Week 4: Difference between revisions
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/neuron.htm Neural] neural folds begin to fuse near the junction between brain and spinal cord, when [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] cells are arising mainly from the neural ectoderm | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/neuron.htm Neural] neural folds begin to fuse near the junction between brain and spinal cord, when [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] cells are arising mainly from the neural ectoderm | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] trigeminal, facial, and postotic ganglia components visible | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] trigeminal, facial, and postotic ganglia components visible<ref><pubmed>17848161</pubmed></ref> | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] migration of vagal level neural crest cells begins (7-10 somite stage) | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] migration of vagal level neural crest cells begins (7-10 somite stage) | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/endocrine7.htm Pituitary] Week 4 hypophysial pouch, Rathke’s pouch, diverticulum from roof | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/endocrine7.htm Pituitary] Week 4 hypophysial pouch, Rathke’s pouch, diverticulum from roof | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/git7.htm GIT - Liver] septum transversum forming liver stroma and hepatic diverticulum forming hepatic trabeculae | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/git7.htm GIT - Liver] septum transversum forming liver stroma and hepatic diverticulum forming hepatic trabeculae<ref><pubmed>9407542</pubmed></ref> | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/neuron.htm Neural] caudal neuropore takes a day to close (closure is approximately at future somitic pair 31/sacral vertebra 2) | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/neuron.htm Neural] caudal neuropore takes a day to close (closure is approximately at future somitic pair 31/sacral vertebra 2) | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/neuron.htm Neural] secondary neurulation begins | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/neuron.htm Neural] secondary neurulation begins | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] cardiac crest, neural crest from rhombomeres 6 and 7 that migrates to pharyngeal arch 3 and from there the truncus arteriosus | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] cardiac crest, neural crest from rhombomeres 6 and 7 that migrates to pharyngeal arch 3 and from there the truncus arteriosus<ref><pubmed>17848161</pubmed> | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] vagal neural crest enter the foregut (20-25 somite stage) | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/ncrest.htm Neural Crest] vagal neural crest enter the foregut (20-25 somite stage) | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
| <center>28</center> | | <center>28</center> | ||
| [[Carnegie_stage_13|Stage 13]] | | [[Carnegie_stage_13|Stage 13]] | ||
| [[File:Stage13_bf1c.jpg|200px|link=Carnegie stage 13]] [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/neuron.htm Neural] the neural tube is normally completely closed, ventricular system now separated from amniotic fluid. Neural crest at spinal level is segregating, and spinal ganglia are in series with the somites. Spinal cord ventral roots beginning to develop. | | [[File:Stage13_bf1c.jpg|200px|link=Carnegie stage 13]] [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/neuron.htm Neural] the neural tube is normally completely closed, ventricular system now separated from amniotic fluid. Neural crest at spinal level is segregating, and spinal ganglia are in series with the somites. Spinal cord ventral roots beginning to develop.<ref><pubmed>3354839</pubmed></ref> | ||
telencephalon cavity appears | telencephalon cavity appears | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/git7.htm GIT - Liver] epithelial cord proliferation enmeshing stromal capillaries | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/git7.htm GIT - Liver] epithelial cord proliferation enmeshing stromal capillaries<ref><pubmed>9407542</pubmed></ref> | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/nose.htm Sense - Smell] Crest comes from the nasal plates | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/nose.htm Sense - Smell] Crest comes from the nasal plates<ref><pubmed>15604533</pubmed></ref> | ||
[http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/skin.htm Skin] 4 weeks - simple ectoderm epithelium over mesenchyme | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/skin.htm Skin] 4 weeks - simple ectoderm epithelium over mesenchyme | ||
Revision as of 15:21, 22 July 2010
Introduction
Key Events of Human Development during the fourth week (week 4) following fertilization or Clinical week 6 (LMP).
These notes cover the fourth week of embryonic development, which is the beginning of organogenesis, (specific tissues and systems are beginning to differentiate) from the trilaminar embryo.
On the embryo surface sensory placodes and limb buds appear. Sensory placodes (otic, lens, nasal) will form specific components of the ear, eye and nose. Limb buds form from ectoderm and mesoderm (somite) components and are the "paddle-like" projections from the trunk which will form all the upper and lower limb components.
Within the embryo, this period of organogensis is usually extended to cover until 8 weeks of development. Folding of the embryo continues and the earliest functioning organ is the heart. Other systems such as the circulatory, digestive, urogenital and nervous system begin to all take shape.
As systems are beginning to develop, each page in this section is only a brief summary with additional links to specific notes covering these systems/tissues. Note that most tissue development during week 4 will also be covered in the system development notes.
- Week 4 Links: Placodes | Lecture - Mesoderm | Lecture - Ectoderm | Lecture - Early Vascular
- Embryo Week: Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | Week 9
Timeline
| Event | ||
| Stage 10 | 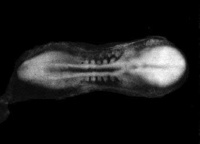 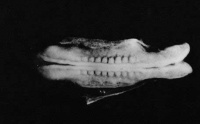
Neural Crest differentiation at spinal cord level from day 22 until day 26 Neural neural folds begin to fuse near the junction between brain and spinal cord, when Neural Crest cells are arising mainly from the neural ectoderm Neural Crest trigeminal, facial, and postotic ganglia components visible[1] Neural Crest migration of vagal level neural crest cells begins (7-10 somite stage) Brain rostral neural tube forms 3 primary brain vesicles (week 4) Respire Week 4 - laryngotracheal groove forms on floor foregut. | |
| Heart begins to beat in Humans by day 22-23, first functioning embryonic organ formed. | ||
| Stage 11 | 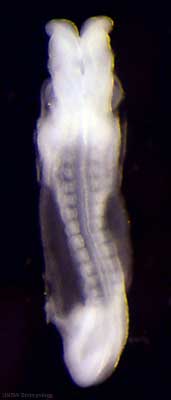
Thyroid thyroid median endodermal thickening in the floor of pharynx Neural rostral (or cephalic) neuropore closes within a few hours; closure is bidirectional, it takes place from the dorsal and terminal lips and may occur in two areas simultaneously. The two lips, however, behave differently. Optic ventricle appears | |
| Stage 12 | 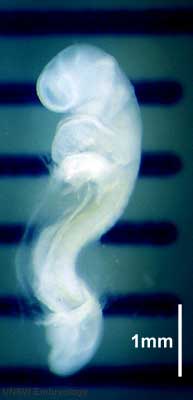
Pituitary Week 4 hypophysial pouch, Rathke’s pouch, diverticulum from roof GIT - Liver septum transversum forming liver stroma and hepatic diverticulum forming hepatic trabeculae[2] Neural caudal neuropore takes a day to close (closure is approximately at future somitic pair 31/sacral vertebra 2) Neural secondary neurulation begins Neural Crest cardiac crest, neural crest from rhombomeres 6 and 7 that migrates to pharyngeal arch 3 and from there the truncus arteriosusCite error: Closing telencephalon cavity appears GIT - Liver epithelial cord proliferation enmeshing stromal capillaries[3] Sense - Smell Crest comes from the nasal plates[4] Skin 4 weeks - simple ectoderm epithelium over mesenchyme Skin 1-3 months ectoderm- germinative (basal) cell repeated division of generates stratified epithelium; mesoderm- differentiates into connective tissue and blood vessels |
Week 4 Movies
Note that many of the movies start in week 4 and continue on through later embryonic development.
Neural
| Neural Plate | Neural Tube |
Mesoderm
| Mesoderm | Somite Structures | Vertebra |
Heart
| Heart Looping | Heart Realign | Heart Atrial Septation | Heart Outflow Septation |
References
Embryo Week: Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Week 7 | Week 8 | Week 9
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Week 4. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Week_4
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G