User:Z3375627: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
The article shows that there was a relationship between calcium and phosphate levels that indicate that lower levels of the two in seminal fluid would result in lower count and motility as well as presence of abnormal forms in the spermatazoa. There did seem to be a paradoxical effect from calcium levels on sperm depending the maturation level of the sperm. In the epididymis, calcium ion stimulate immature sperm whereas in ejaculated semen, it inhibits sperm motility. | The article shows that there was a relationship between calcium and phosphate levels that indicate that lower levels of the two in seminal fluid would result in lower count and motility as well as presence of abnormal forms in the spermatazoa. There did seem to be a paradoxical effect from calcium levels on sperm depending the maturation level of the sperm. In the epididymis, calcium ion stimulate immature sperm whereas in ejaculated semen, it inhibits sperm motility. | ||
--[[User:Z8600021|Mark Hill]] These are useful references and descriptions, fix the reference formatting. (5/5) | |||
==lab 2== | ==lab 2== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 29: | ||
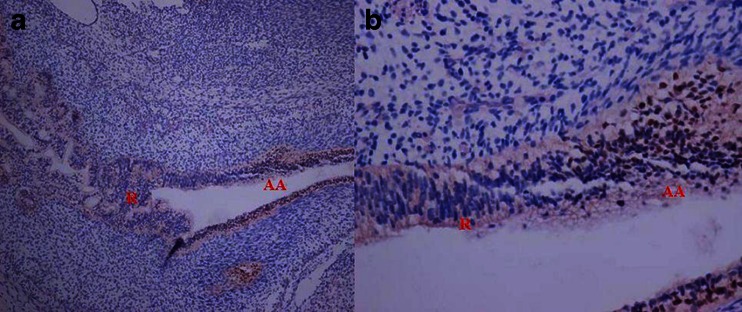
P63 staining of human anorectum in the 10th week. There was considerable proliferation activity within the epithelia of rectum and anal canal. The P63 immunoreaction still remained strongly immunoreactive on the epithelium of the anal canal while the rectum exhibited no reaction<ref><pubmed>23736768</pubmed>| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23736768]</ref> | P63 staining of human anorectum in the 10th week. There was considerable proliferation activity within the epithelia of rectum and anal canal. The P63 immunoreaction still remained strongly immunoreactive on the epithelium of the anal canal while the rectum exhibited no reaction<ref><pubmed>23736768</pubmed>| [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23736768]</ref> | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
==Lab 3== | ==Lab 3== | ||
Revision as of 22:07, 6 October 2014
Welcome to the 2014 Embryology Course!
- Links: Timetable | How to work online | One page Wiki Reference Card | Moodle
- Each week the individual assessment questions will be displayed in the practical class pages and also added here.
- Copy the assessment items to your own page and provide your answer.
- Note - Some guest assessments may require completion of a worksheet that will be handed in in class with your student name and ID.
| Individual Lab Assessment |
|---|
|
| Lab 12 - Stem Cell Presentation Assessment | More Info | |
|---|---|---|
| Group | Comment | Mark (10) |
| 1/8 |
|
7 |
| 2 |
|
7.5 |
| 3 |
|
7.5 |
| 4 |
|
8.5 |
| 5 |
|
8.5 |
| 6 |
|
8.5 |
| 7 |
|
7.5 |
Online Assessment
Lab 1
Article 1
<<pubmed>24520460</pubmed>>
method & findings
women aged 20 to 29 with homogenous characteristics of basal hormone levels, duration of infertility, Body mass index, antral follicle count and age were split into 4 groups of differing endometrial wall thickness (1 <7mm, 2 7-10mm, 3 10-14, 4 >14mm). thickness was measure using TV- USG in the midsagittal plane on the day of hCG administration when 1 or 2 follicles reached 17mm in size. 35-36 hours following hCG for final maturation, TV- USGguided needle aspiration of the follicular fluid was carried out, as was ICSI in all cases. Luteal phase was supported on the oocyte "pick-up" day until serum pregnancy test 12 days later. Clinical pregnancy could be confirmed by presence of fetal sac or fetal cardiac activity 2 weeks later via ultrasound.
