File list
From Embryology
This special page shows all uploaded files.
| Date | Name | Thumbnail | Size | User | Description | Versions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15:12, 20 January 2009 | Chick15h.jpg (file) |  |
3 KB | MarkHill | chicken embryo 15 hours from fertilization. | 1 |
| 20:44, 13 May 2009 | Hearing cartoon.jpg (file) |  |
43 KB | MarkHill | Cartoon showing the 3 main divisions of the ear. Image source: UNSW Embryology, modified from NIH image. | 1 |
| 20:49, 13 May 2009 | 600px stage14.jpg (file) |  |
27 KB | MarkHill | Human Embryo stage 14 Image source: UNSW Embryology © Dr Mark Hill, Image cannot be reproduced without permission. | 1 |
| 20:49, 13 May 2009 | 600px stage23.jpg (file) |  |
26 KB | MarkHill | Human Embryo stage 23 Image source: UNSW Embryology © Dr Mark Hill, Image cannot be reproduced without permission. | 1 |
| 20:56, 13 May 2009 | Stage14compare23.jpg (file) |  |
32 KB | MarkHill | Human Embryo comparison of embryo sizes between Stage 14 and Stage 23 http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwhuman/Stages/Images/stage14compare23.jpg Image source: UNSW Embryology © Dr Mark Hill, Image cannot be reproduced without permission. | 1 |
| 21:00, 13 May 2009 | Head arches cartoon.jpg (file) |  |
29 KB | MarkHill | Head Arches Cartoon http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/images/head/head_arches.jpg Image Source: UNSW Embryology | 1 |
| 21:06, 13 May 2009 | Stage13 B2 excerpt.gif (file) |  |
26 KB | MarkHill | Stage 13 embryo Section B2 excerpt showing pharynx http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwpig/pigb/B2L.htm Image Source: UNSW Embryology © Dr Mark Hill, no image reproduction without permission. | 1 |
| 21:09, 13 May 2009 | Pharynx cartoon.jpg (file) |  |
88 KB | MarkHill | Historic drawing of Pharynx http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/Notes/images/head/pharynx.jpg Image source: Gray's Anatomy, modified by Dr Mark Hill | 1 |
| 21:14, 13 May 2009 | Stage13 pharyngeal arch excerpts.gif (file) |  |
86 KB | MarkHill | Stage 13 Embryo Pharyngeal arch appearance in excerpts from head cross-sections A6 to B6. Showing arches 1 to 4. http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/wwwpig/system/pigarch.gif | 1 |
| 23:06, 13 May 2009 | Eustacian tube angle.jpg (file) |  |
48 KB | MarkHill | Newborn to adult Eustachian (auditory, otopharyngeal or pharyngotympanic) tube. Connects middle ear cavity to nasopharynx portion of pharynx Ventilation - pressure equalization in the middle ear Clearance - allow fluid drainage from the middle ear Tube | 1 |
| 23:10, 13 May 2009 | FASface.jpg (file) | 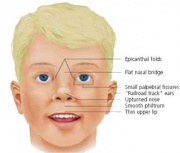 |
8 KB | MarkHill | Facial Appearance of FAS Some, or all, of the following facial features are associated with FAS * Microcephaly - leads to small head circumference * Palpebral fissure - short opening of eye * Epicanthal folds - fold of skin at inside of corner of eye * M | 1 |
| 23:18, 13 May 2009 | Pharyngeal arch structure cartoon.gif (file) |  |
5 KB | MarkHill | Pharyngeal Arch structure cartoon Image Source: UNSW Embryology | 1 |
| 23:19, 13 May 2009 | Palate structure cartoon.jpg (file) |  |
14 KB | MarkHill | Palate structure cartoon Image Source: UNSW Embryology | 1 |
| 23:41, 13 May 2009 | Pharyngeal arch cartilages.jpg (file) |  |
26 KB | MarkHill | Pharyngeal Arch cartilages Source: UNSW Embryology | 1 |
| 14:18, 28 May 2009 | Gray1109 female urogenital sinus.gif (file) |  |
28 KB | MarkHill | Urogenital sinus of female human embryo of eight and a half to nine weeks old. (From model by Keibel) Image Source: Anatomy of the Human Body (1918) Henry Gray (1825–1861) | 1 |
| 14:21, 28 May 2009 | Gray1110 common male female genital.gif (file) | 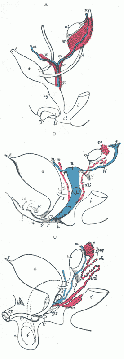 |
55 KB | MarkHill | Diagrams to show the development of male and female generative organs from a common type. (Allen Thomson.) | 1 |
| 14:25, 28 May 2009 | Gray1116 hindgut 32-33days.gif (file) |  |
52 KB | MarkHill | Tail end of human embryo thirty-two to thirty-three days old. (From model by Keibel.) | 1 |
| 15:54, 21 July 2009 | Chris.gif (file) |  |
13 KB | MarkHill | Large embryology icon Image | 1 |
| 15:57, 21 July 2009 | Mhicon08.jpg (file) | 6 KB | MarkHill | Mark Hill icon image 2008 | 1 | |
| 15:18, 22 July 2009 | Braune2 B1.jpg (file) |  |
413 KB | MarkHill | 1 | |
