User:Z3290618: Difference between revisions
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
==Lab Seven== | ==Lab Seven== | ||
1. Are satellite cells (a) necessary for muscle hypertrophy and (b) generally involved in hypertrophy? | |||
a) Satellite cells are not necessary for muscle hypertrophy. | |||
b) They are however generally involved as their numbers increase during this pathology. | |||
2. Why does chronic low frequency stimulation cause a fast to slow fibre type shift? | |||
Under chronic low frequency stimulation, fast-twitch fibres receive the same input as slow-twitch fibres. Over a period of stimulation, the fast-twitch fibres will undergo changes in their protein structure, responding to the cronic low frequency stimulation. These protein changes will result in the fast-twitch fibres resembling the slow-twitch fibres. Effectively, giving fast-twitch fibres prolonged slow-twitch stimulation causes the shift. | |||
==Lab Eight== | ==Lab Eight== | ||
Revision as of 08:34, 22 September 2011
Lab 4 Online Assessment
- The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
- Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
- Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching. (Add to project page and your individual assessment page)
Lab One
Identify the origin of In Vitro Fertilization and the 2010 nobel prize winner associated with this technique.
- In 1973 the Monash University team achieved In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF). However, it only lasted a few days. On 25 July 1978, the first IVF baby was born in the UK.
Robert Edwards was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for the development of in vitro fertilization"
Identify a recent paper on fertilisation and describe its key findings.
- Hansen et al. (2002). The Risk of Major Birth Defects after Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection and in Vitro Fertilization. The New England Journal of Medicine" 342:725-730
- In a comparison of IVF conceived, intracytoplasmic sperm injection and naturally conceived children, the rate of major birth defects was seen to be double in assisted conception. At one year of age, the ratio of birth defects in the IVF and intracytoplasmic sperm injected children was 2.0. This figure was derived after adjustment for maternal age, sex of infant etc. Before adjustment the figure was higher (9:4.2).
Identify 2 congenital anomalies.
- Spina bifida
- Hydrocephalus
--Mark Hill 09:54, 3 August 2011 (EST) You need to answer these 3 questions before Lab 2.
Lab Two
Lab Three
What is the maternal dietary requirement for late neural development?
- Iodine: 400-600mg through course of pregnancy. A deficiency can cause cretinism and hypothyroidism.
Upload a picture relating to you group project.
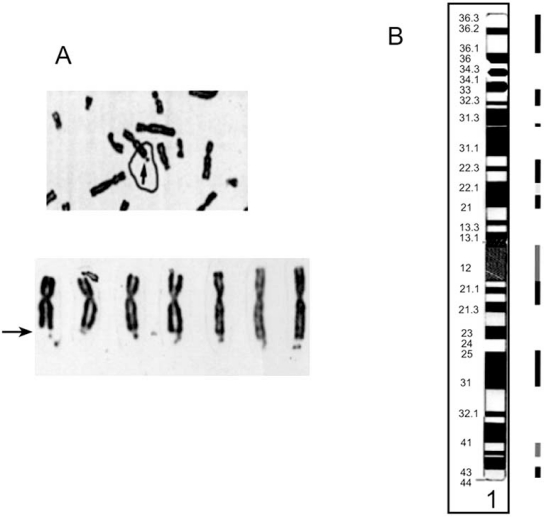 File: Fragile site appearance and distribution
File: Fragile site appearance and distribution
--Mark Hill 23:41, 20 August 2011 (EST) Why did you upload this image as a screen shot? It has a lower resolution and may not accurately show the original image. It should have been downloaded from this page (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3018726/figure/F7/) as a jpg file (CG-11-447_F7.jpg). Then renamed and uploaded to the site. Please do not use screenshots for uploading files. Repeat this exercise if you wish to get the marks for this part of the question.
Lab Four
The allantois, identified in the placental cord, is continuous with what anatomical structure?
The allantois is continuous with the Urachus to connect to the fetal bladder.
Identify the 3 vascular shunts, and their location, in the embryonic circulation.
Ductus Arteriosus is located between the Arch of Aorta and the pulmonary artery. In adulthood, this shunt closes, forming the Ligamentum Arteriosum. Similarly, the Foramen Ovalis allows blood to bypass the pulmonary circulation by shunting blood from the right to left atria. The Ductus Venosus (later Ligamentum venosus) shunts fetal blood from the umbilical vein directly to the inferior vena cava.
Identify the Group project sub-section that you will be researching.
I will be doing Signs and Symptoms of Fragile-X syndrome.
Lab Five
Which side (L/R) is most common for diaphragmatic hernia and why?
The left side is the more common for diaphragmatic hernia due the early closure of the right side of the pluroperitoneal cavity.
Lab Six
Lab Seven
1. Are satellite cells (a) necessary for muscle hypertrophy and (b) generally involved in hypertrophy?
a) Satellite cells are not necessary for muscle hypertrophy. b) They are however generally involved as their numbers increase during this pathology.
2. Why does chronic low frequency stimulation cause a fast to slow fibre type shift?
Under chronic low frequency stimulation, fast-twitch fibres receive the same input as slow-twitch fibres. Over a period of stimulation, the fast-twitch fibres will undergo changes in their protein structure, responding to the cronic low frequency stimulation. These protein changes will result in the fast-twitch fibres resembling the slow-twitch fibres. Effectively, giving fast-twitch fibres prolonged slow-twitch stimulation causes the shift.
Lab Eight
Lab Nine
Lab Ten
Lab Eleven
Lab Twelve
Attendance
--Z3290618 12:55, 28 July 2011 (EST)
--z3290618 12:38, 4 August 2011 (EST)
--z3290618 12:22, 18 August 2011 (EST)
--z3290618 11:29, 25 August 2011 (EST)
--z3290618 11:37, 1 September 2011 (EST)
--z3290618 12:50, 15 September 2011 (EST)