Museum of Natural History Berlin - 2013 Seminar: Difference between revisions
m (→Anatomies) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
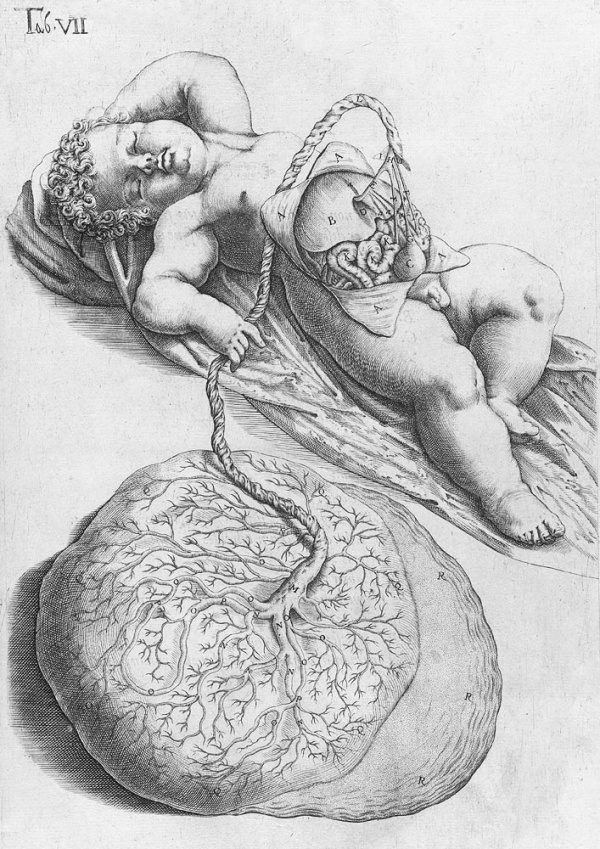
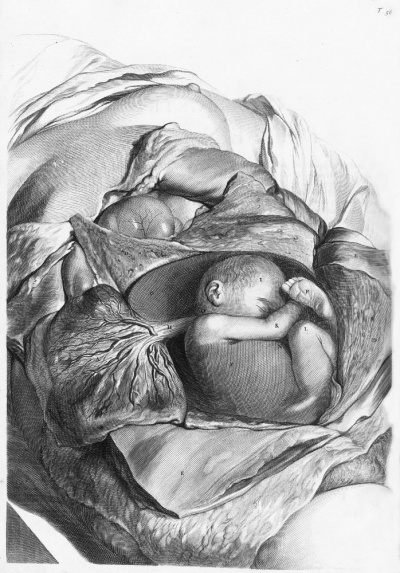
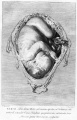
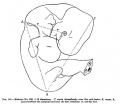
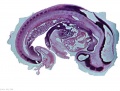
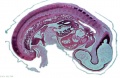
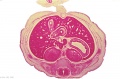
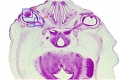
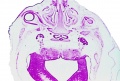
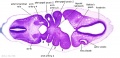
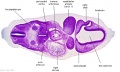
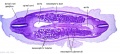
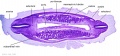
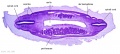
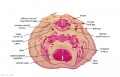
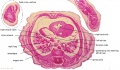
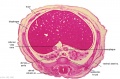
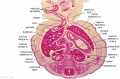
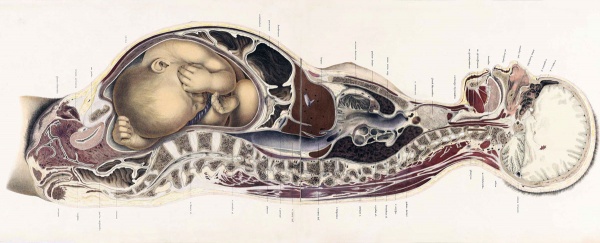
<center>[[Image:BrauneB1.jpg|600px]]</center> | <center>[[Image:BrauneB1.jpg|600px]]</center> | ||
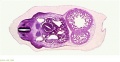
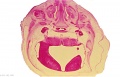
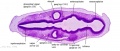
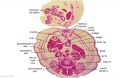
<center>Position of the Uterus and Fetus at Term (Wilhelm Braune, Topographisch-anatomischer Atlas, 1872)</center> | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
{| | |||
| col width=500px|Embryology is a cornerstone of both Medical Education for medical students and Developmental Biology for science students. In this presentation I will explore how the teaching of Embryology has evolved in our Medical School with the entry into the digital age and the expansion of new teaching and research techniques. | |||
This entire presentation will remain available online if you would like to explore in your own time! | This entire presentation will remain available online if you would like to explore in your own time! | ||
| | |||
'''Seminar Summary''' | |||
# Historic background | |||
# Embryo staging and collections | |||
# Previous teaching techniques | |||
# Online education | |||
# Medicine | |||
# Science | |||
# Questions | |||
|} | |||
== | ==Early History== | ||
===Anatomies=== | ===Anatomies=== | ||
(16<sup>th</sup> to 18<sup>th</sup> century) | (16<sup>th</sup> to 18<sup>th</sup> century) | ||
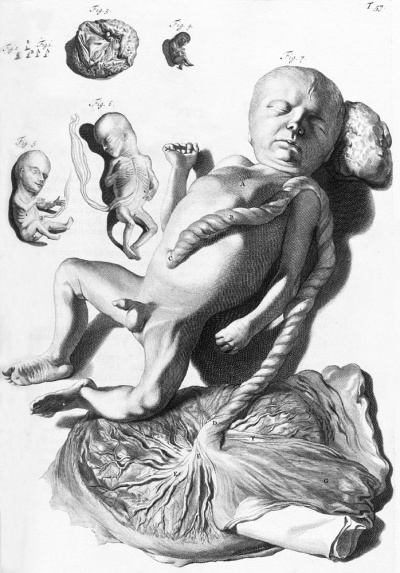
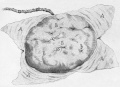
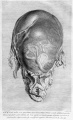
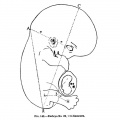
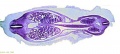
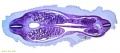
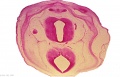
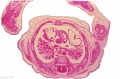
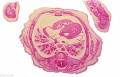
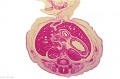
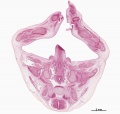
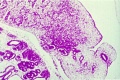
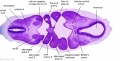
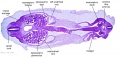
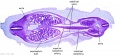
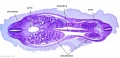
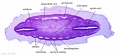
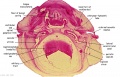
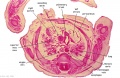
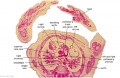
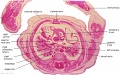
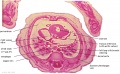
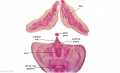
[[File:Spiegel1626_table07.jpg|600px]] | |||
Placenta and Fetus (Spiegel and Casseri, ''De formato foetu liber singularis'', 1626) | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! Example Anatomies | |||
|- | |||
| bgcolor="white"| | |||
[[Embryology_History_-_17th_and_18th_Century_Anatomies|17th and 18th Century Anatomies]] | [[Embryology_History_-_17th_and_18th_Century_Anatomies|17th and 18th Century Anatomies]] | ||
===Galletti | '''Spiegel and Casseri''' - ''De formato foetu liber singularis'' (1626) Published posthumously by Spigelius' son-in-law, the physician Liberalis L. Crema of Padua. | ||
<gallery> | |||
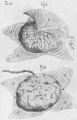
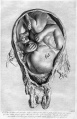
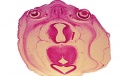
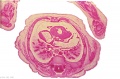
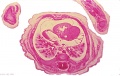
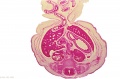
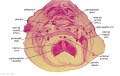
File:Spiegel1626_table05.jpg|Table 5 Placenta Fetal and Maternal Side | |||
File:Spiegel1626_table05fig1.jpg|Table 5 Fig. 1 Placenta Fetal Side | |||
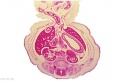
File:Spiegel1626_table05fig2.jpg|Table 5 Fig. 2 Placenta Maternal Side | |||
File:Spiegel1626_table07.jpg|Table 7 Placenta and Fetus | |||
</gallery> | |||
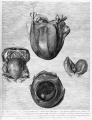
'''Govard Bidloo''' - ''Ontleding des menschelyken lichaams'', Amsterdam: By de weduwe van Joannes van Someren, de erfgenaamen van Joannes van Dyk, Hendrik en de weduwe van Dirk Boom, 1690. | |||
{| | |||
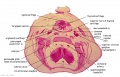
| [[File:Bidloo1690 table57.jpg|400px]] | |||
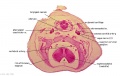
| [[File:Bidloo1690_table56.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
| Fetal Growth | |||
| Fetus and Uterus | |||
|} | |||
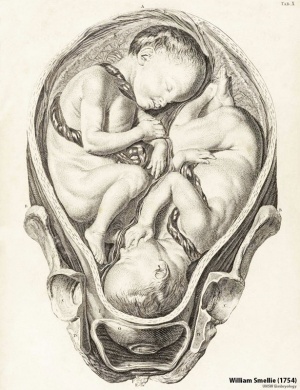
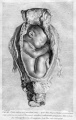
'''William Smellie''' - ''A sett of anatomical tables, with explanations, and an abridgment, of the practice of midwifery'' (1754) He also helped develop the delivery forceps which by the late eighteenth century were a well-known standard obstetrical instrument. [[Embryology_History_-_William_Smellie#A_Set_of_Anatomical_Tables_with_Explanations|Set of Anatomical Tables]] | |||
[[File:Smellie1754 table 10 twins.jpg|300px]] | |||
Table 10 showing a twin pregnancy, from ''A sett of anatomical tables, with explanations, and an abridgment, of the practice of midwifery'' (1754) | |||
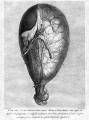
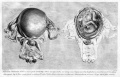
'''William Hunter''' - ''Anatomia uteri humani gravidi tabulis illustrata'' = The anatomy of the human gravid uterus exhibited in figures (1774) [[Embryology History - William Hunter|William Hunter]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:William Hunter 1774 titlepage.jpg|Title page | |||
File:William Hunter 1774 plate 11.jpg|Plate 11 | |||
File:William Hunter 1774 plate 12.jpg|Plate 12 | |||
File:William Hunter 1774 plate 13.jpg|Plate 13 | |||
File:William Hunter 1774 plate 16.jpg|Plate 16 | |||
File:William Hunter 1774 plate 20.jpg|Plate 20 | |||
File:William Hunter 1774 plate 23.jpg|Plate 23 | |||
File:William Hunter 1774 plate 26.jpg|Plate 26 | |||
File:William Hunter 1774 plate 27.jpg|Plate 27 | |||
</gallery> | |||
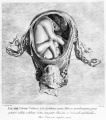
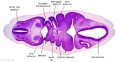
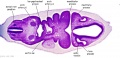
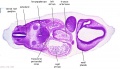
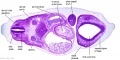
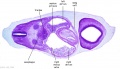
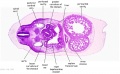
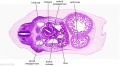
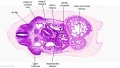
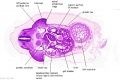
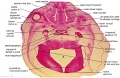
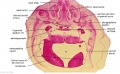
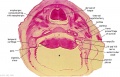
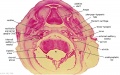
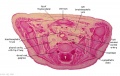
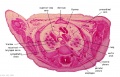
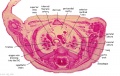
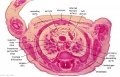
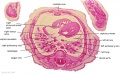
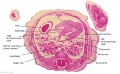
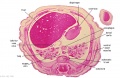
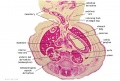
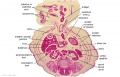
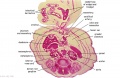
'''Wilhelm Braune''' - Topographisch-anatomischer Atlas : nach Durchschnitten an gefrornen Cadavern, Leipzig: Verlag von Veit & Comp., 1867-1872. [[Book_-_An_Atlas_of_Topographical_Anatomy_(1877)|An Atlas of Topographical Anatomy (1877)]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
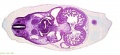
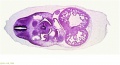
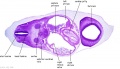
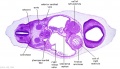
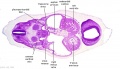
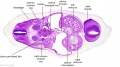
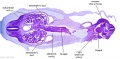
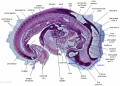
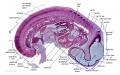
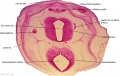
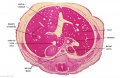
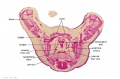
File:BrauneB1.jpg|Plate 29 and 30. Uterus and Fetus Position at Term | |||
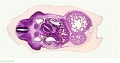
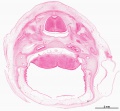
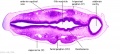
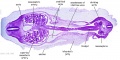
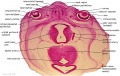
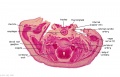
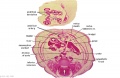
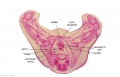
File:BrauneB2.jpg|Plate 29 and 30. Section through Uterus and Fetus | |||
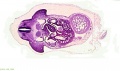
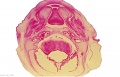
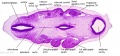
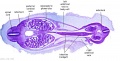
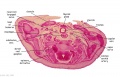
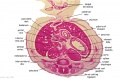
File:BrauneA1.jpg|Plate 29 and 30. Uterus without Fetus | |||
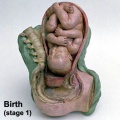
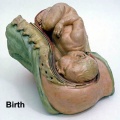
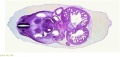
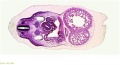
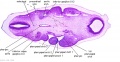
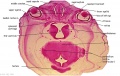
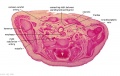
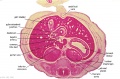
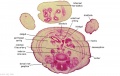
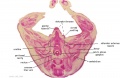
File:BrauneC1.jpg|Plate 31. Uterus and Fetus Position at Birth | |||
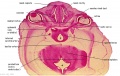
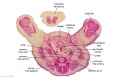
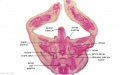
File:BrauneC3.jpg|Plate 31. Section through Uterus and Fetus | |||
File:BrauneC2.jpg|Plate 31. Uterus without Fetus | |||
</gallery> | |||
|} | |||
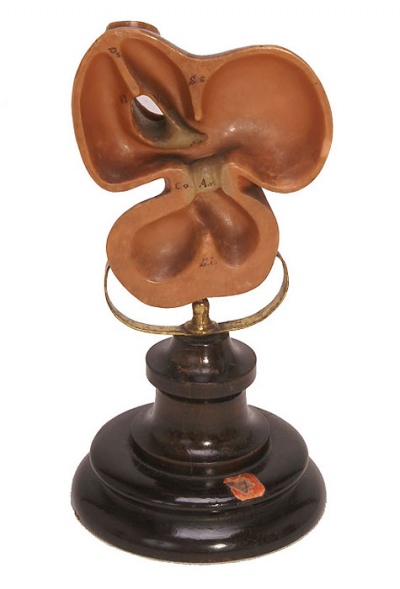
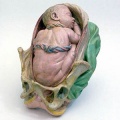
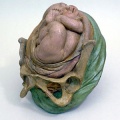
===Galletti Models=== | |||
(late 18<sup>th</sup> century) | (late 18<sup>th</sup> century) | ||
| Line 28: | Line 101: | ||
! Galletti Models | ! Galletti Models | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Obstetric models life-size wax models and scaled (1:3) terracotta models, examples of techniques for teaching medicine and obstetrics to midwives and surgery students at the end of the 18th century. | | bgcolor="white"|Obstetric models life-size wax models and scaled (1:3) terracotta models, examples of techniques for teaching medicine and obstetrics to midwives and surgery students at the end of the 18th century. | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 116: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Beginning Last Century - 1900's== | |||
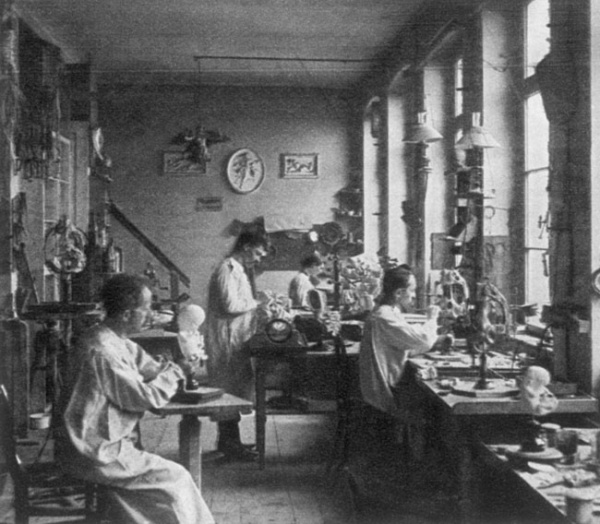
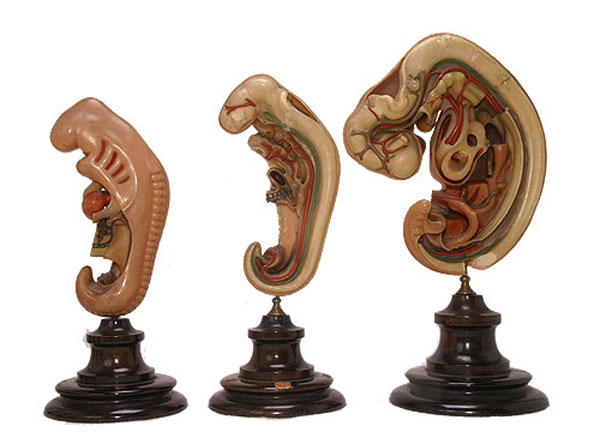
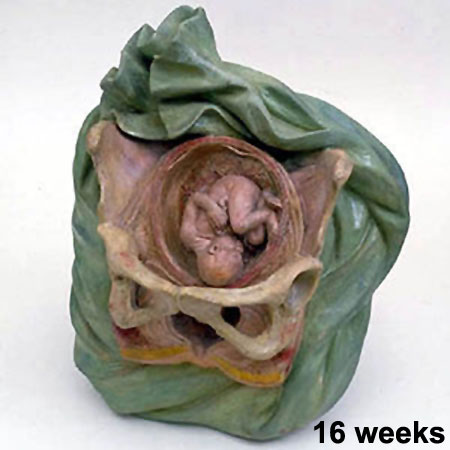
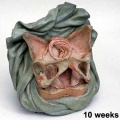
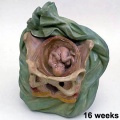
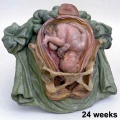
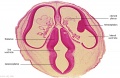
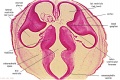
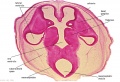
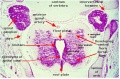
===Ziegler Models=== | ===Ziegler Models=== | ||
(19<sup>th</sup> to early 20<sup>th</sup> century) | (19<sup>th</sup> to early 20<sup>th</sup> century) | ||
| Line 53: | Line 126: | ||
! Ziegler Models (1860's - ) | ! Ziegler Models (1860's - ) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | bgcolor="white"| | ||
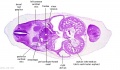
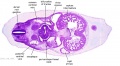
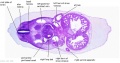
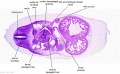
'''Embryos''' | '''Embryos''' | ||
| Line 83: | Line 156: | ||
|} | |} | ||
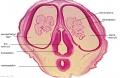
===Carnegie and Blechschmidt Models=== | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Osborne_Heard.jpg|400px]] | |||
| [[File:Blechschmidt model icon.jpg|300px]] | |||
|- | |||
| Carnegie Models | |||
Osborne O. Heard (1891–1983) produced over 700 wax-based embryo reconstructions models for the Carnegie Institute. Models were produced by the lost-wax casting process and were more detailed than the earlier Ziegler (1880's) embryo models. | |||
| Blechschmidt Models | |||
Erich Blechschmidt (1904–92) independently developed new methods of embryo reconstruction, 200,000 serial sections of embryos and 64 models. (University of Goettingen, Germany) | |||
|} | |||
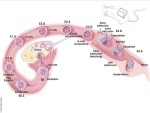
===Embryo Collections and Staging=== | |||
{{Embryo Collections}} | |||
{| | |||
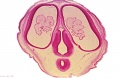
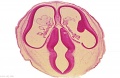
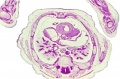
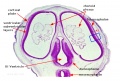
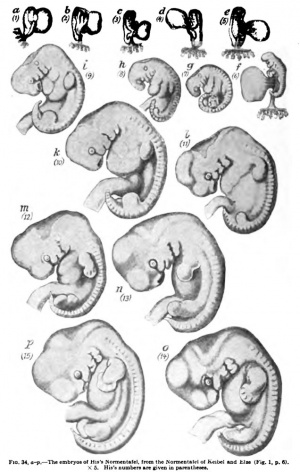
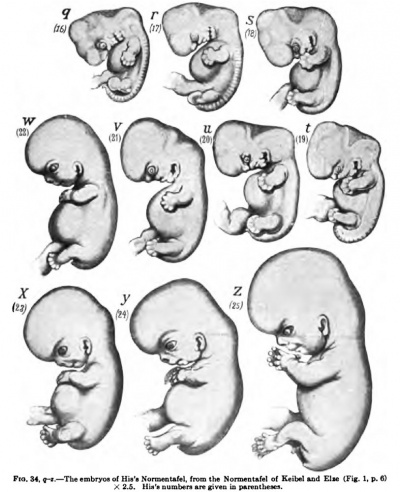
| [[File:Keibel_Mall_034a.jpg|300px]] | |||
| [[File:Keibel_Mall_034b.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Embryology_History_-_Wilhelm_His|His's Normentafel]] (human embryo staging) | |||
|- | |||
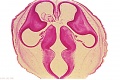
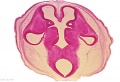
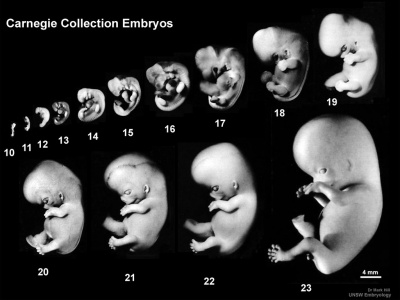
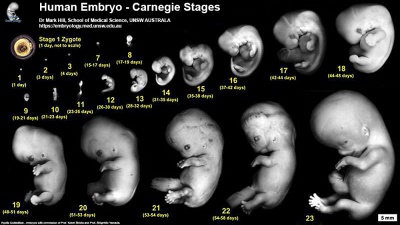
| [[File:Human Carnegie stage 10-23.jpg|400px]] | |||
| [[File:Human Carnegie stage 1-23.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |||
| Carnegie Collection (USA) | |||
| Kyoto Collection (Japan) | |||
|} | |||
{{Carnegie stages}} | |||
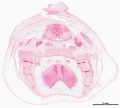
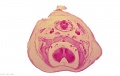
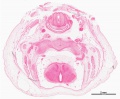
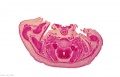
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! Embryo Staging | |||
|- | |||
|<gallery> | |||
Keibel_Mall_141.jpg | |||
Keibel_Mall_142.jpg | |||
Keibel_Mall_143.jpg | |||
Keibel_Mall_144.jpg | |||
Keibel_Mall_145.jpg | |||
Keibel_Mall_146.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
|} | |||
===Animal Models=== | |||
* Experimental embryology - involving manipulation of animal models. | |||
* Imaging development - electron microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, confocal microscopy, ultrasound, tomography. | |||
* Research fields - molecular biology, in vitro fertilisation, stem cells. | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Chick E12.jpg|100px]] | |||
| [[File:Adult frogs 01.jpg|150px]] | |||
| [[File:Rat.jpg|120px]] | |||
| [[File:Mouse E0-E5.jpg|150px]] | |||
| [[File:Fly_antennapedia_head.jpg|150px]] | |||
| [[File:Larvae1.png|150px]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Chicken Development|Chicken]] | |||
| [[Frog Development|Frog]] | |||
| [[Rat Development|Rat]] | |||
| [[Mouse Development|Mouse]] | |||
| [[Fly Development|Fly]] | |||
| [[Zebrafish Development|Zebrafish]] | |||
|} | |||
{{Animals}} | |||
==Recent Embryology Education== | |||
{| | |||
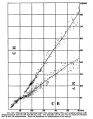
| [[File:Anatomy teaching USA graph.jpg|600px]] | |||
