Neural Exam Movies: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:WHO_motor_development_milestones.jpg| | ==Introduction== | ||
[[File:WHO_motor_development_milestones.jpg|thumb|300px|WHO motor development milestones]] | |||
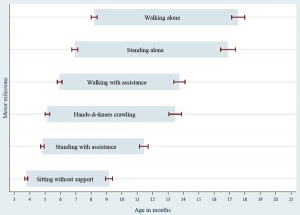
Neurological development continues postnatally with both growth and reorganization of the central nervous system. The amount of simple physical growth is shown by the skeletal flexibility designed around the brain and spinal cord, which allows continued postnatal growth of these structures. The World Health Organization (WHO) recently identified early postnatal motor skill development in terms of "motor milestones". | |||
The following movies demonstrate normal and abnormal postnatal neurological development assessment procedures. The newborn neuromuscular system can be initially assessed by 6 quick tests (posture, square window, arm recoil, popliteal angle, scarf sign and heel to ear). Later developmental assessment includes behaviour, reflexes (primitive and postural), muscular tone, and motor (gross, fine, co-ordination). This is examined in the newborn, 3 months, 6 months, 12 months and at 30 months of age. There are several primitive reflexes (rooting, sucking reflexes, Moro, grasp) that change (are repressed) with development of the central nervous system.These movies were designed by PD Larsen and SS Stensaas, Utah School of Medicine. | |||
==Newborn== | ==Newborn== | ||
Revision as of 12:32, 11 June 2010
Introduction
Neurological development continues postnatally with both growth and reorganization of the central nervous system. The amount of simple physical growth is shown by the skeletal flexibility designed around the brain and spinal cord, which allows continued postnatal growth of these structures. The World Health Organization (WHO) recently identified early postnatal motor skill development in terms of "motor milestones".
The following movies demonstrate normal and abnormal postnatal neurological development assessment procedures. The newborn neuromuscular system can be initially assessed by 6 quick tests (posture, square window, arm recoil, popliteal angle, scarf sign and heel to ear). Later developmental assessment includes behaviour, reflexes (primitive and postural), muscular tone, and motor (gross, fine, co-ordination). This is examined in the newborn, 3 months, 6 months, 12 months and at 30 months of age. There are several primitive reflexes (rooting, sucking reflexes, Moro, grasp) that change (are repressed) with development of the central nervous system.These movies were designed by PD Larsen and SS Stensaas, Utah School of Medicine.
Newborn
- Neural Exam Movies: normal behaviour | cranial nerves | Newborn Tone - resting posture | upper extremity | arm traction | arm recoil | scarf sign | hand position | lower extremity | leg traction | leg recoil | popliteal angle | heel to ear | neck tone | head lag | head control | Newborn Positions - prone | ventral suspension | vertical suspension | Newborn Reflexes - deep tendon reflexes | plantar reflex | suck, root | Moro | Galant | stepping | grasp | Newborn Head - head shape and sutures | head circumference | Neonatal Diagnosis
Newborn Behaviour
|
|
| normal behaviour | cranial nerves |
Newborn Tone
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
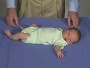
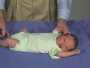
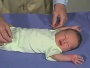
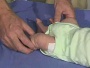
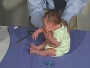
| resting posture | upper extremity | arm traction | arm recoil | scarf sign | hand position | lower extremity |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| leg traction | leg recoil | popliteal angle | heel to ear | neck tone | head lag | head control |
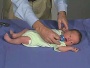
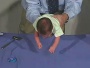
Newborn Positions
|

|
|
| prone | ventral | vertical |
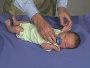
Newborn Reflexes
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| deep tendon reflexes | plantar reflex | suck, root | Moro | Galant | stepping | grasp |
Newborn Head
|

|
| shape, sutures | circumference |
Newborn Abnormal
Newborn Abnormal Links: behaviour | cranial nerves | Newborn Tone - resting posture | upper extremity | arm traction | arm recoil | scarf sign | hand position | lower extremity | leg traction | leg recoil | popliteal angle | heel to ear | neck tone | head lag | head control | Newborn Positions - prone | ventral suspension | vertical suspension | Newborn Reflexes - deep tendon reflexes | plantar reflex | suck, root | Moro | Galant | stepping | grasp | Newborn Head - head shape and sutures | head circumference
Newborn Behaviour
|

|
| abnormal behaviour | cranial nerves |
Newborn Tone

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
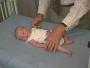
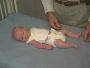
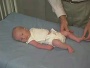
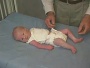
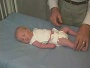
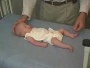
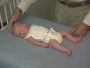
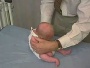
| resting posture | upper extremity | arm traction | arm recoil | scarf sign | hand position | lower extremity |
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
| leg traction | leg recoil | popliteal angle | heel to ear | neck tone | head lag | head control |
Newborn Positions

|
|
|
| prone | ventral | vertical |
Newborn Reflexes
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
| deep tendon reflexes | plantar reflex | suck, root | Moro | Galant | stepping | grasp |
Newborn Head
|

|
| shape, sutures | circumference |