| 15:54, 24 July 2009 | UNSW Course Outline 2009 ANAT2341 Embryology.pdf (file) | 573 KB | MarkHill | PDF Version of 2009 course outline for ANAT2341 Embryology. Lectures and Laboratories are subject to change without notice and may also be replaced by specialist invited Guest Lecturers. | 1 | |
| 15:16, 27 July 2009 | Cell cycle1.jpg (file) |  |
23 KB | MarkHill | Cartoon of Cell Cycle (large) Showing phases and cyclin levels Source: Mark Hill | 1 |
| 15:24, 27 July 2009 | Historic 1882 mitosis drawing.jpg (file) |  |
36 KB | MarkHill | Drawing of cells with chromosomes and during mitosis by Walther Flemming (1882) Zellsubstanz, Kern und Zelltheilung. Leipzig, Verlag von F.C.W. Vogel. Date: 1882 Author: Walther Flemming. Professor der Anatomie in Kiel. Permission: Walther Flemming died i | 1 |
| 15:25, 27 July 2009 | Mitosis fl.jpg (file) |  |
21 KB | MarkHill | Rieder's research team uses fluorescent dyes to label the dividing newt lung cells. The scientists use newt lung cells in their studies because these cells are large, easy to see into, and are biochemically similar to human lung cells. Photo: Conly Riede | 1 |
| 15:26, 27 July 2009 | Mitosis meiosis1.jpg (file) |  |
73 KB | MarkHill | Mitosis and meiosis, the two types of cell division. Source: Genetics Home Reference, National Library of Medicine, USA http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/illustrations/mitosismeiosis Government information at NLM Web sites is in the public domain. Public | 1 |
| 16:18, 27 July 2009 | Trisomy21arrow.gif (file) |  |
5 KB | MarkHill | Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children. Image Source: UNSW Embryology http://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au | 1 |
| 16:19, 27 July 2009 | Trisomy21male.jpg (file) |  |
10 KB | MarkHill | Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children. The frequency of trisomy 21 in the population is approximately 1 | 1 |
| 16:19, 27 July 2009 | Trisomy21female.jpg (file) |  |
12 KB | MarkHill | Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosome 21 in a parent who is chromosomally normal and is one of the most common chromosomal abnormalities in liveborn children. The frequency of trisomy 21 in the population is approximately 1 | 1 |
| 11:10, 28 July 2009 | XXhpgaxis.gif (file) |  |
22 KB | MarkHill | Figure 1 The female hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis. The hypothalamus produces and secretes luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone (LHRH) into a system of blood vessels that link the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. LHRH stimulates the pitui | 1 |
| 11:14, 28 July 2009 | Ovary5x.gif (file) |  |
162 KB | MarkHill | Low power view of cat ovary cortex and some medullary region. Note that in many follicles the oocyte is not visible due to its relatively small size and the position of the plane of section through the follicle. Features: germinal epithelium, tunica albu | 1 |
| 11:26, 28 July 2009 | Oocytenumber.jpg (file) |  |
41 KB | MarkHill | Human Ovary oocyte number from embryo to adult Graph based on data from: Hassold, etal., Environ Mol Mutagen 1996. 28: 167-175 | 1 |
| 09:51, 30 July 2009 | Gray0005.gif (file) |  |
104 KB | MarkHill | Oocyte development and polar body formation Source: Gray's Anatomy | 1 |
| 12:20, 2 August 2009 | Icon-Quiz.jpg (file) | 5 KB | S8600021 | quiz icon | 1 | |
| 09:48, 3 August 2009 | Pregnancy test.gif (file) |  |
22 KB | MarkHill | Pregnancy test available to the public. Based upon the detection of human chorionic gonadotrophin - (hCG) Placental hormone initially secreted by cells (syncitiotrophoblasts) from the implanting conceptus during week two, supporting the ovarian corpus lu | 1 |
| 11:27, 3 August 2009 | Tubal pregnancy historic.jpg (file) |  |
12 KB | MarkHill | The most common form of ectopic pregnancy is Tubal Pregnancy when implantation begins before the blastocyst has reached the uterine cavity. Historic image source: Reinier de Graaf (1641-1673), a Dutch physician who studied pregnancy in rabbits, copied | 1 |
| 11:29, 3 August 2009 | Tubal pregnancy.gif (file) |  |
41 KB | MarkHill | Ectopic tubal pregnancy Embryo implants and begins developing prematurely in the fallopian tube (uterine horn). Image shows surgically removed, formalin-fixed fallopian tube which has been opened to reveal human embryo and placenta. (approx Carnegie stag | 1 |
| 13:30, 3 August 2009 | Stage7 primitive streak labelled.jpg (file) |  |