The article found that of the women in group 1 (endometrial wall = <7mm) there was a dramatic reduction in Implantation rate, CPR, and ongoing pregnancy rate (OPR)compared to group 2, 3 and 4. There didnt seem to be a significant difference between 2, 3, and 4 in this catagory of result. Retrieved oocyte number, transferred embryo number, and the fertilization, cleavage, and implantation rates (IR) was also found to be similar in all four groups. Results then showed that women of an endometrial wall thickness of less than 7mm would experience a significantly lower clinical pregnancy rate (although no threshold was observed)
Article 2
<<pubmed>PMC3879877</pubmed>>
method & findings
Seminal plasma concentrations of pH, total Calcium, ionized calcium, and inorganic phosphate were recorded in 80 male patients to find a correlation of the substances to mobility and spermatazoa count. The 31 patients who were recorded as having hypomotility (<60%) exhibited lower calcium concentrations (0.19+0.01mmol/L) compared with the normal motility group ( 0.24+0.01mmol/L). The same was observed with phosphate levels (hypo= 5.64+1.62mmol/L normal= 7.83+1.27 ). No noticable differences were observed in the pH levels betweeen the two groups. Of those in the hypomotile group, there was a greater occurance of abnormal form in the spermatazoa, 36% compared to the normal groups 5%. The mobility and count of the spermatazoa was performed using a binocular microscope and improved neubauer counting chamber.
The article shows that there was a relationship between calcium and phosphate levels that indicate that lower levels of the two in seminal fluid would result in lower count and motility as well as presence of abnormal forms in the spermatazoa. There did seem to be a paradoxical effect from calcium levels on sperm depending the maturation level of the sperm. In the epididymis, calcium ion stimulate immature sperm whereas in ejaculated semen, it inhibits sperm motility.
--Mark Hill These are useful references and descriptions, fix the reference formatting. (5/5)
lab 2
P63 staining of human anorectum in the 10th week. There was considerable proliferation activity within the epithelia of rectum and anal canal. The P63 immunoreaction still remained strongly immunoreactive on the epithelium of the anal canal while the rectum exhibited no reaction[1]
Lab 3
Hindgut development during the human fetal stages
1.<pubmed>10716947</pubmed> 2.<pubmed>12171973</pubmed> 3.<pubmed>23073994</pubmed>
Lab 4
Identify a paper that uses cord stem cells therapeutically and write a brief (2-3 paragraph) description of the paper's findings. PMID21939170
<<pubmed>21939170</pubmed>>
Research was conducted into the ability for a non-haematopoietic population of Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) within adult bone marrow to inhibit the poliferation of tumour cells. Bone marrow was aquired and dilated with 1X PBS (phosphate buffered saline and prepared for immunophenotyping using a FACSCaliber flow cytometer and then stained.
Introduced to BV173 Tumour cells (a human B cell precursor leukemia). After an incubation period of 18hours in 37°C, these cells were harvested and thymidine incorporation was measured by liquid scintillation spectroscopy. An inhibitory effect pronounced when there is a direct cell to cell contact. The cell cycle analysis revealed a substantial reduction in DNA synthesis in presence of MSC arresting tumour cell proliferation in G0/G1 phase of cell cycle. This prevented the tumour cells to enter into S phase of cell cycle.
There are a number of developmental vascular "shunts" present in the embryo that are closed postnatally. Identify these shunts and their anatomical location.
- The foramen ovale - An opening in the interatrial septum allowing some blood to bypass the pulmonary circuit by passing from the right atrium directly to the left atrium. Postnatal, this fuses shut to leave the fossa ovale
- The ductus arteriosus - A short, muscular vessel that connects the pulmonary artery to the descending aorta allowing the blood that didnt pass through the foramen ovale to bypass pulmonary circulation.. Ligamentum arteriosum is the remnant after postnatal closure.
- The ductus venosus – Shunts blood from the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava, bypassing the fetal liver and delivering oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetal heart. Ligamentum venosum is the remnant after postnatal closure.
Lab Attendance
- Lab 1 --Z3375627 (talk) 12:51, 6 August 2014 (EST)
- Lab 2 --Z3375627 (talk) 11:45, 13 August 2014 (EST)
- Lab 3 --Z3375627 (talk) 12:09, 20 August 2014 (EST)
- Lab 4 --Z3375627 (talk) 12:27, 27 August 2014 (EST)
- Lab 5 --Z3375627 (talk) 13:05, 3 September 2014 (EST)
- Lab 6 --Z3375627 (talk) 12:48, 10 September 2014 (EST)
- Lab 7 --Z3375627 (talk) 12:06, 17 September 2014 (EST)
- Lab 8 --Z3375627 (talk) 11:41, 24 September 2014 (EST)
- Lab 9
- Lab 10