File:Oxidative Stress Response in Friedreich Ataxia.jpg: Difference between revisions
(Diagram of the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway in control and patient cells under basal conditions and during oxidative stress. Under basal conditions, the Nrf2-Keap1 complex, or a sub-pool of it attached to the mitochondrial outer membrane by the PGAM5 prot) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Diagram of the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway in control and patient cells under basal conditions and during oxidative stress. | '''Oxidative Stress Response in Friedreich Ataxia''' | ||
---- | |||
==Diagram of the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway in control and patient cells under basal conditions and during oxidative stress.== | |||
Under basal conditions, the Nrf2-Keap1 complex, or a sub-pool of it attached to the mitochondrial outer membrane by the PGAM5 protein, is bound to the actin stress filament network of control cells. B. In frataxin-depleted cells, characterized by abnormal iron handling, the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway is profoundly altered by the need to cope with elevated H2O2 levels. Removing H2O2 with the catalase mimetic Euk134 corrects these alterations. C. Treating control cells with oligomycin or tBHQ results in major oxidative stress that destabilizes the actin-Nrf2-Keap1 complex, leading to Nrf2 release and phosphorylation. Nuclear translocation of Nrf2 results in the recruitment of the co-activator(s) needed for Phase II antioxidant transcription. D. In frataxin-depleted cells, the oxidative insult induced by oligomycin (endogenous) or tBHQ (exogenous) cannot be counterbalanced by the induction of Phase II antioxidants, so that the cells are extremely sensitive to oxidation. Again, Euk134 treatment restores the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway, allowing transcription of Phase II antioxidants. | Under basal conditions, the Nrf2-Keap1 complex, or a sub-pool of it attached to the mitochondrial outer membrane by the PGAM5 protein, is bound to the actin stress filament network of control cells. B. In frataxin-depleted cells, characterized by abnormal iron handling, the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway is profoundly altered by the need to cope with elevated H2O2 levels. Removing H2O2 with the catalase mimetic Euk134 corrects these alterations. C. Treating control cells with oligomycin or tBHQ results in major oxidative stress that destabilizes the actin-Nrf2-Keap1 complex, leading to Nrf2 release and phosphorylation. Nuclear translocation of Nrf2 results in the recruitment of the co-activator(s) needed for Phase II antioxidant transcription. D. In frataxin-depleted cells, the oxidative insult induced by oligomycin (endogenous) or tBHQ (exogenous) cannot be counterbalanced by the induction of Phase II antioxidants, so that the cells are extremely sensitive to oxidation. Again, Euk134 treatment restores the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway, allowing transcription of Phase II antioxidants. | ||
Copyright Paupe et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.wwwproxy0.library.unsw.edu.au/pmc/articles/PMC2617762/] | ==Copyright Paupe et al.== | ||
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. | |||
'''Reference''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.wwwproxy0.library.unsw.edu.au/pmc/articles/PMC2617762/ PMC:2617762] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:38, 14 August 2011
Oxidative Stress Response in Friedreich Ataxia
Diagram of the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway in control and patient cells under basal conditions and during oxidative stress.
Under basal conditions, the Nrf2-Keap1 complex, or a sub-pool of it attached to the mitochondrial outer membrane by the PGAM5 protein, is bound to the actin stress filament network of control cells. B. In frataxin-depleted cells, characterized by abnormal iron handling, the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway is profoundly altered by the need to cope with elevated H2O2 levels. Removing H2O2 with the catalase mimetic Euk134 corrects these alterations. C. Treating control cells with oligomycin or tBHQ results in major oxidative stress that destabilizes the actin-Nrf2-Keap1 complex, leading to Nrf2 release and phosphorylation. Nuclear translocation of Nrf2 results in the recruitment of the co-activator(s) needed for Phase II antioxidant transcription. D. In frataxin-depleted cells, the oxidative insult induced by oligomycin (endogenous) or tBHQ (exogenous) cannot be counterbalanced by the induction of Phase II antioxidants, so that the cells are extremely sensitive to oxidation. Again, Euk134 treatment restores the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway, allowing transcription of Phase II antioxidants.
Copyright Paupe et al.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Reference PMC:2617762
File history
Yi efo/eka'e gwa ebo wo le nyangagi wuncin ye kamina wunga tinya nan
| Gwalagizhi | Nyangagi | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 11:25, 14 August 2011 | 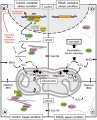 | 561 × 695 (178 KB) | Z3294943 (talk | contribs) | Diagram of the actin-Nrf2 signaling pathway in control and patient cells under basal conditions and during oxidative stress. Under basal conditions, the Nrf2-Keap1 complex, or a sub-pool of it attached to the mitochondrial outer membrane by the PGAM5 prot |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: