Talk:Endocrine - Placenta Development: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | |||
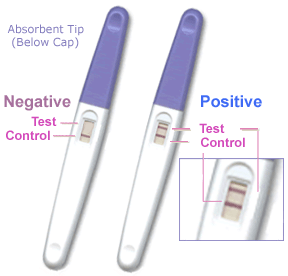
[[File:Pregnancy_test.gif|thumb|Pregnancy Test]] | |||
For complete notes on placenta development and function see [[Placenta Development]]. | |||
{{Template:Endocrine Links}} | [[Lecture - Placenta Development]] | |||
* Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) - like leutenizing hormone, supports corpus luteum in ovary, pregnant state rather than menstrual, maternal urine in some pregnancy testing | |||
* Human chorionic somatommotropin (hCS) - or placental lactogen stimulate (maternal) mammary development | |||
* Human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT) | |||
* Human chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH) | |||
* progesterone and estrogens - support maternal endometrium | |||
* Relaxin | |||
* Placenta - Maternal (decidua) and Fetal (trophoblastic cells, extraembryonic mesoderm) components | |||
* Endocrine function - maternal and fetal precursors, synthesis and secretion | |||
** Protein Hormones - chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) or placental lactogen (hPL), chorionic thyrotropin (hCT), chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH) | |||
*** hCG - up to 20 weeks, fetal adrenal cortex growth and maintenance | |||
*** hCS – rise through pregnancy, stimulates maternal metabolic processes, breast growth | |||
** Steroid Hormones - progesterone (maintains pregnancy), estrogens (fetal adrenal/placenta) | |||
<div id="google_translate_element"></div><script> | <div id="google_translate_element"></div><script> | ||
Revision as of 12:51, 15 April 2012
Introduction
For complete notes on placenta development and function see Placenta Development.
| Lecture - Placenta Development
- Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) - like leutenizing hormone, supports corpus luteum in ovary, pregnant state rather than menstrual, maternal urine in some pregnancy testing
- Human chorionic somatommotropin (hCS) - or placental lactogen stimulate (maternal) mammary development
- Human chorionic thyrotropin (hCT)
- Human chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH)
- progesterone and estrogens - support maternal endometrium
- Relaxin
- Placenta - Maternal (decidua) and Fetal (trophoblastic cells, extraembryonic mesoderm) components
- Endocrine function - maternal and fetal precursors, synthesis and secretion
- Protein Hormones - chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) or placental lactogen (hPL), chorionic thyrotropin (hCT), chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH)
- hCG - up to 20 weeks, fetal adrenal cortex growth and maintenance
- hCS – rise through pregnancy, stimulates maternal metabolic processes, breast growth
- Steroid Hormones - progesterone (maintains pregnancy), estrogens (fetal adrenal/placenta)
- Protein Hormones - chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) or placental lactogen (hPL), chorionic thyrotropin (hCT), chorionic corticotropin (hCACTH)
<script>
function googleTranslateElementInit() {
new google.translate.TranslateElement({
pageLanguage: 'en'
}, 'google_translate_element');
} </script><script src="//translate.google.com/translate_a/element.js?cb=googleTranslateElementInit"></script>