Trends in anatomy disciplines contact teaching hours based on data from USA survey. | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! About this graph | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Online survey were constructed to gather basic information about gross anatomy, microscopic anatomy, neuroscience/neuroanatomy, and embryology courses. | |||
* 2009 total of 130 allopathic and 25 osteopathic medical schools in USA. | |||
* Number of responses (Gross anatomy 65, Microscopic anatomy 45, Neuroscience/Neuroanatomy 31, Embryology 43) | |||
'''Reference''' | |||
<pubmed>19890982</pubmed> | |||
|} | |||
| Less contact time, but a growing list of new clinically relevant topics. | |||
* [[Assisted Reproductive Technology]] (In vitro fertilization) | |||
* [[Stem Cells]] | |||
* [[Molecular Development]] (genetics, epigenetics, inheritance) | |||
* [[Prenatal Diagnosis]] (genetic, ultrasound, [[Media:MRI_Stage_23_ventricular%2Binlet_septation.mov|MRI]], fetal cells in maternal) | |||
* [[Fetal Surgery]] (prenatal medicine) | |||
|} | |||
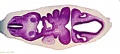
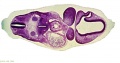
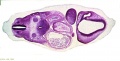
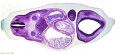
===Embryo Serial Sections=== | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:Microfiche_reader.jpg]] | |||
| Microfiche Reader used in Medicine and Science classes from 1975 to 1995. | |||
View embryo section 49 images (7x7 matrix) in 3 sets: | |||
# [[Carnegie_stage_13_-_serial_sections|Stage 13 Embryo]] (mid-embryonic period) | |||
# [[Carnegie_stage_22_-_serial_sections|Stage 22 Embryo]] (end embryonic period) | |||
# [[Carnegie stage 22 - selected serial sections|Selected Stage 22 images]] (selected organs and tissues from end embryonic) | |||
Identify key organs and tissues in these sections and compare appearance at different periods of development. | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! Microfiche Unlabeled Images | |||
|- | |||
| {{Stage13ULicon120}} | |||
|- | |||
| {{Stage22ULicon120}} | |||
|- | |||
| {{Stage22SULicon120}} | |||
|} | |||
===1997 Online=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Microfiche_reader.jpg|pre-1997 | |||
File:Embryology website 2001.jpg|2001 | |||
File:Embryology website 2004.jpg|2004 | |||
File:Embryology website 2007.jpg|2007 | |||
File:Embryology_DVD_2007.jpg|2007 DVD | |||
Front-page-image.jpg|[[Main_Page|2009 - onward]] | |||
</gallery> | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! Microfiche Labeled Images | |||
|- | |||
| {{Stage13Licon120}} | |||
|- | |||
| {{Stage22Licon120}} | |||
|- | |||
| {{Stage22SLicon120}} | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! Technology Timeline | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2"|[[File:Mark_Hill.jpg|50px]] | |||
The changing technology environment we have experienced in the last 50 years, and more recently in the last 20 "internet years". | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* '''1961''' - Microfiche - miniaturise data, images and text. | |||
* '''1962''' - Slide carousel projector - transport and display content easily. | |||
* '''1960s''' - Overhead projectors - prepared and flexible in-class. | |||
* '''1977''' - Apple computers. | |||
* '''1981''' - IBM computers. | |||
* '''1982''' - Microsoft MS-DOS. | |||
* '''1990''' - Powerpoint - electronic slides. | |||
* '''1991''' - Quicktime - multimedia platform for images and animations. | |||
* '''1993''' - [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mosaic_(web_browser) Mosaic] first web browser. | |||
* '''1994''' - Netscape Navigator web browser. | |||
* '''1995''' - Internet Explorer web browser. | |||
* '''1996''' - Flash - multimedia platform for images and animations. | |||
| | |||
* '''1997''' - Embryology site first online. | |||
