Talk:Lecture - Mesoderm Development: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! ECHO360 Recording | |||
|- | |||
| Link added after Lecture. | |||
[[File:ECHO360_icon.gif|right|link=https://lectures.unsw.edu.au/ess/portal/section/5157_00900]] 2015 | |||
Links only work with currently enrolled UNSW students. | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! 2015 Group Project Topic - Assisted Reproductive Technology | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:Assisted reproductive technology in Australia and New Zealand 2012.jpg|thumb|150px|ART in Australia (2012)]] | |||
Some Potential Topics | |||
* Your own selected topic (consult coordinator) | |||
* oocyte quality | |||
* spermatozoa quality | |||
* prenatal genetic diagnosis | |||
* frozen oocytes | |||
* in vitro oocyte development | |||
* assisted hatching | |||
* cryopreserved ovarian tissue | |||
* oncofertility | |||
* 3 person embryos | |||
* fertility drugs | |||
* Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) | |||
* ART for genetic disorders | |||
* male infertility | |||
* female infertility | |||
[[Assisted Reproductive Technology]] | |||
|} | |||
[[Media:ANAT2341_Lecture_5_-_2014_Mesoderm_Development.pdf|2014 Lecture 5 PDF]] | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" | |||
! ECHO360 Recording | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:ECHO360_icon.gif|right|link=https://lectures.unsw.edu.au/ess/portal/section/691ba9a0-7c35-4ad2-8fd0-846db7771557]] | |||
[[Lecture - Mesoderm Development|Lecture 5]] - [https://lectures.unsw.edu.au/ess/echo/presentation/0dd38e63-89a4-4464-9edb-75dcc3932fda Rich Media Playback] | [https://lectures.unsw.edu.au/ess/echo/presentation/0dd38e63-89a4-4464-9edb-75dcc3932fda/media.m4v Vodcast Playback] | [https://lectures.unsw.edu.au/ess/echo/presentation/0dd38e63-89a4-4464-9edb-75dcc3932fda/media.mp3 Podcast Playback] | |||
|} | |||
[http://lectopia.telt.unsw.edu.au/lectopia/lectopia.lasso?ut=153&id=110461 2011 Lecture 5 Audio] | |||
=Mesoderm Development= | =Mesoderm Development= | ||
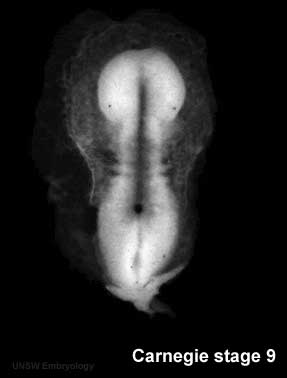
[[Image:Stage9sm.jpg|thumb|Carnegie stage 9 showing somite formation]] | [[Image:Stage9sm.jpg|thumb|Carnegie stage 9 showing somite formation]] | ||
| Line 22: | Line 72: | ||
** mesenchymal to epithelial transitions | ** mesenchymal to epithelial transitions | ||
===Heart=== | ===Heart=== | ||
| Line 70: | Line 80: | ||
[[Image:Mesoderm cartoon4.gif]] | [[Image:Mesoderm cartoon4.gif]] | ||
==Chicken Model - Somite formation== | ==Chicken Model - Somite formation== | ||
| Line 155: | Line 101: | ||
* notochord forms nucleus pulposus of intervertebral disc (IVD) | * notochord forms nucleus pulposus of intervertebral disc (IVD) | ||
== | ==Lecture Links== | ||
* '''Mesoderm Slides''' [[2009_Lecture_5|2009 Lecture]] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/pdf/ANAT2341L6Mesoderms1.pdf Mesoderm Lecture 2008 - 1 slide/page ] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/pdf/ANAT2341L6Mesoderms4.pdf Lecture 3 2008 Slides - 4 slides/page] | [http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/pdf/ANAT2341L6Mesoderms6.pdf Mesoderm Lecture 2008 Slides - 6 slides/page] | |||
| [ | |||
| [ | |||
| | |||
==Take the Quiz== | ==Take the Quiz== | ||
| Line 211: | Line 139: | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:04, 15 August 2016
| ECHO360 Recording |
|---|
| Link added after Lecture.
2015
Links only work with currently enrolled UNSW students. |
| 2015 Group Project Topic - Assisted Reproductive Technology |
|---|
|
Some Potential Topics
|
| ECHO360 Recording |
|---|
|
Lecture 5 - Rich Media Playback | Vodcast Playback | Podcast Playback |
Mesoderm Development
Introduction
| File:Mesoderm_001_icon.jpg</wikiflv> | This animation shows the migration of mesoderm throughout the embryonic disc during gastrulation. |
We have seen the following processes during early human development so far: fertilization and blastocyst development in the first week, implantation in the second week, early placentation and bilaminar to trilaminar in the third week. In the third to fourth week we will now follow the development of the trilaminar embryo as each layer begins to differentiate into the primordia of different tissues within the embryo. From this point onward the lectures will not be in a strict timeline format as we will have to follow each layer (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) forward through its early development, and then jump back to discuss the next layer.
This lecture will look at mesoderm development and formation of the body cavities.
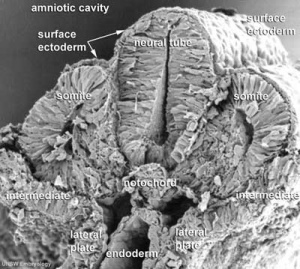
Mesoderm means the "middle layer" and it is from this layer that nearly all the bodies connective tissues are derived. In early mesoderm development a number of transient structures will form and then be lost as tissue structure is patterned and organised. Humans are vertebrates, with a "backbone", and the first mesoderm structure we will see form after the notochord will be somites.
Coelom, meaning "cavity", and major fluid-filled cavities can be seen to form both within the embryo (intraembryonic coelom) and outside the embryo (extraembryonic coelom). The intraembryonic coelom is the single primitive cavity that lies within the mesoderm layer that will eventually form the 3 major anatomical body cavities (pericardial, pleural, peritoneal).
Mesenchyme
- Embryonic connective tissue, describes the cell morphology (Histology is not epithelial organization)
- epithelial to mesenchymal transitions
- mesenchymal to epithelial transitions
Heart
- prechordal splanchnic mesderm forms cardiac mesoderm (week 4)
- splanchnic mesoderm lying above the notochord
- initially as a simple tube
- first organ to form in the embryo
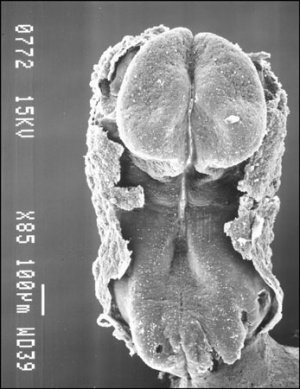
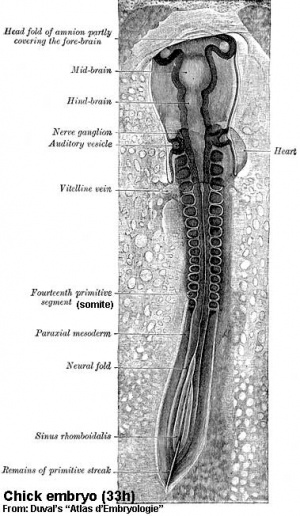
Chicken Model - Somite formation
- Chicken Stages -regular appearance of somites (somitomere to somite) allowed early experimenters to accurately stage the embryo Chicken Development
- Advantages - accessible, easy to manipulate, limb grafts/removal, chimeras, developmental processes
- taxon-Gallus gallus, develops and hatches in 20-21 days, fertilized eggs easily maintained in humidified incubators
- Embryo Staged growth Series of Embryonic Chicken Growth Hamburger & Hamilton J. Morphology, 88 49 - 92, 1951 Hamburger Hamilton Stages
- Other vertebrate animal models - Fish (Zebrafish), Frog (Xenopus)
Chick Embryo Mesoderm
- Body Musculature - Myotome derivatives-mouse embryo
- Lateral Plate Mesoderm
- Limb Musculature
- Dermomyotome- Muscle (MyoD)
- MyoD Pax 3
Somite Differentiation
- migrating neural crest cells enter cranial half, will form dorsal root ganglia (DRG)
- sclerotome bulges ventro-medially towards notochord, then surround and engulf notochord
- mainly growth of surrounding tissues not movement of sclerotome
- notochord forms nucleus pulposus of intervertebral disc (IVD)
Lecture Links
- Mesoderm Slides 2009 Lecture | Mesoderm Lecture 2008 - 1 slide/page | Lecture 3 2008 Slides - 4 slides/page | Mesoderm Lecture 2008 Slides - 6 slides/page
Take the Quiz