Talk:Renal System - Abnormalities: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
* asymptomatic renal ectopia | * asymptomatic renal ectopia | ||
===Urorectal Septum Malformation=== | ===Urorectal Septum Malformation=== | ||
Revision as of 10:41, 3 June 2010
- Renal ectopy
- Renal fusion
- asymptomatic renal ectopia
Urorectal Septum Malformation
- thought to be a deficiency in caudal mesoderm which in turn leads to the malformation of the urorectal septum and other structures in the pelvic region.
- Recent research has also identified the potential presence of a persistent urachus prior to septation of the cloaca (common urogenital sinus).
Bladder
- absent or small bladder -
associated with renal agenesis.
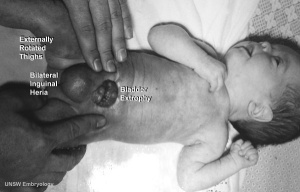
Bladder Exstrophy
- developmental abnormality associated with bladder development.
- origins appear to occur not just by abnormal bladder development, but by a congenital malformation of the ventral wall of abdomen (between umbilicus and pubic symphysis).
- There may also be other anomolies associated with failure of closure of abdominal wall and bladder (epispadias, pubic bone anomolies).
Ureter and Urethra
- Ureter - Duplex Ureter
- Urethra- Urethral Obstruction and Hypospadias
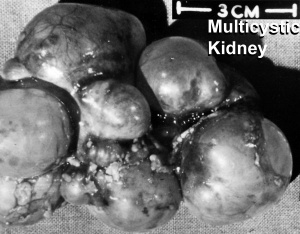
Polycystic Kidney Disease
- diffuse cystic malformation of both kidneys
- cystic malformations of liver and lung often associated, Often familial disposition
- Two types
- Infantile (inconsistent with prolonged survival)
- Adult (less severe and allows survival)
- Autosomal dominant PKD disease - recently identified at mutations in 2 different human genes encoding membrane proteins (possibly channels)
Wilms' Tumor
- (nephroblastoma) Named after Max Wilms, a German doctor who wrote first medical articles 1899
- most common type of kidney cancer children
- WT1 gene - encodes a zinc finger protein
- Both constitutional and somatic mutations disrupting the DNA-binding domain of WT1 result in a potentially dominant-negative phenotype
- some blastema cells (mass of undifferentiated cells) persist to form a ‘nephrogenic rest’
- Most rests become dormant or regress but others proliferate to form hyperplastic rests
- any type of rest can then undergo a genetic or epigenetic change to become a neoplastic rest
- can proliferate further to produce a benign lesion (adenomatous rest) or a malignant Wilms’ tumour
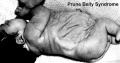
Prune Belly Syndrome
- lower urinary tract obstruction
- mainly male
- fetal urinary system ruptures leading to collapse and "prune belly" appearance.