File:Steps in a classic array CGH-analysis used for the most common chromosomal abnormalities.png: Difference between revisions
(This figure shows the steps in BAC array CGH. (1) BAC clones are selected from a physical map of the genome. (2) DNA samples are extracted from selected BAC clones and their identity is confirmed by DNA fingerprinting or sequence analysis. (3) A multi-ste) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
'''Copyright:'''This is an open access article. Unrestricted non-commercial use is permitted provided the original work is properly cited.<ref>Stefano G., Erika C., Francesca M., Giusy S., Francesca G., Michela B., Anna M. N., Antonio N., Ercole B., Laura B. and Giuseppe N.(2010) Design, Construction and Validation of Targeted BAC Array-Based CGH Test for Detecting the Most Commons Chromosomal Abnormalities. ‘’Genomic Insights.’’ 3:9-21</ref> | '''Copyright:'''This is an open access article. Unrestricted non-commercial use is permitted provided the original work is properly cited.<ref>Stefano G., Erika C., Francesca M., Giusy S., Francesca G., Michela B., Anna M. N., Antonio N., Ercole B., Laura B. and Giuseppe N.(2010) Design, Construction and Validation of Targeted BAC Array-Based CGH Test for Detecting the Most Commons Chromosomal Abnormalities. ‘’Genomic Insights.’’ 3:9-21</ref> | ||
{{Template:2011 Student Image}} | |||
Revision as of 00:49, 5 October 2011
This figure shows the steps in BAC array CGH. (1) BAC clones are selected from a physical map of the genome. (2) DNA samples are extracted from selected BAC clones and their identity is confirmed by DNA fingerprinting or sequence analysis. (3) A multi-step amplification process generates sufficient material from each clone for array spotting. Each clone is spotted in replicate onto a solid support. (4) Reference DNA and test DNA are differentially labeled with cyanine 3 and cyanine 5 respectively. (5) The two labeled products are combined and hybridized onto the spotted slide. (6) Images from hybridized slides are obtained by scanning in two channels. Signal intensity ratios from individual spots can be displayed as a simple plot (7) or by using more complex software such as SeeGH, which can display copy number alterations throughout the whole genome (8).
Copyright:This is an open access article. Unrestricted non-commercial use is permitted provided the original work is properly cited.[1]
- Note - This image was originally uploaded as part of a student project and may contain inaccuracies in either description or acknowledgements. Students have been advised in writing concerning the reuse of content and may accidentally have misunderstood the original terms of use. If image reuse on this non-commercial educational site infringes your existing copyright, please contact the site editor for immediate removal.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, May 5) Embryology Steps in a classic array CGH-analysis used for the most common chromosomal abnormalities.png. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Steps_in_a_classic_array_CGH-analysis_used_for_the_most_common_chromosomal_abnormalities.png
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
- ↑ Stefano G., Erika C., Francesca M., Giusy S., Francesca G., Michela B., Anna M. N., Antonio N., Ercole B., Laura B. and Giuseppe N.(2010) Design, Construction and Validation of Targeted BAC Array-Based CGH Test for Detecting the Most Commons Chromosomal Abnormalities. ‘’Genomic Insights.’’ 3:9-21
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 00:16, 5 October 2011 | 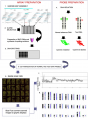 | 601 × 814 (283 KB) | Z3289829 (talk | contribs) | This figure shows the steps in BAC array CGH. (1) BAC clones are selected from a physical map of the genome. (2) DNA samples are extracted from selected BAC clones and their identity is confirmed by DNA fingerprinting or sequence analysis. (3) A multi-ste |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: