Talk:Endocrine System Development: Difference between revisions
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Endocrinology - An Integrated Approach== | ==Endocrinology - An Integrated Approach== | ||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | ||
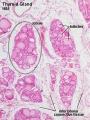
! | ! Thyroid | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:Endocrinology - An Integrated Approach.png|80px]] | | [[File:Endocrinology - An Integrated Approach.png|80px]] | ||
Revision as of 12:54, 20 November 2012
| About Discussion Pages |
|---|
On this website the Discussion Tab or "talk pages" for a topic has been used for several purposes:
Glossary Links
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Endocrine System Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Talk:Endocrine_System_Development |
Introduction
Endocrinology - An Integrated Approach
| Thyroid | |
|---|---|

|
Endocrinology - An Integrated Approach Stephen Nussey and Saffron Whitehead
St. George's Hospital Medical School, London, UK Oxford: BIOS Scientific Publishers; 2001. ISBN-10: 1-85996-252-1 Copyright © 2001, BIOS Scientific Publishers Limited. Bookshelf |
Chapter 3. The thyroid gland
| |

|
Stephen Nussey and Saffron Whitehead.
St. George's Hospital Medical School, London, UK Oxford: BIOS Scientific Publishers; 2001. ISBN-10: 1-85996-252-1 Copyright © 2001, BIOS Scientific Publishers Limited. |
Chapter 1. Principles of endocrinology
Chapter 1. Principles of endocrinology
- Functions of hormones and their regulation
- Chemical signalling - endocrine, paracrine, autocrine and intracrine mechanisms
- Chemical classification of hormones and their synthesis
- Hormone synthesis
- Transport of hormones in the circulation and their half-lives
- Hormone receptors - cell surface
- Hormone receptors - intracellular
- Hormones and gene transcription
- Hormone receptor regulation
- Neuroendocrine interactions
- Hormones and the immune system
- Hormones, growth promotion and malignancy
- Genes, mutations and endocrine function
- Clinical evaluation of endocrine disorders
Chapter 2. The endocrine pancreas
Chapter 2. The endocrine pancreas
- Glucose turnover
- Anabolic and catabolic phases of glucose metabolism
- Actions of insulin and glucagon
- Lipid metabolism - insulinopenia and diabetic ketosis
- Protein metabolism and the anabolic actions of insulin
- Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
- Etiology of type 1 DM
- Prevention of type 1 DM
- Structure, synthesis and metabolism of insulin and glucagon
- Anatomical features of pancreatic islets in relation to hormone secretion and its control
- Control of insulin and glucagon secretion
- Type 2 DM
- Causes of DM
- Genetic disorders of β-cell function
- Counter-regulatory hormones and DM
- Complications of DM
- Macrovascular circulatory changes
- Microvascular changes - diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy
- Diabetes and the neuropathic foot
- Diabetes and insulin resistance of pregnancy
- Development of the pancreas: effects of DM on organogenesis
- Treatment of DM - rationale and practical considerations
- Hypoglycemia
- Physiological responses to hypoglycemia and its treatment
- Hypoglycemia and insulinoma
- Hypoglycemia in infancy
- Disorders of the α, γ and PP cells of the islets
- Clinical case questions
Chapter 3. The thyroid gland
- Iodine intake
- Anatomical features of the thyroid gland
- Iodine trapping and thyroid function
- Synthesis of thyroid hormones
- Actions of thyroid hormones
- Control of thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion
- Hyperthyroidism — Graves' disease
- Surgical anatomy and embryology of the thyroid gland
- Primary hypothyroidism — Hashimoto's disease and myxedema
- Secondary hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroidism in infancy and childhood
- Thyroid hormone resistance
- Non-thyroid illness (‘sick euthyroid’ syndrome)
- Transport and metabolism of thyroid hormones
- Biochemical measurements of thyroid hormone status
- Thyroid growth
- Nodular thyroid disease
- Thyroid cancer
- Clinical case questions
Chapter 4. The adrenal gland
- Specificity of the biological effects of adrenal steroid hormones
- Cholesterol and steroid synthesis in the adrenal cortex
- Anatomical and functional zonation in the adrenal cortex
- Glucocorticoid receptors
- Actions of glucocorticoids and clinical features of Cushing's syndrome
- Adrenal cortical androgens
- Hypothalamic control of adrenocortical steroid synthesis - CRH and vasopressin
- Pituitary control of adrenocortical steroids - ACTH
- Feedback control of glucocorticoids
- Excess glucocorticoids: biochemical investigation of Cushing's syndrome
- Measurements of cortisol in blood, urine and saliva
- Dynamic tests of endocrine function
- Imaging the adrenal gland
- Treatment of Cushing's syndrome
- Nelson's syndrome
- Excess adrenal androgens - congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
- Deficiency of adrenocortical secretions - Addison's disease
- Aldosterone and the control of salt and water balance
- Transport and metabolism of adrenocortical steroids
- Selective mineralocorticoid excess and deficiency
- The adrenal medulla and pheochromocytoma
- Catecholamine synthesis and secretion
- Diagnosis and treatment of pheochromocytomas
- Clinical case questions
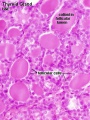
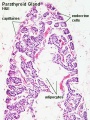
Chapter 5. The parathyroid glands and vitamin D
Chapter 5. The parathyroid glands and vitamin D
- Calcium and phosphate in serum and its measurement
- Intracellular calcium concentration
- Calcium and phosphate balance
- Hormonal control of serum Ca2+ and Pi concentrations
- Sources, metabolism and transport of vitamin D
- Classical actions of vitamin D on intestine and bone
- Parathyroid glands and PTH synthesis
- Control of PTH secretion
- Actions of PTH
- Hypercalcemia and primary hyperparathyroidism
- Hyperparathyroidism and multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN)
- Hypercalcemia and vitamin D excess
- Hypercalcemia and malignancy
- Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrp)
- Treatment of hypercalcemia
- Mutations of the Ca2+ or PTH receptors
- Hypocalcemia and its treatment
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Non-classical actions of vitamin D
- Vitamin D resistance and rickets
- Hormones and the skeleton
- Structure, formation and function of bone
- Osteoporosis
- Paget's disease (osteitis deformans)
- Calcitonin and calcitonin gene-related peptide
- Clinical case questions
Chapter 6. The gonad
- Genetic determination of sexual differentiation
- Sexual differentiation of the gonads and internal reproductive tracts
- Sexual differentiation of the external genitalia
- Control of steroid production in the fetal gonads
- Puberty
- GnRH and the control of gonadotrophin synthesis and secretion
- The gonadotrophins - LH and FSH - and their actions
- Endocrine changes in puberty
- Precocious sexual development
- Delayed puberty
- Premature adrenarche
- Acne, hair growth and hirsutism
- The breast - premature development, hypoplasia and gynecomastia
- Testicular function
- Control of testicular function
- Transport, metabolism and actions of androgens
- Spermatogenesis
- Erection and ejaculation
- Ovarian control and the menstrual cycle
- Transport, metabolism and actions of ovarian steroids
- The ovary - folliculogenesis and oogenesis
- Non-steroidal factors in the control of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis
- Ovulation, menstruation and its problems
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Contraception
- Infertility
- Ovulation induction and assisted conception
- Ovarian failure, the menopause and andropause
- Hormonal replacement therapy (HRT) and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMS)
- Clinical case questions
Chapter 7. The pituitary gland
Chapter 7. The pituitary gland
- Anatomical and functional connections of the hypothalamo-pituitary axis
- Embryology of the pituitary gland
- Craniopharyngioma
- Blood supply of the hypothalamo-pituitary axis
- Sheehan's syndrome
- Growth and somatotrophin deficiency
- Growth hormone - secretory patterns and control
- Actions of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factors
- GH replacement therapy
- GH excess - gigantism and acromegaly
- Pituitary adenomas - incidence and treatment
- Prolactinomas
- Prolactin and its control
- Circadian rhythms and the suprachiasmatic nucleus
- The pineal gland and melatonin
- Autonomic functions of the hypothalamus
- Obesity
- The neural lobe of the pituitary gland - AVP and oxytocin
- Clinical case questions
Chapter 8. Cardiovascular and renal endocrinology
Chapter 8. Cardiovascular and renal endocrinology
- Endocrinology of heart failure
- Paracrine and autocrine regulation of blood pressure: the endocrinology of sepsis
- Hormones and blood cell production - erythropoietin
- Carcinoid
- Clinical case questions
References
Effects of environmental endocrine disruptors on pubertal development
J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2011 Mar;3(1):1-6. Epub 2011 Feb 23.
Ozen S, Darcan S.
Pediatric Endocrinology Unit, Mersin Children Hospital, Mersin, Turkey. Abstract The onset and course of puberty are under the control of the neuroendocrine system. Factors affecting the timing and regulation of the functions of this system may alter the onset and course of puberty. Several environmental endocrine disruptors (EDs) with significant influences on the normal course of puberty have been identified. Numerous animal and human studies concerning EDs have been conducted showing that these substances may extensively affect human health; nevertheless, there are still several issues that remain to be clarified. In this paper, the available evidence from animal and human studies on the effects of environmental EDs with the potential to cause precocious or delayed puberty was reviewed.Conflict of interest:None declared.
PMID 21448326
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3065309
2012
Neurobehavioral risk is associated with gestational exposure to stress hormones
Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jul;7(4):445-459.
Sandman CA, Davis EP. Source Department of Psychiatry & Human Behavior, Women and Children's Health and Well-Being Project, University of California, Irvine, Orange, CA, USA.
Abstract
The developmental origins of disease or fetal programming model predict that early exposures to threat or adverse conditions have lifelong consequences that result in harmful outcomes for health. The maternal endocrine 'fight or flight' system is a source of programming information for the human fetus to detect threats and adjust their developmental trajectory for survival. Fetal exposures to intrauterine conditions including elevated stress hormones increase the risk for a spectrum of health outcomes depending on the timing of exposure, the timetable of organogenesis and the developmental milestones assessed. Recent prospective studies, reviewed here, have documented the neurodevelopmental consequences of fetal exposures to the trajectory of stress hormones over the course of gestation. These studies have shown that fetal exposures to biological markers of adversity have significant and largely negative consequences for fetal, infant and child emotional and cognitive regulation and reduced volume in specific brain structures.
PMID 23144647
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
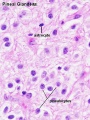
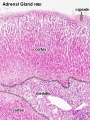
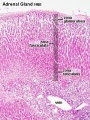
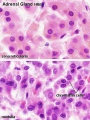
Histology
Adult
Embryonic
Terms
adrenocorticotropin - (ACTH or corticotropin) anterior pituitary, peptide hormone
antidiuretic hormone - (ADH) hypothalamus, peptide hormone
atrial natriuretic factor - (ANP) heart, , peptide hormone
calcitonin - (CT) C cells of thyroid, peptide hormone
follicle stimulating hormone - (FSH) pituitary, protein hormone
growth hormone - (GH) pituitary, peptide hormone
human chorionic gonadotropin - (hCG) pancreas glycoprotein hormone with 2 subunits (alpha and beta joined non covalently). Similar in structure to luteinizing hormone (LH), hCG exists in multiple hormonal and non-endocrine agents (regular hCG, hyperglycosylated hCG and the free beta-subunit of hyperglycosylated hCG). PMID: 19171054
lutenizing hormone - (LH) pituitary, protein hormone
melaocyte stimulating hormone - (MSH) pituitary, peptide hormone
prolactin - (PRL) pituitary, peptide hormone
parathyroid hormone - (PTH) parathyroid, peptide hormone
thyroid hormone - (TH) thyroid,amino acid derivative
thyroid stimulating hormone - (TSH) pituitary, protein hormone