* '''1998''' - Google internet search. | |||
* '''1998''' - [http://www.blackboard.com/About-Bb/Our-Story.aspx Blackboard] course management system. | |||
* '''2001''' - [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia Wikipedia] online encyclopaedia running on [http://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/MediaWiki Mediawiki]. | |||
* '''2002''' - [http://moodle.org/ Moodle] course management system. | |||
* '''2004''' - [https://www.facebook.com/ Facebook] social networking service. | |||
* '''2004''' - Embryology website reformatted as 3 column webpages. | |||
* '''2006''' - [https://twitter.com Twitter] microblogging service. | |||
* '''2009''' - Embryology site transferred to new wiki format. | |||
* '''2010''' - [http://itunes.apple.com/au/app/ibooks/id364709193?mt=8 iBooks] e-book application for iPads. | |||
* '''2012''' - ?? | |||
|} | |||
===Online Development=== | |||
{| | |||
| [[Movies]] | |||
* Textbook animations | |||
* [[ILP2006_-_Carnegie_stage_Animations|Serial section reconstructions]] | |||
* Research movies | |||
[[Audio]] | |||
| {{Human development movie 1}} | |||
|- | |||
| [[Glossary]] | |||
| [[A|A]] | [[B|B]] | [[C|C]] | [[D|D]] | [[E|E]] | [[F|F]] | [[G|G]] | [[H|H]] | [[I|I]] | [[J|J]] | [[K|K]] | [[L|L]] | [[M|M]] | [[N|N]] | [[O|O]] | [[P|P]] | [[Q|Q]] | [[R|R]] | [[S|S]] | [[T|T]] | [[U|U]] | [[V|V]] | [[W|W]] | [[X|X]] | [[Y|Y]] | [[Z|Z]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Human_Abnormal_Development|Abnormal Development]] | |||
| {{Abnormality Links}} | |||
|} | |||
===2004 New Medicine Program=== | |||
* Previously lectures and practicals covering a semester. | |||
* Embryology became "integrated" into new cross-discipline courses. | |||
====Lecture Example==== | |||
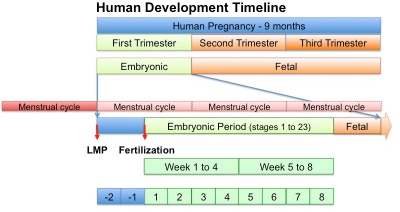
[[File:Human development timeline graph 02.jpg|thumb|400px|[[Quicktime_Movie_-_Human_Development_Timeline|Human Development Timeline]]]] | |||
[[BGDA_Lecture_-_Development_of_the_Embryo/Fetus_1|BGD - Development of the Embryo/Fetus 1]] | |||
* Replace powerpoint slides | |||
* Can be formatted for printing | |||
* Accessible at all times (including [[Help:Mobile_Access|Mobile Access]]) | |||
* Can be opened during associated practical class | |||
* Links to: | |||
** Textbooks | |||
** Related online pages, including practical, audio etc. | |||
** Movies | |||
** Glossary | |||
====Practical Example==== | |||
[[BGDA_Practical_-_Fertilization_to_Implantation|BGD - Practical Fertilization to Implantation]] | |||
* Organised into a timeline | |||
* Each page worked through with the demonstrator | |||
* Independent time to ask questions | |||
* Students can cut n paste for their own notes | |||
* [[Foundations_Quiz|Online Quizzes]] | [[:Category:Quiz|Category:Quiz]] | |||
====Student Project Examples==== | |||
[[Medicine Student Projects]] | |||
* Part of the Medicine undergraduate program allows for individual students to work on research or educational projects related to medicine. | |||
* The projects are academically supervised and are described as an "Independent Learning Project" (ILP). | |||
{| | |||
| [[Image:Navigation bar 1.jpg|300px|center|link=Cardiac_Embryology]] | |||
[[Image:Navigation bar 2.jpg|300px|center|link=Cardiac_Embryology]] | |||
[[Image:Basic Heart Development Timeline.jpg|300px|center|link=Cardiac_Embryology]] | |||
<center>Navigation menus</center> | |||
| [[File:ILP2006 Generating the surface .gif]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Cardiac_Embryology|'''Cardiac Embryology Tutorial''']] | |||
| valign=top|[[ILP2006_-_Carnegie_stage_Animations|'''Carnegie Stage Embryo 3D Animations''']] | |||
|} | |||
{| | |||
| valign=top|[[Science Student Projects]] | |||
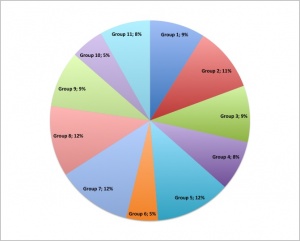
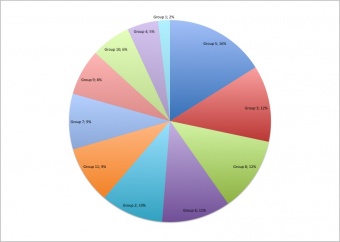
* Since 2009 undergraduate science students have been preparing online group projects as part of their ANAT2341 Embryology course. | |||
* Student group (4-5 students) selects a specific topic within the main theme that they then research and work collaboratively on that topic throughout the semester. | |||
* Project is discussed online. | |||
* Assessed by peers, before being finally edited for submission as their group assessment component for the course. | |||
* Group and [[ANAT2341_2011_Students#Quick_Groups_Assessment_-_30_Sep|Individual contributions]] can also be monitored. | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | |||
! Project Teams - which are working. | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:2011_Project_Group_1-11_edits.jpg|300px]] | |||
| [[File:2011_Talk_Group_1-11_edits.jpg|340px]] | |||
|- | |||
| All Project page edits by Group | |||
| All Discussion page edits by Group | |||
|} | |||
| [[File:Project_timeline.png|200px]] | |||
|} | |||
==Online== | |||
===Notes=== | |||
(Shown in the lefthand menu) | |||
* [[Human_System_Development|System Development]] | |||
* [[Embryonic Development]] | |||
* [[Special:Categories|Categories]] | |||
* [[Assisted Reproductive Technology]] | |||
* [[Stem Cells]] | |||
* [[:Category:Quiz|Quizzes]] - Example [[Foundations_Quiz|Medicine - Foundation Quiz]] | |||
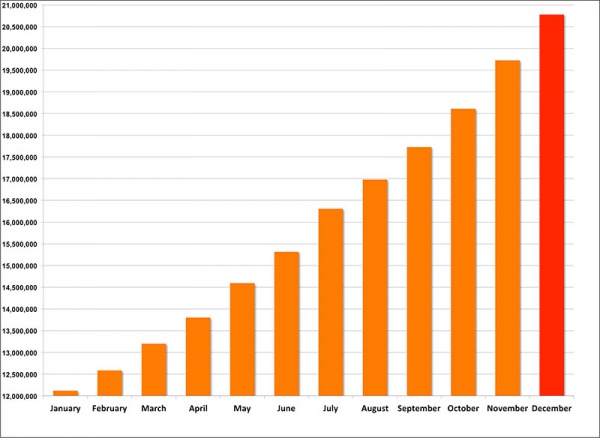
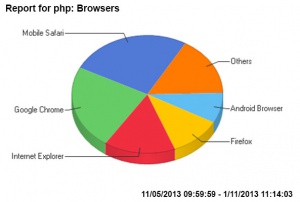
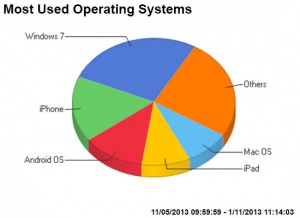
===Statistics=== | |||
[[File:Wikiviewstats2013.jpg|600px|link=new]] | |||
[[File:Php-most_used_browsers_May-Oct_2013.jpg|300px]][[File:Php-most_used_operating_systems_May-Oct_2013.jpg|300px]] | |||
===eBooks=== | |||
{| | |||
| [[File:IBooks_icon.jpg|link=Embryology_iBooks]] | |||
| [[Embryology iBooks]] 2013 software update now allows iBooks to be downloaded and read on tablets, laptops and desktop computers. | |||
|} | |||
==Final Remarks== | |||
* I remind you that I do not intend to cover everything shown on this seminar page. Some content can be returned to and studied in your own time. | |||
* Embryology education will continue to evolve online as new technologies and research techniques are developed. | |||
* Finally, and most importantly, I thank all my [[Contributors]] who have helped make this a site so rich in embryology content. | |||
'''External Link:''' Museum für Naturkunde - [http://www.naturkundemuseum-berlin.de DE] | [http://www.naturkundemuseum-berlin.de/en EN] | |||
{{External Links}} | |||
[[Category:Education]][[Category:2013]] | |||
{{Footer}} | {{Footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:25, 26 November 2013
- 11:00 25th November 2013 Translate page - German
The Evolution of Embryology Education
Introduction
| Embryology is a cornerstone of both Medical Education for medical students and Developmental Biology for science students. In this presentation I will explore how the teaching of Embryology has evolved in our Medical School with the entry into the digital age and the expansion of new teaching and research techniques.
|
Seminar Summary
|
Early History
Anatomies
(16th to 18th century)
Placenta and Fetus (Spiegel and Casseri, De formato foetu liber singularis, 1626)
| Example Anatomies | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
17th and 18th Century Anatomies Spiegel and Casseri - De formato foetu liber singularis (1626) Published posthumously by Spigelius' son-in-law, the physician Liberalis L. Crema of Padua. Govard Bidloo - Ontleding des menschelyken lichaams, Amsterdam: By de weduwe van Joannes van Someren, de erfgenaamen van Joannes van Dyk, Hendrik en de weduwe van Dirk Boom, 1690.
William Smellie - A sett of anatomical tables, with explanations, and an abridgment, of the practice of midwifery (1754) He also helped develop the delivery forceps which by the late eighteenth century were a well-known standard obstetrical instrument. Set of Anatomical Tables Table 10 showing a twin pregnancy, from A sett of anatomical tables, with explanations, and an abridgment, of the practice of midwifery (1754)
Wilhelm Braune - Topographisch-anatomischer Atlas : nach Durchschnitten an gefrornen Cadavern, Leipzig: Verlag von Veit & Comp., 1867-1872. An Atlas of Topographical Anatomy (1877) |
Galletti Models
(late 18th century)
| Galletti Models |
|---|
| Obstetric models life-size wax models and scaled (1:3) terracotta models, examples of techniques for teaching medicine and obstetrics to midwives and surgery students at the end of the 18th century.
|
Beginning Last Century - 1900's
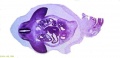
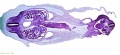
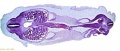
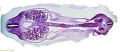
Ziegler Models
(19th to early 20th century)
Ziegler Freiburg workshop (c 1912). Ziegler Models | Embryology Models
| Ziegler Models (1860's - ) |
|---|
|
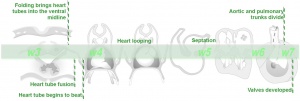
Embryos Brain Development Heart Development |
Carnegie and Blechschmidt Models
Embryo Collections and Staging
|
|
| His's Normentafel (human embryo staging) | |
|
|
| Carnegie Collection (USA) | Kyoto Collection (Japan) |
- Carnegie Stages: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | About Stages | Timeline
| Embryo Staging |
|---|
Animal Models
- Experimental embryology - involving manipulation of animal models.
- Imaging development - electron microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, confocal microscopy, ultrasound, tomography.
- Research fields - molecular biology, in vitro fertilisation, stem cells.
|

|
|
|

|
|
| Chicken | Frog | Rat | Mouse | Fly | Zebrafish |
| Animal Development: axolotl | bat | cat | chicken | cow | dog | dolphin | echidna | fly | frog | goat | grasshopper | guinea pig | hamster | horse | kangaroo | koala | lizard | medaka | mouse | opossum | pig | platypus | rabbit | rat | salamander | sea squirt | sea urchin | sheep | worm | zebrafish | life cycles | development timetable | development models | K12 |
Recent Embryology Education
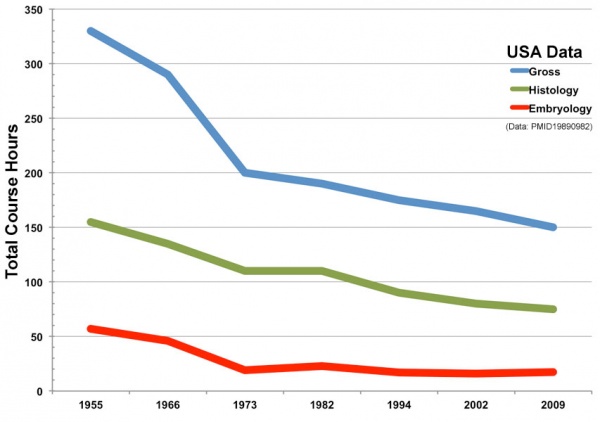
Trends in anatomy disciplines contact teaching hours based on data from USA survey.
|
Less contact time, but a growing list of new clinically relevant topics.
|
Embryo Serial Sections
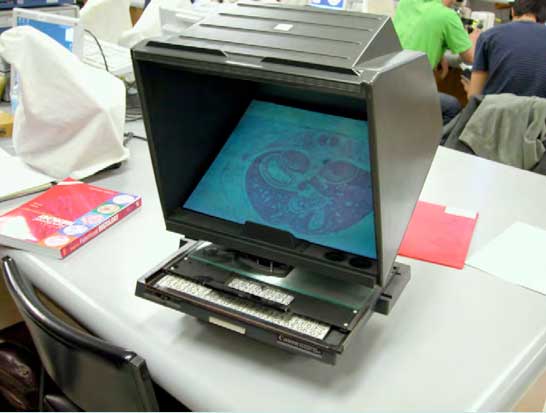

|
Microfiche Reader used in Medicine and Science classes from 1975 to 1995.
View embryo section 49 images (7x7 matrix) in 3 sets:
|
| Microfiche Unlabeled Images | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1997 Online
| Technology Timeline | |
|---|---|

The changing technology environment we have experienced in the last 50 years, and more recently in the last 20 "internet years". | |
|
|
Online Development
Movies
|
| ||||
| Glossary | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ||||
| Abnormal Development |
|
2004 New Medicine Program
- Previously lectures and practicals covering a semester.
- Embryology became "integrated" into new cross-discipline courses.
Lecture Example
BGD - Development of the Embryo/Fetus 1
- Replace powerpoint slides
- Can be formatted for printing
- Accessible at all times (including Mobile Access)
- Can be opened during associated practical class
- Links to:
- Textbooks
- Related online pages, including practical, audio etc.
- Movies
- Glossary
Practical Example
BGD - Practical Fertilization to Implantation
- Organised into a timeline
- Each page worked through with the demonstrator
- Independent time to ask questions
- Students can cut n paste for their own notes
- Online Quizzes | Category:Quiz
Student Project Examples
- Part of the Medicine undergraduate program allows for individual students to work on research or educational projects related to medicine.
- The projects are academically supervised and are described as an "Independent Learning Project" (ILP).
|
|

|
| Cardiac Embryology Tutorial | Carnegie Stage Embryo 3D Animations |
Science Student Projects
|
|
Online
Notes
(Shown in the lefthand menu)
- System Development
- Embryonic Development
- Categories
- Assisted Reproductive Technology
- Stem Cells
- Quizzes - Example Medicine - Foundation Quiz
Statistics
eBooks
| Embryology iBooks 2013 software update now allows iBooks to be downloaded and read on tablets, laptops and desktop computers. |
Final Remarks
- I remind you that I do not intend to cover everything shown on this seminar page. Some content can be returned to and studied in your own time.
- Embryology education will continue to evolve online as new technologies and research techniques are developed.
- Finally, and most importantly, I thank all my Contributors who have helped make this a site so rich in embryology content.
External Link: Museum für Naturkunde - DE | EN
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 20) Embryology Museum of Natural History Berlin - 2013 Seminar. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Museum_of_Natural_History_Berlin_-_2013_Seminar
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G