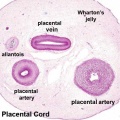
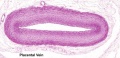
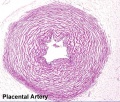
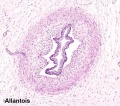
Placenta - Cord
Introduction
The placenta (Greek, plakuos = flat cake) named on the basis of this organs appearance. The placental cord, umbilical cord, is the connecting region between the functional placenta and the embryo/fetal umbilical region. This extraembryonic structure contains the placental blood vessels.
There are essentially 3 separate aortic/venous circulatory systems: umbilical, systemic and vitelline. The umbilical system is lost at birth, the vitelline contributes to the portal system and the systemic (embryonic) is extensively remodelled to fom the the cardiovascular system.
| System Links: Introduction | Cardiovascular | Coelomic Cavity | Endocrine | Gastrointestinal Tract | Genital | Head | Immune | Integumentary | Musculoskeletal | Neural | Neural Crest | Placenta | Renal | Respiratory | Sensory | Birth |
Placental Cord Histology
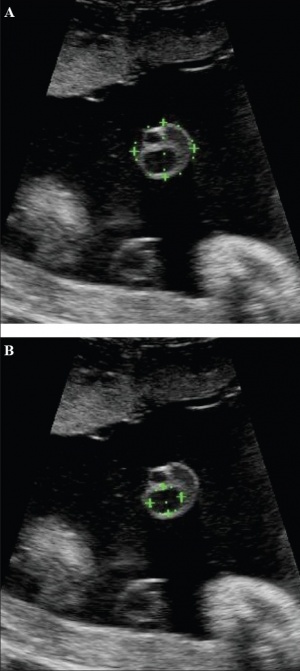
Placental Cord Ultrasound
Cord Abnormalities
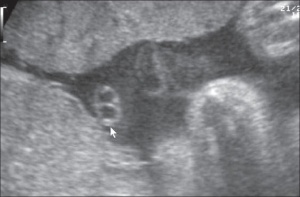
Cord Vessel Number
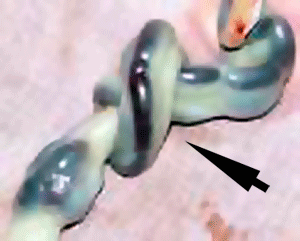
Cord Knotting
There are few abnormalities associated with umbilical cord development, other that abnormally short or long cords, which in most cases do not cause difficulties.
In some cases though, long cords can wrap around limbs or the fetus neck, which can then restrict blood flow or lead to tissue or nerve damage, and therefore effect develoment.
Cord knotting can also occur (1%) in most cases these knots have no effect, in some cases of severe knotting this can prevents the passage of placental blood.
See WebPath images: umbilical cord knot 1 | umbilical cord knot 2 | Pseudoknot of umbilical cord, gross
References
Umbilical cord torsion
Rare umbilical cord torsion, even without knot formation can also affect placental blood flow, even leading to fetal demise.
Hallak M, Pryde PG, Qureshi F, Johnson MP, Jacques SM, Evans MI. Constriction of the umbilical cord leading to fetal death. A report of three cases. J Reprod Med. 1994 Jul;39(7):561-5. Review.
See WebPath images: Torsion of umbilical cord, gross | Torsion of umbilical cord, with fetal demise, gross
Cord Length
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Placenta - Cord. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Placenta_-_Cord
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G