Search results
From Embryology
Page title matches
- [[Neural_-_Mesencephalon_Development|mesencephalon]]<noinclude>[[Category:Template]][[Category:Term Link]][[Category:Neural]]<137 bytes (14 words) - 14:41, 8 May 2018
- Mesencephalon ({{midbrain}}) forms the adult tectum, cerebral peduncle, pretectum and cer ...dal diencephalon as a short-range signal, but also regulates the growth of mesencephalon as a long-range signal."8 KB (1,134 words) - 13:19, 25 February 2020
- ===Misexpression of Gbx2 throughout the mesencephalon by a conditional gain-of-function transgene leads to deletion of the midbra ===Characterizing the mesencephalon using susceptibility-weighted imaging===4 KB (468 words) - 13:05, 16 June 2015
Page text matches
- - myelencephalon - metencephalon - mesencephalon - diencephalon - telencephalon ...l to head). The correct order is: {{telencephalon}} - {{diencephalon}} - {{mesencephalon}} - {{metencephalon}} - {{myelencephalon}}. See the [[Template:Neural Table3 KB (329 words) - 10:25, 16 March 2020
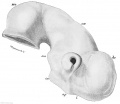
File:Keibel Mall 2 165.jpg ==Fig. 165. Mesencephalon and telencephalon of a human embryo from the end of the fourth week== he, cerebral vesicle; in, infundibulum; ma, mammillary process; mi, mesencephalon; op, torus opticus; t, lamina ferminalis; zw, diencephalon.(1,037 × 900 (166 KB)) - 10:32, 21 February 2014- | valign=top| Mesencephalon | valign=top| Mesencephalon934 bytes (100 words) - 13:03, 4 November 2010
- [[Neural_-_Mesencephalon_Development|mesencephalon]]<noinclude>[[Category:Template]][[Category:Term Link]][[Category:Neural]]<137 bytes (14 words) - 14:41, 8 May 2018
- ...ganglion originating from neural crest of caudal diencephalon and cranial mesencephalon ...ganglion originating from neural crest of caudal diencephalon and cranial mesencephalon; trigeminal placode935 bytes (111 words) - 14:03, 22 June 2015
- [[Neural - Mesencephalon Development|midbrain]]<noinclude>[[Category:Template]][[Category:Term Link]132 bytes (14 words) - 11:46, 25 February 2020
- - prosencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, myelencephalon, rhombencephalon - telencephalon, diencephalon, metencephalon, mesencephalon, myelencephalon2 KB (300 words) - 00:14, 26 August 2009
- ...ttempting to both understand the development and mapping of the [[Neural - Mesencephalon Development|midbrain]] and [[Neural - Medulla Oblongata Development|medulla ...lla_Oblongata_Development|Medulla]] | [[Neural_-_Mesencephalon_Development|Mesencephalon]] | [[Embryology History - Florence Sabin|Florence Sabin]]1 KB (141 words) - 07:26, 10 November 2017
- | valign=top| {{Mesencephalon}} (midbrain) | valign=top| {{Mesencephalon}}2 KB (159 words) - 13:38, 25 February 2020
- | valign=top| [[Neural_-_Mesencephalon_Development|Mesencephalon]] | valign=top| [[Neural_-_Mesencephalon_Development|Mesencephalon]]2 KB (219 words) - 11:40, 5 February 2016

File:Primary Brain Vesciles.pdf ...3 primary brain vesicles are formed; forebrain (prosencephalon) midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon). These structures then differentiate into(453 KB) - 09:52, 25 October 2017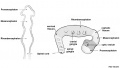
File:CNS primary vesicles.jpg # midbrain (mesencephalon) ...ondary vesicles.jpg|5 secondary vesicles]] (telencephalon - diencephalon - mesencephalon - metencephalon - myelencephalon)(987 × 562 (49 KB)) - 16:48, 18 May 2017- ===Misexpression of Gbx2 throughout the mesencephalon by a conditional gain-of-function transgene leads to deletion of the midbra ===Characterizing the mesencephalon using susceptibility-weighted imaging===4 KB (468 words) - 13:05, 16 June 2015
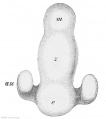
File:Keibel Mall 2 161.jpg .... II2, p. 183, Fig. 187.) Xca. 50. au, opiio vesicle; e, telencephalon; m, mesencephalon; z, diencephalon.(621 × 700 (46 KB)) - 10:34, 21 February 2014- ...es to enlarge, the prosencephalon and rhombencephalon subdivide, while the mesencephalon expands. This gives rise to five secondary brain vesicles: * '''cephalic flexure''' pushes the mesencephalon upwards2 KB (203 words) - 00:56, 8 March 2013
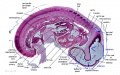
File:Embryo stage13- brain flexures.jpg # cranial (cephalic) flexure - pushes mesencephalon upwards(1,000 × 623 (82 KB)) - 11:43, 17 May 2010- ...es to enlarge, the prosencephalon and rhombencephalon subdivide, while the mesencephalon expands. This gives rise to five secondary brain vesicles: * '''cephalic flexure''' pushes the mesencephalon upwards2 KB (224 words) - 00:57, 8 March 2013
File:Week4.jpg ...arising from the neural crest cells contributed by the prosencephalon. The mesencephalon is also believed to contribute neural crest cells for migration.(521 × 712 (75 KB)) - 19:12, 3 October 2012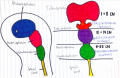
File:Primary Brain.png ...3 primary brain vesicles are formed; forebrain (prosencephalon) midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon). These structures then differentiate into(1,005 × 655 (681 KB)) - 12:39, 26 October 2017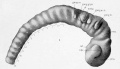
File:Johnson1917 plate02fig01.jpg ...numbers are indicated brain and spinal-cord neuromeres, numbered from the mesencephalon backward. The black lines and numbers indicate the position of the body-seg(800 × 460 (46 KB)) - 10:29, 27 April 2012