13 KB | MarkHill | Human Embryonic disc (Carnegie stage 7) viewed from amniotic side showing the primitive streak labelled. Gastrulation occurs through the primitive streak cells migrate continuously through week 3 into week 4. Initial cells replace hypoblast as an epithel | 1 |
| 13:45, 3 August 2009 | Stage7 SEM1.jpg (file) |  |
40 KB | MarkHill | Human embryo (Carnegie stage 7) scanning electron micrograph original file name PresomiteSt7d17dorsal.jpg Image Source: Prof Kathy Sulik scanning electron micrographs of the Carnegie stages of the early human embryo. No reproduction without permission | 1 |
| 13:47, 3 August 2009 | Stage7 SEM2.jpg (file) |  |
27 KB | MarkHill | PresomiteSt7d17lateral.jpg | 1 |
| 14:09, 3 August 2009 | Stage7 features.jpg (file) |  |
9 KB | MarkHill | Carnegie Stages 7 Features: embryonic disc, primitive node, primative streak, primitive groove, yolk sac Facts: Week 3, 15 - 17 days, 0.4 mm View 1: embryonic disc, showing the epiblast viewed from the amniotic (dorsal) side. Events: Gastrulation is | 1 |
| 14:13, 3 August 2009 | Stage7 axes.jpg (file) |  |
9 KB | MarkHill | Carnegie Stages 7 Features: embryonic disc, primitive node, primative streak, primitive groove, yolk sac Facts: Week 3, 15 - 17 days, 0.4 mm View 1: embryonic disc, showing the epiblast viewed from the amniotic (dorsal) side. Events: Gastrulation is | 1 |
| 14:37, 3 August 2009 | Placenta anchoring villi.jpg (file) |  |
167 KB | MarkHill | Placenta anchoring villi Histological image showing the junctional region between the trophoblast shell of the conceptus and the maternal decidua. In week 2, the trophoblast shell cells proliferate and form a syncitiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast lay | 1 |
| 14:56, 3 August 2009 | Stage7 axial process.jpg (file) |  |
11 KB | MarkHill | Carnegie Stages 7 showing direction of axial process extension from primitive node. Features: embryonic disc, primitive node, primative streak, primitive groove, yolk sac Facts: Week 3, 15 - 17 days, 0.4 mm View 1: embryonic disc, showing the epiblast | 1 |
| 15:36, 3 August 2009 | Stage8 nodal cilia.jpg (file) |  |
50 KB | MarkHill | Human embryo (Carnegie stage 8) This image is a high power selected region at the primitive node showing the cilia that are thought to rotate in one direction leading to a gradient of factors establishing the early left/right axis of the embryo. scannin | 1 |
| 20:38, 3 August 2009 | Primitive streak cell migration.jpg (file) |  |
92 KB | S8600021 | DiI labelling in HH8 embryos reveals behaviour and trajectories of cells from the primitive streak. (A, B, C) Long-term time-lapse imaging of embryos labelled in Hensen's node (A), the anterior (B) or posterior primitive streak (C) with DiI. Embryos wer | 1 |
| 20:54, 3 August 2009 | Stage7.jpg (file) |  |
7 KB | S8600021 | Human Embryo Carnegie stage 7 Features: embryonic disc, primitive node, primative streak, primative groove, yolk sac Facts: Week 3, 15 - 17 days, 0.4 mm View 1: embryonic disc, showing the epiblast viewed from the amniotic (dorsal) side. Kyoto Collect | 1 |
| 21:54, 3 August 2009 | Gray0064.gif (file) |  |
30 KB | S8600021 | Transverse section of a human embryo of the third week to show the differentiation of the primitive segment. (Kollmann.) ao. Aorta. m.p. Muscle-plate. n.c. Neural canal. sc. Sclerotome. s.p. cutis-plate. Image Source: Anatomy of the Human Body (1918) H | 1 |
| 21:59, 3 August 2009 | Chicken endoderm origin.jpg (file) |  |
53 KB | S8600021 | Schematic drawing of definitive endoderm origin. (A) Precursors of the primitive streak have been mapped to Koller's sickle (KS) at prestreak stages (green dots), and (B) are within the primitive streak at stage 2 (red, PS). (C) The rostral third of t | 1 |
| 22:27, 3 August 2009 | Stage7 SEM4.jpg (file) |  |
60 KB | S8600021 | Human embryo (Carnegie stage 7) Scanning electron micrograph detail showing primitive pit (original file name PresomiteSt7d17primitivepit.jpg) '''Image Source:''' Prof Kathy Sulik scanning electron micrographs of the Carnegie stages of the early human | 1 |
| 22:30, 3 August 2009 | Stage8 SEM1.jpg (file) |  |
25 KB | S8600021 | Human embryo (Carnegie stage 8) scanning electron micrograph Features: brain fold, neural groove, amniotic sac, presomitic mesoderm, embryonic disc, primitive node, primative streak, primative groove, connecting stalk Facts: Week 3, 17 - 19 days, 1.0 - | 1 |