Respiratory System - Postnatal: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
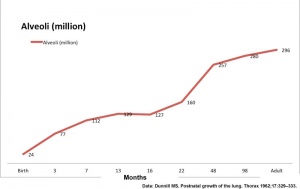
[[File:Postnatal alveoli number.jpg|thumb|Postnatal alveoli number]] | [[File:Postnatal alveoli number.jpg|thumb|Postnatal alveoli number]] | ||
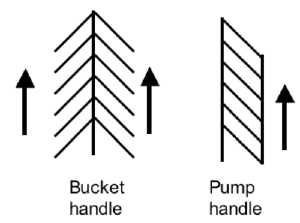
[[File:Neonatal rib orientation.jpg|thumb|Rib orientation]] | [[File:Neonatal rib orientation.jpg|thumb|Rib orientation]] | ||
===Alveolar Stage=== | |||
* The postnatal lung, with '''alveoli''' forming. | |||
* Expansion of gas exchange alveoli, vascular beds (capillaries), lymphatics and innervation. | |||
:'''Links:''' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2920089/figure/f2-ehp.0901856/ Principal stages of lung development in humans] | |||
===Alveoli=== | ===Alveoli=== | ||
* At birth about 15% of adult alveoli number have formed | * At birth about 15% of adult alveoli number have formed | ||
| Line 21: | Line 28: | ||
* [[Talk:SH_Lecture_-_Respiratory_System_Development#Respiratory_Alveoli|Alveoli Number]] | * [[Talk:SH_Lecture_-_Respiratory_System_Development#Respiratory_Alveoli|Alveoli Number]] | ||
==Respiratory Rate== | |||
* neonatal rate is higher (30-60 breaths/minute) than adult (12-20 breaths/minute). | * neonatal rate is higher (30-60 breaths/minute) than adult (12-20 breaths/minute). | ||
** tachypnea - (Greek, rapid breathing) an increased respiratory rate of greater than 60 breaths/minute in a quiet resting baby | ** tachypnea - (Greek, rapid breathing) an increased respiratory rate of greater than 60 breaths/minute in a quiet resting baby | ||
| Line 47: | Line 54: | ||
|} | |} | ||
===Rib | ==Rib Orientation== | ||
===Infant Rib=== | |||
* | * lies virtually horizontal | ||
* | * allowing diaphragmatic breathing only. | ||
===Adult Rib=== | |||
*lies oblique (both anterior and lateral views) | |||
* allows for both pump-handle and bucket handle types of inspiration. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 11:26, 1 March 2012
Introduction
This site mainly focuses on prenatal development, but the respiratory system is one of those that continues to grow and change postnatally. This page includes some topics related to this postnatal development.
Some Recent Findings
References | Recent References
Alveolar Stage
- The postnatal lung, with alveoli forming.
- Expansion of gas exchange alveoli, vascular beds (capillaries), lymphatics and innervation.
Alveoli
- At birth about 15% of adult alveoli number have formed
- 20 - 50 million to in the adult about 300 million.
- remaining subdivisions develop in the first few postnatal years
- Alveoli Number
Respiratory Rate
- neonatal rate is higher (30-60 breaths/minute) than adult (12-20 breaths/minute).
- tachypnea - (Greek, rapid breathing) an increased respiratory rate of greater than 60 breaths/minute in a quiet resting baby
| Age | Rate (breaths/minute) |
| Infant (birth - 1 year) | 30 - 60 |
| Toddler (1 - 3 years) | 24 - 40 |
| Preschool (3 - 6 years) | 22 - 34 |
| School age (6 - 12 years) | 18 - 30 |
| Adolescent (12 - 18 years) | 12 - 16 |
Rib Orientation
Infant Rib
- lies virtually horizontal
- allowing diaphragmatic breathing only.
Adult Rib
- lies oblique (both anterior and lateral views)
- allows for both pump-handle and bucket handle types of inspiration.
References
Reviews
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed>1</pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed>
Articles
<pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed> <pubmed></pubmed>
Search PubMed
Search Pubmed: PostnatalTract Development |
Terms
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 25) Embryology Respiratory System - Postnatal. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Respiratory_System_-_Postnatal
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G