2009 Group Project 4
MOUSE
Timeline of Development
- Development of the Mouse Embryo
Staging
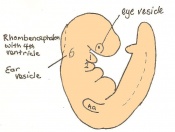
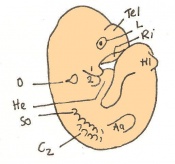
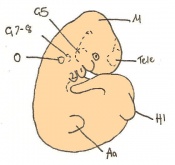
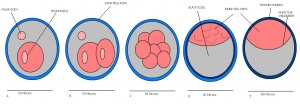
Mouse embryonic development commences once the female's egg or oocyte has become fertilized by the male's sperm. Mouse development has a gestation period of 19-21 days, and can range in different strains of mice. The development of an embryo can be categorized into different stages including cell number, somite stages and morphology. The most common method of staging is by Theiler (1989) which categorizes mouse development into prenatal and postnatal stages consisting of 26 and 2 stages respectively.
| Theiler Stage | Embryonic Age in Days Post Coitum (dpc) | Stage Characteristic | Cell Characteristics | Zona Pellucida | Location | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0-0.9
(range 0-0.25) |
One-celled embryo (fertilized) | One cell | Present | Ampulla | |
| 2 | 1
(range 1-2.5) |
Dividing egg | 2-4 cells
- 1st cleavage after 24hrs |
Present | Travelling down oviduct | |
| 3 | 2
(range 1-3.5) |
Morula (early to fully compacted) | 4-16 cells | Present | Oviduct. Usually near utero-tubal junction. | |
| 4 | 3
(range 2-4) |
Change from Morula to Blastocyst
-Intra-cellular matrix present -Blastocoelic cavity evident |
16-40 compacted cells
-Inner cell mass -Outer layer of trophectoderm cells |
Present | Uterine lumen | |
| 5 | 4
(range 3-5.5) |
Zona free Blastocyst (hatching) | Blastocyst is ready to implant as surrounding cell layer of zona pelludica is lost | Absent | Uterine lumen |
Dr Mark Hill 2009, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
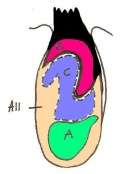
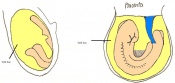
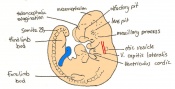
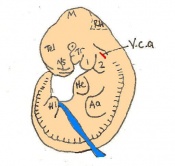
Once the mouse blastocyst has implanted on the uterine wall, the embryo undergoes many changes in size and shape to form a cylindrical structure. Cell proliferation of embryonic ectoderm is activated and results in an increase in embryonic tissue volume. Along with this growth, is the growth of the inner cell mass and trophectoderm layer. The inner cell mass and trophectodermal cells proliferate into the space made by the blastocoel cavity to form a layer of epiblast cells and the pro-amniotic cavity. This results in two layers;
- the inner epiblast layer
- the outer visceral endoderm layer.
This stage or egg cylinder stage is evident of the well defined extra-embryonic and embryonic regions. The embryo can now be visualized with a dorsal and ventral surface. These two surfaces consist of the pro-amniotic cavity surface of epiblast cells on the dorsal surface and the outer layer of visceral endoderm cells on the ventral surface.
| Theiler Stage | Embryonic age in Days Post Coitum (dpc) | Stage Characteristic | Cell characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 4.5 (range 4-5.5)
Human carnegie stage: 4 |
Attachment of blastocyst
-Implantation |
Embryonic Endoderm present covering the blastocoelic cells of the inner cell mass. | |
| 7 | 5 (range 4.5-6)
Human carnegie stage: 5 |
Implantation
-Egg cylinder formation -Ectoplacental cone |
Inner cell mass increases in size
-Epiblast formation (enlarged mass) -Proximal cells are cuboidal in shape -Mural trophectoderm is lined by primary endoderm | |
| 8 | 6 (range 5-6.5)
Human carnegie stage: 5 |
Differentiation of egg cylinder into embryonic and extra-embryonic regions
-Pro-amniotic cavity formation |
Trophoblast giant cells invade maternal tissue
-Maternal blood invades the ectoplacental cone -Reichert's membrane appears -Implantation site is 2x3mm | |
| 9 a) | Pre-streak | Advanced Endometrial and egg cylinder stage
-First evidence of embryonic axis |
Morphological difference can be seen between embryonic and extra-embryonic ectoderm
-Maternal blood further invades ectoplacental cone -Uterine crypts lose their original lumen | |
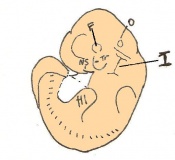
| 9 b) | Early streak | Gastrulation begins (later in stage) | First mesodermal cells produced | |
| 10 a) | Mid streak
Human carnegie stage: 8 |
Amnion formation | The amniotic fold starts to form from posterior tissue of primitive streak bulging. | |
| 10 b) | 7 (range 6.5-7.5)
Mid streak to late streak Human carnegie stage: 8 |
Amnion formation | Amniotic fold cavities form a single cavity to form exocoelom | |
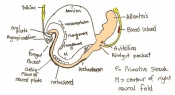
| 10 c) | 7 (range 6.5-7.5) | Amnion formation | Allantoic bud first become evident
-Gastrulation continues -Primitive node is visible -Amnion begins to close | |
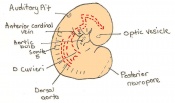
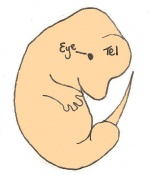
| 11 a) | 7.5 (range 7.25-8)
Human carnegie stage: 9 |
Formation of neural plate and presomites | Amniotic cavity is sealed to form 3 cavities (amniotic cavity, exocoelom and ectoplacental cleft)
-Neural plate can be seen anteriorly -Notochodal plate can be seen in the midline and subjacent to neural groove | |
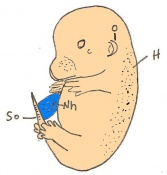
| 11 b) | 7.5 (range 7.25-8) | Allantoic bud elongates
-Head process begins to develop | ||
| 11 c) | 7.5 (range 7.25-8) | Head folds begin to form from the enlargement of the rostral end of neural plate (early head fold)
-Neural groove is seen | ||
| 11 d) | 7.5 (range 7.25-8) | Head folds enlarge further (late head fold)
-Formation of foregut pocket begins |
History of Model Use
Genetics
Current Embryology Research
References
1. Dr Mark Hill 2009, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G [1]
2. Bard, Kaufman, Dubreuil, Brune, Burger, Baldock, Davidson (1998). An internet accessible database of mouse development anatomy based on a systemic nomenclature, Mechanisms of development, (74) 111-120.
ANAT2341 group projects
Project 1 - Rabbit | Project 2 - Fly | Project 3 - Zebrafish | Group Project 4 - Mouse | Project 5 - Frog | Students Page | Animal Development