Testis Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
'''Links:''' [[Y Chromosome]] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/week1_3b.htm Week 1 - Spermatogenesis] | [[Ovary_Development|Ovary]] | [[Puberty Development|Puberty]] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/genitalXY.htm original page] | '''Links:''' [[Y Chromosome]] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/week1_3b.htm Week 1 - Spermatogenesis] | [[Ovary_Development|Ovary]] | [[Puberty Development|Puberty]] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/genitalXY.htm original page] | ||
==Development Overview== | |||
===Sex Determination=== | |||
* Humans (week 5-6) | |||
* Germ cells migrate into gonadal ridge | |||
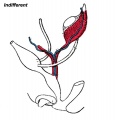
* Gonads (male/female) identical at this stage, Indifferent | |||
===Gonad Development=== | |||
* dependent on sex chromosome | |||
* Y testes | |||
* No Y ovary | |||
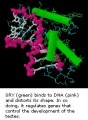
SRY | |||
SRY protein (Testes determining factor, TDF) binds DNA | |||
Transcription factor, Bends DNA 70-80 degrees | |||
===Internal Genital Organs=== | |||
* All embryos form paired | |||
* Mesonephric duct, see kidney development | |||
* Paramesonephric duct, Humans 7th week Invagination of coelomic epithelium Cord grows and terminates on urogenital sinus | |||
* Male Gonad (testes) secretes Mullerian duct inhibitory factor (MDIF) which causes regression of paramesonephric duct | |||
* Male Gonad (testes) secretes Testosterone which retains mesonephric duct | |||
===External Genital Organs=== | |||
* All embryos initially same (indifferent) | |||
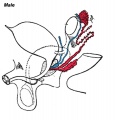
Testosterone differentiates male | |||
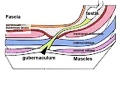
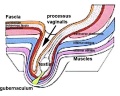
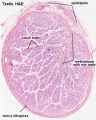
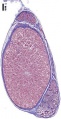
==Additional Images== | ==Additional Images== | ||
Revision as of 08:56, 3 May 2010
Introduction
The male gonad is the testis. The initial difference in male and female gonad development are dependent on testis-determining factor (TDF) the protein product of the Y chromosome SRY gene. Recent studies have indicated that additional factors may also be required for full differentiation.
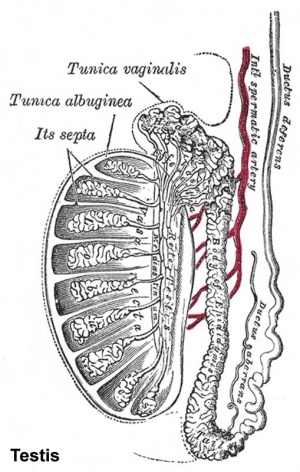
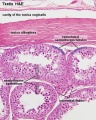
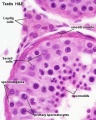
The seminiferous tubules are considered the parenchyma of the testis.
Links: Y Chromosome | Week 1 - Spermatogenesis | Ovary | Puberty | original page
Development Overview
Sex Determination
- Humans (week 5-6)
- Germ cells migrate into gonadal ridge
- Gonads (male/female) identical at this stage, Indifferent
Gonad Development
- dependent on sex chromosome
- Y testes
- No Y ovary
SRY
SRY protein (Testes determining factor, TDF) binds DNA Transcription factor, Bends DNA 70-80 degrees
Internal Genital Organs
- All embryos form paired
- Mesonephric duct, see kidney development
- Paramesonephric duct, Humans 7th week Invagination of coelomic epithelium Cord grows and terminates on urogenital sinus
- Male Gonad (testes) secretes Mullerian duct inhibitory factor (MDIF) which causes regression of paramesonephric duct
- Male Gonad (testes) secretes Testosterone which retains mesonephric duct
External Genital Organs
- All embryos initially same (indifferent)
Testosterone differentiates male