Respiratory System - Postnatal
Introduction
This site mainly focuses on prenatal development, but the respiratory system is one of those that continues to grow and change postnatally. This page includes some topics related to this postnatal development.
Some Recent Findings
References | Recent References
Lung - Alveolar Stage
- The postnatal lung, with alveoli forming.
- Expansion of gas exchange alveoli, vascular beds (capillaries), lymphatics and innervation.
- Very premature infants will still be at the earlier Saccular stage.
Preterm Saccular Stage
- week 24 to near term.
- most peripheral airways form widened "airspaces", termed saccules.
- saccules widen and lengthen the airspace (by the addition of new generations).
- future gas exchange region expands significantly.
- Fibroblastic cells also undergo differentiation, they produce extracellular matrix, collagen, and elastin.
- May have a role in epithelial differentiation and control of surfactant secretion.
- Alveolar Cells Type II (Type II pneumocytes)
- begin to secrete surfactant, levels of secretion gradually increase to term.
- allows alveoli to remain inflated
- Vascular tree - also grows in length and diameter during this time.
- Thyroid hormone required for differentiation and stimulate surfactant production.
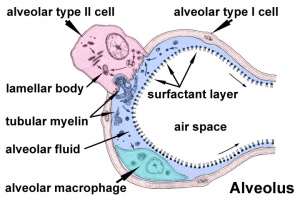
Alveolar Cells
Alveolar Type I cells
- small alveolar cells, type I pneumocytes
- very flat cells (thin as 0.05 µm)
- form most of the surface of the alveolar walls
- may contribute epithelium on both faces of the alveolar wall
Alveolar Type II cells
- large alveolar cells, type II pneumocytes
- irregular to cuboidal shaped cells
- contain large number of granules called lamellar bodies, these are the precursors to pulmonary surfactant (phospholipid mixture).
- end month 6 alveolar cells type 2 appear and begin to secrete surfactant - premature babies have difficulties associated with insufficient surfactant.
Alveolar Macrophages
- remove particulate matter that enters the alveoli with inspired air
- migrate over alveolar epithelium and phagocytose particulate matter
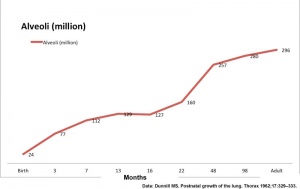
Alveoli Number
- At birth about 15% of adult alveoli number have formed
- 20 - 50 million to in the adult about 300 million.
- remaining subdivisions develop in the first few postnatal years
| Age (months) | Alveoli (million) | Respiratory Airways (million) | Generations of Airways |
| Birth | 24 | 1.5 | |
| 3 | 86 | 1.8 | |
| 3 | 77 | 2.5 | 21 |
| 3 | 73 | 2.0 | |
| 7 | 112 | 3.7 | |
| 13 | 129 | 4.5 | 22 |
| 16 | 127 | 4.7 | |
| 22 | 160 | 7.1 | |
| 48 | 257 | 7.9 | |
| 98 | 280 | 14.0 | 23 |
| Adult | 296 | 14.0 | 23 |
Graph data[1]
Respiratory Rate
- neonatal rate is higher (30-60 breaths/minute) than adult (12-20 breaths/minute).
- tachypnea - (Greek, rapid breathing) an increased respiratory rate of greater than 60 breaths/minute in a quiet resting baby
| Age | Rate (breaths/minute) |
| Infant (birth - 1 year) | 30 - 60 |
| Toddler (1 - 3 years) | 24 - 40 |
| Preschool (3 - 6 years) | 22 - 34 |
| School age (6 - 12 years) | 18 - 30 |
| Adolescent (12 - 18 years) | 12 - 16 |
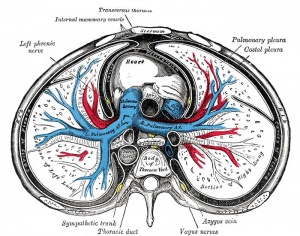
Pleural Cavity
- The anatomical body cavity in which the lungs develop and lie.
- The pleural cavity forms in the lateral plate mesoderm as part of the early single intraembryonic coelom.
- This cavity is initially continuous with pericardial and peritoneal cavities and form initially as two narrow canals
- later becomes separated by folding (pleuropericardial fold, pleuroperitoneal membrane) and the later formation of the diaphragm
pleuropericardial fold - (pleuropericardial membrane) An early embryonic fold which restricts the communication between pleural cavity and pericardiac cavity, contains both the cardinal vein and phrenic nerve.
pleuroperitoneal membrane - An early embryonic membrane that forms inferiorly at the septum transversum to separate peritoneal cavity from pleural cavity.
Pleura
- serous membrane covers the surface of the lung and the spaces between the lobes
- arranged as a closed invaginated sac
- two layers (pulmonary, parietal) continuous with each other, the potential space between them is the pleural cavity
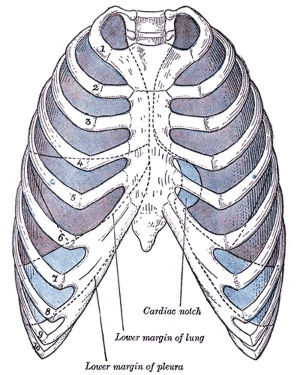
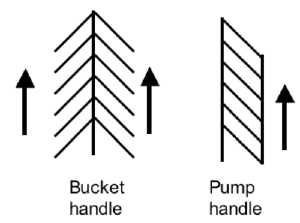
Rib Orientation
Infant Rib
- lies virtually horizontal
- allowing diaphragmatic breathing only.
Adult Rib
- lies oblique (both anterior and lateral views)
- allows for both pump-handle and bucket handle types of inspiration.
References
Reviews
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed>
Articles
<pubmed>1094872</pubmed> <pubmed>139844</pubmed>| PDF
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed>
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: PostnatalTract Development |
Terms
- antenatal before birth.
- alveoli number at birth - from 20 - 50 million and eventually in the adult 300 million.
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia - (BPD) the most common serious sequela of premature birth.
- Bronchiolitis - is a viral infection of the lower respiratory tract and most common lower respiratory tract infection in infants. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is responsible for 70 percent of all cases overall and Parainfluenza, adenovirus and influenza account for most of the remaining cases. (HSTAT Management of Bronchiolitis in Infants and Children)
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) causes include smoking (85–90 percent of all cases), genetic factors (alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency), passive smoking (children), occupational exposures, air pollution, and hyperresponsive airways. (HSTAT Management of Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
- Clara cells non-ciliated cell found in the small airways (bronchioles) consisting of ciliated simple epithelium, these cells secrete glycosaminoglycans (Clara cell secretory protein, CCSP) to protect the bronchiole lining.
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH) disorder with an incidence of 1 in 2500 live births.
- fetal breathing-like movements (FBMs) or Fetal respiratory movements are thought to be regular muscular contrations occurring in the third trimester, preparing the respiratory muscular system for neonatal function and to have a role in late lung development.
- FEV - Forced Expiratory Volume
- forced expiratory volume - (FEV) Spirometry term for the fraction of the forced vital capacity that is exhaled in a specific number of seconds. Abbreviated FEV with a subscript indicating how many seconds the measurement lasted.
- glucocorticoid treatment - antenatal therapy to promote the maturation of the human fetal lung. Given as a synthetic glucocorticoid between 24 and 32 weeks of pregnancy to promote lung maturation in fetuses at risk of preterm delivery.
- lamellar bodies the storage form of surfactant in type II alveolar cells, seen as centrically layered "packages" of phospholipid. A count of lamellar bodies can be used as an assay for measuring fetal lung maturity.
- maternal diabetes if not controlled in pregnancy may delay fetal pulmonary maturation.
- Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn (PPHN) serious newborn condition due to due to the failure of closure one of the prenatal circulatory shunts, the ductus arteriosus. Occurs in about 1-2 newborns per 1000 live births and results in hypoxemia. (More? Respiratory Development - Birth)
- Pharyngitis inflammation of the pharynx involving lymphoid tissues of the posterior pharynx and lateral pharyngeal bands.
- pneumocyte or alveolar type I and type II cells.
- pulmonary hypoplasia can be due to anencephaly, renal hypoplasia or abnormalities of the thoracic cage
- pulmonary neuroendocrine cells (PNEC) single or innervated clusters of cells (neuroepithelial bodies) that line the airway epithelium, thought to have a role in regulating fetal lung growth and differentiation. At birth may also act as airway oxygen sensors involved in newborn adaptation. These cells synthesis and release amine (serotonin, 5-HT) and a several neuropeptides (bombesin).
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) due to a surfactant deficiency at birth, particulary in preterm birth.
- secondary alveolar septa formed during the alveolar stage and are formed by projections of connective tissue and a double capillary loop.
- Spirometry - clinical measure of respiratory airflow.
- surfactant produced by alveolar type II cells is a mixture of lipids and proteins that both maintains alveolar integrity and plays a role in the control of host defense and inflammation in the lung.
- Surfactant therapy (American Academy of Pediatrics Policy | Canadian Paediatric Society Recommendations)
- thyroid hormone involved in the regulation of fetal lung development.
- vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) a secreted growth factor acting through receptors on endothelial cells to regulate vasculogenesis through their development, growth and function.
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 18) Embryology Respiratory System - Postnatal. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Respiratory_System_-_Postnatal
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G