and Symptoms, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis
--Dona Cho 17:17, 24 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 5
Which side (L/R) is most common for diaphragmatic hernia and why?
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia is a condition where there is an incomplete closure of the diaphragm. This more commonly appears on the left side as the left side fuses after the right side. [5]
--Dona Cho 22:33, 30 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 6
1. What week of development do the palatal shelves fuse?
In the development of the human embryo the palatal shelves fuse in week 9. [6]
2. What early animal model helped elucidate the neural crest origin and migration of neural crest cells?
Quail-Chick Chimeras model was used to find out the origin and migration of neural crest cells. This model is effective because of the different mechanisms quail and chick genetic materials are packaged into nucleus. This serves as a natural cell labeling technique. [7]
3. What abnormality results from neural crest not migrating into the cardiac outflow tract?
The abnormality is 'Tetralogy of Fallot'.
--Dona Cho 18:54, 14 September 2011 (EST)
Lab 7
1. Are satellite cells (a) necessary for muscle hypertrophy and (b) generally involved in hypertrophy?
(a)Satellite cells are not necessary for muscle hypertrophy (b)Satellite cells do play a part in hypertrophy as it is involved in regeneration and hyperplasia.
2. Why does chronic low frequency stimulation cause a fast to slow fibre type shift?
When chronic low frequency stimulation takes place cell death and formation occurs. Consequently satellite cells are activated and changed from a fast fiber type to a slow fiber type. This chronic low frequency stimulation leads to the fibers shifting from fast to slow type so that it is more resistant to fatigue and damage.
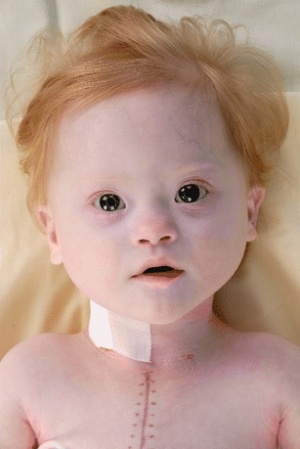
3. Write a comment about the online page on Trisomy 21 based upon the group assessment criteria.
--Dona Cho 00:01, 22 September 2011 (EST)
- ↑ http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/_/dict.aspx?word=allantois
- ↑ http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001113.htm
- ↑ http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/_/dict.aspx?word=ductus+venosus
- ↑ http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Browse/Heart.html
- ↑ http://www.cdhsupport.org/apsacdh.php
- ↑ http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php?title=Palate_Development
- ↑ http://www.springerlink.com/content/x2253071263g8733/#section=82925&page=1