Endocrine - Thyroid Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
===Adult Histology=== | ===Adult Histology=== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File: | File:Thyroid_histology_001.jpg|Thyroid (low power) | ||
File:Thyroid_histology_002.jpg|Thyroid (high power) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 25 April 2010
Introduction
| Lecture - Head Development | original page
- Functions from wk10, required for neural development, stimulates metabolism (protein, carbohydrate, lipid), reduced/absence = cretinism (see abnormalities)
Hormones - (amino acid derivatives) Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3)
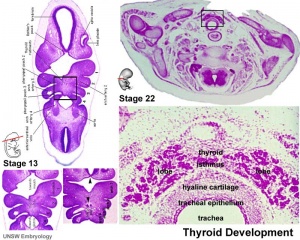
Thyroid Development
- thyroid median endodermal thickening in the floor of pharynx, outpouch – thyroid diverticulum
- tongue grows, cells descend in neck
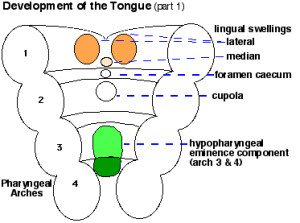
- thyroglossal duct - proximal end at the foramen cecum of tongue thyroglossal duct
- thyroid diverticulum - hollow then solid, right and left lobes, central isthmus
Thyroid Timeline
- 24 days - thyroid median endodermal thickening in the floor of pharynx, outpouch – thyroid diverticulum
- Week 11 - colloid appearance in thyroid follicles, iodine and thyroid hormone (TH) synthesis
growth factors (insulin-like, epidermal) stimulates follicular growth
Fetal Thyroid Hormone
- Initial secreted biologically inactivated by modification, late fetal secretion develops brown fat
- Iodine deficiency- during this period, leads to neurological defects (cretinism)
- Birth - TSH levels increase, thyroxine (T3) and T4 levels increase to 24 h, then 5-7 days postnatal decline to normal levels
References
Reviews
Articles
Search PubMed
Search April 2010
- Endocrine Development - All (14277) Review (4620) Free Full Text (3140)
Search Pubmed: thyroid development
Additional Images
Adult Histology
Terms
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, June 3) Embryology Endocrine - Thyroid Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Endocrine_-_Thyroid_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G