User:Z3291643: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
1. What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development? | 1. What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development? | ||
Vit B12. Abstract at PMID 19255021 | |||
2. Upload a picture relating to your group project. | 2. Upload a picture relating to your group project. | ||
Revision as of 15:37, 17 August 2011
Lab 4 Online Assessment
- The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
--Z3291643 12:55, 28 July 2011 (EST)
Lab 1 Assessment
1. Identify the origin of In Vitro Fertilization and the 2010 nobel prize winner associated with this technique.
‘in vitro’ fertilization is Latin for ‘in glass’ fertilization and is a treatment for infertility, whereby the sperm fertilizes the ovum outside the body and is then implanted back into the patient’s uterus. The first successful IVF birth, Louise Brown, occurred in 1978 with the help of Patrick Steptoe and Robert Edwards. Edwards was awarded the 2010 nobel prize in medicine for his achievement.
2. Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings.
The aim of this paper was to investigate whether age <=25 played a role in the reproductive outcome of women undergoing IVF. Infertile patients aged between 19 and 25 years of age were compared to infertile patients aged 30-35 years to determine primarily fertilization rates and the number of top quality embryos. The results were unexpected as the younger subjects had lower fertilization rates and reduced embryo quality. [1]
3. Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
Trisomy 21 and cleft palate
References
Nazemian Z, Esfandiari N, Javed M, Casper RF. (2011) The effect of age on in vitro fertilization outcome: is too young possible? J Assist Reprod Genet. 25: 101-106.
--Mark Hill 10:01, 3 August 2011 (EST) These answers are fine.
--z3291643 13:02, 4 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 2 Assessment
1. Identify the ZP protein that spermatozoa binds and how is this changed (altered) after fertilization.
ZP3 acts as a receptor for the sperm. This is followed by the acrosome reaction, whereby acrosomal contents digest the ZP and allow the sperm surface proteins to bind to the ZP2. After fertilization, cortical reaction takes place where cortical granules are exocytosed. This results in the removal of carbohydrate from ZP3 and cleavage of ZP2 to harden the ZP. These changes occur to prevent polyspermy.
2. Identify a review and a research article related to your group topic.
This research article showed genotype-phenotype correlations in Angelman Syndrome (AS). They have concluded that deletion patients had worse developmental outcomes than non deletion patients. Abstract at PMID 20729760
This review article is really comprehensive and gives a good background knowledge of AS. Astract at PMID 20445456
--Z3291643 12:42, 11 August 2011 (EST)
Lab 3 Assessment
1. What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?
Vit B12. Abstract at PMID 19255021
2. Upload a picture relating to your group project.
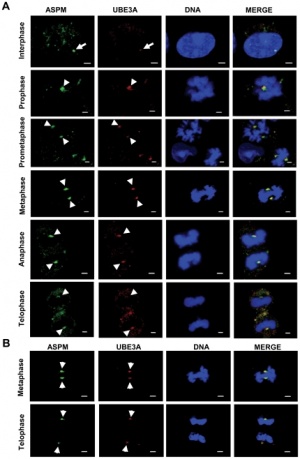
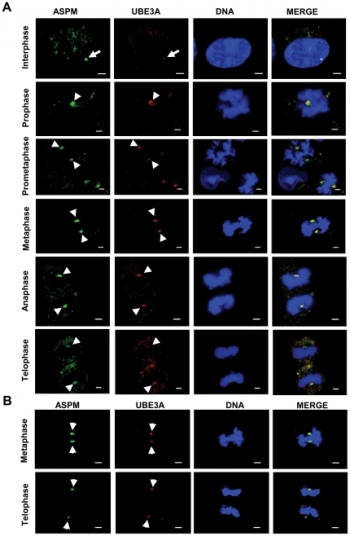
UBE3A colocalizes with ASPM at the centrosome throughout mitosis
UBE3A colocalizes with ASPM at the centrosome. (A) Indirect immunofluorescence of HEK293 cells at interphase and different phases of mitosis stained with antibodies against ASPM and UBE3A (anti-UBE3A-sc-8926). Note colocalization of UBE3A with ASPM at the centrosome throughout mitosis (arrowheads). Note weak centrosomal staining of UBE3A in an interphase cell (arrow). (B) Indirect immunofluorescence of A549 cells stained with antibodies against UBE3A (anti-UBE3A-sc-8926) and ASPM at metaphase and telophase. Note colocalization of UBE3A with ASPM at the centrosome (arrowheads). Scale bar=2 µm.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3102111/?tool=pubmed
Copyright Singhmar, Kumar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
- ↑ <pubmed>21042842</pubmed>