Smooth Muscle Development: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
===Interstitial cells of Cajal=== | ===Interstitial cells of Cajal=== | ||
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) are peripheral nervous system | * Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) are peripheral nervous system neuron found in some smooth muscle organs. | ||
* function as pacemaker cells, neuromodulation or mechanosensory roles. | |||
Revision as of 23:56, 1 December 2013
Introduction
There are 3 different types of muscle: skeletal, cardiac and smooth. This page describes smooth muscle development, descriptions of cardiac muscle and smooth muscle development can be found in other notes.
- Smooth muscle is mesoderm in origin and contributes to many different tissues including the muscular wall of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, artery walls, bladder wall, uterus, seminiferous tubules and ductus deferens.
- Smooth muscle is non-striated in appearance, lacking the regular organisation of sarcomeres seen in skeletal and cardiac muscle.
- Smooth Muscle Links: Smooth Muscle Development | Smooth Muscle Histology | Blood Vessel | Uterus | Urinary Bladder | Mesoderm
Some Recent Findings
|
| More recent papers |
|---|
|
This table allows an automated computer search of the external PubMed database using the listed "Search term" text link.
More? References | Discussion Page | Journal Searches | 2019 References | 2020 References Search term: Smooth Muscle Embryology <pubmed limit=5>Smooth Muscle Embryology</pubmed> |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract consists of two thick outer muscle layers (longitudinal and circular) and a thin muscularis mucosa layer.
Neural Innervation
- 1857 Meissner was the first to describe a nerve plexus in the submucosa of the bowel wall.
- 1864 Auerbach described the myenteric plexus between the longitudinal and circular muscle layers.
- 1981 LeDouarin describes neural crest contribution to both plexuses.
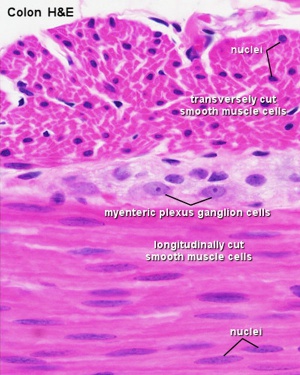
Myenteric Plexus
- Auerbach's Plexus
- functions for peristalsis and gastric mixing.
- Coordinated waves of descending inhibition followed by waves of descending excitation
- + Extrinsic parasympathetic cholinergic nerves (vagal and sacral) excite peristalsis and stimulate
- - Sympathetic noradrenergic nerves inhibit the transit of gut contents
Submucosal Plexus
- Meissner's Plexus
- functions for secretion and absorption.
Interstitial cells of Cajal
- Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) are peripheral nervous system neuron found in some smooth muscle organs.
- function as pacemaker cells, neuromodulation or mechanosensory roles.
Histology Images
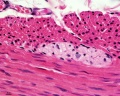
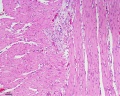
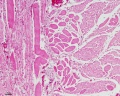
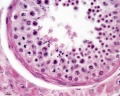
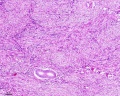
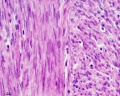
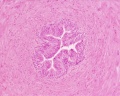
- Smooth Muscle Histology: Labeled Colon low | Labeled Colon high | Colon x40 | Colon x40 | Ileum x10 | Oesophagus x10 | Seminiferous tubule x40 | Uterus myometrium x10 | Uterus myometrium x40 |
References
- ↑ <pubmed>21677291</pubmed>
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed Central Images: smooth muscle
Search Pubmed: Smooth Muscle Development
Additional Images
Terms
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology Smooth Muscle Development. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Smooth_Muscle_Development
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G