Talk:Lecture - Placenta Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
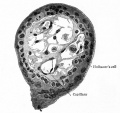
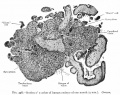
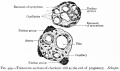
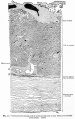
==Historic - Fetal Membranes Images== | ==Historic - Fetal Membranes Images== | ||
| Line 77: | Line 78: | ||
* [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=12914725&dopt=Abstract Evain-Brion D, Malassine A.] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Display&dopt=pubmed_pubmed&from_uid=12914725&tool=ExternalSearch [See Related Articles]] Human placenta as an endocrine organ. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2003 Aug;13 Suppl A:S34-7. | * [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=12914725&dopt=Abstract Evain-Brion D, Malassine A.] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Display&dopt=pubmed_pubmed&from_uid=12914725&tool=ExternalSearch [See Related Articles]] Human placenta as an endocrine organ. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2003 Aug;13 Suppl A:S34-7. | ||
==Take the Quiz== | |||
<quiz display=simple> | |||
{The maternal endometrium response to trophoblast invasion is called the decidual reaction. | |||
|type="()"} | |||
+ true | |||
- false | |||
|| Yes, the endometrium becomes decisualised, deposits fibrinoid and also forms epithelial plaques. | |||
{The human placenta is classified as : | |||
|type="()"} | |||
- Endotheliochorial | |||
+ Haemochorial | |||
- Epitheliochoria | |||
- Mesoeliochorial | |||
||Haemochorial - placenta where the chorion comes in direct contact with maternal blood (human) | |||
{Stem villi - or terminal villi, are the region of main exchange, surrounded by maternal blood in intervillous spaces. | |||
|type="()"} | |||
- true | |||
+ false | |||
|| Stem villi - or anchoring villi, cytotrophoblast cells attached to maternal tissue. | |||
{The 4 cellular layers separating maternal and fetal blood in sequence are: | |||
|type="()"} | |||
- spiral artery wall, Nichbaur layer, cytotrophoblast and Hofbaur layer | |||
+ syncitiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast, villi connective tissue and fetal capillary endothelium | |||
- maternal lacuna, trophoblast layer, endothelial and fetal red blood cell | |||
- fetal capillary endothelium, villi connective tissue, cytotrophoblast and syncitiotrophoblast | |||
||Maternal and fetal blood normally do not mix and all exchange occurs across these cellular layers. Later in development the syncitiotrophoblast layer may not be continuous on the villi surface. | |||
</quiz> | |||
Revision as of 16:21, 9 August 2012
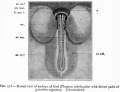
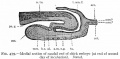
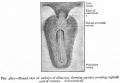
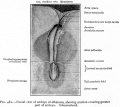
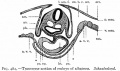
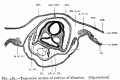
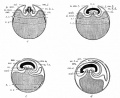
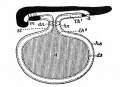
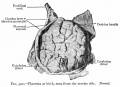
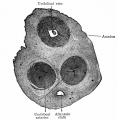
Historic - Fetal Membranes Images
Search
- Bookshelf placenta | placental villi development |
- Pubmed placenta development | placenta | placental villi |
Textbook References
- Human Embryology Larson Ch7 p151-188 Heart, Ch8 p189-228 Vasculature
- The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology (6th ed.) Moore and Persaud Ch14: p304-349
Other textbooks
- Before we Are Born (5th ed.) Moore and Persaud Ch12; p241-254
- Essentials of Human Embryology Larson Ch7 p97-122 Heart, Ch8 p123-146 Vasculature
- Human Embryology Fitzgerald and Fitzgerald Ch13-17: p77-111
UNSW Embryology Links
- Placenta Slides Placenta Lecture 8 2008 | Placenta Lecture 2008 - 1 slide/page | Placenta Lecture 2008 Slides - 4 slides/page | Placenta Lecture 2008 Slides - 6 slides/page
- Placenta Movies Heart Movies | Heart Looping | Atrial Septation | Realignment | Ventricular Septation | Heart Septation Models | Historic Heart Movie |
- Placenta Notes Introduction | Abnormalities | Stage 13/14 | Human (Stage22) | Histology | Villi Development | Maternal Decidua | Vascular Beds | Molecular | Postnatal | Endocrine Placenta
Online Textbooks
- Developmental Biology by Gilbert, Scott F. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Inc.; c2000 - Figure 11.30. Human embryo and placenta after 40 days of gestation | Figure 15.11. Transfer of oxygen from the mother to the fetus in human embryos | Formation of extraembryonic membranes | Figure 15.9. Circulatory system of the early avian embryo
- Endocrinology: An Integrated Approach Nussey, S.S. and Whitehead, S.A. London:Taylor & Francis; c2001
Search
- Bookshelf placenta | placental villi development |
- Pubmed placenta development | placenta | placental villi |
Reviews
- Vogel P. [See Related Articles] The current molecular phylogeny of Eutherian mammals challenges previous interpretations of placental evolution. Placenta. 2005 Sep-Oct;26(8-9):591-6.
- Cross JC. [See Related Articles] How to make a placenta: mechanisms of trophoblast cell differentiation in mice--a review. Placenta. 2005 Apr;26 Suppl A:S3-9.
- Simmons DG, Cross JC. [See Related Articles] Determinants of trophoblast lineage and cell subtype specification in the mouse placenta. Dev Biol. 2005 Aug 1;284(1):12-24.
- Rama S, Rao AJ. [See Related Articles] Regulation of growth and function of the human placenta. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003 Nov;253(1-2):263-8.
- Evain-Brion D, Malassine A. [See Related Articles] Human placenta as an endocrine organ. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2003 Aug;13 Suppl A:S34-7.
Take the Quiz