Neural Exam - Newborn reflexes - grasp: Difference between revisions
From Embryology
(Created page with '{| border='0px' |- | <wikiflv height="265" width="320" autoplay="false" logo="false">Newborn n 26.flv|Newborn-normal-behaviour.jpg</wikiflv> | valign="top" |This 5-day-old infant…') |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| border='0px' | {| border='0px' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| < | | <html5media height="300" width="320">File:Newborn n 26.mp4</html5media> | ||
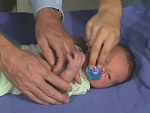
| valign="top" |This 5-day-old infant is in the alert, quiet state. | | valign="top" |[[File:Newborn n 26.jpg|right|150px]]This 5-day-old infant is in the alert, quiet state. | ||
* Placement of the examiner’s finger in the palm of the hand or on the sole of the foot will cause flexion and grasping of the fingers or toes. | * Placement of the examiner’s finger in the palm of the hand or on the sole of the foot will cause flexion and grasping of the fingers or toes. | ||
* One should avoid touching the dorsum of the hand while eliciting the grasp reflex because stimulating the back of the hand causes a hand opening reflex to occur. | * One should avoid touching the dorsum of the hand while eliciting the grasp reflex because stimulating the back of the hand causes a hand opening reflex to occur. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
---- | |||
{{Template:Newborn NeuroExam}} | |||
{{Template:PediNeuroLogic Exam}} | {{Template:PediNeuroLogic Exam}} | ||
[[Category:Human Neonatal]] | [[Category:Human Neonatal]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:18, 19 June 2014
| <html5media height="300" width="320">File:Newborn n 26.mp4</html5media> | This 5-day-old infant is in the alert, quiet state.
|
- Neural Exam Movies: normal behaviour | cranial nerves | Newborn Tone - resting posture | upper extremity | arm traction | arm recoil | scarf sign | hand position | lower extremity | leg traction | leg recoil | popliteal angle | heel to ear | neck tone | head lag | head control | Newborn Positions - prone | ventral suspension | vertical suspension | Newborn Reflexes - deep tendon reflexes | plantar reflex | suck, root | Moro | Galant | stepping | grasp | Newborn Head - head shape and sutures | head circumference | Neonatal Diagnosis
| Movie Source - Paul D. Larsen |
|---|
| Movies from the PediNeuroLogic Exam website are used by permission of Paul D. Larsen, M.D., University of Nebraska Medical Center and Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D., University of Utah School of Medicine. Additional materials were drawn from resources provided by Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation, Buenos Aires, Argentina; Kathleen Digre, M.D., University of Utah; and Daniel Jacobson, M.D., Marshfield Clinic, Wisconsin. The movies are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-ShareAlike 2.5 License. |
| Links: Neural Exam Movies | Movies |
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 19) Embryology Neural Exam - Newborn reflexes - grasp. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Neural_Exam_-_Newborn_reflexes_-_grasp
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G